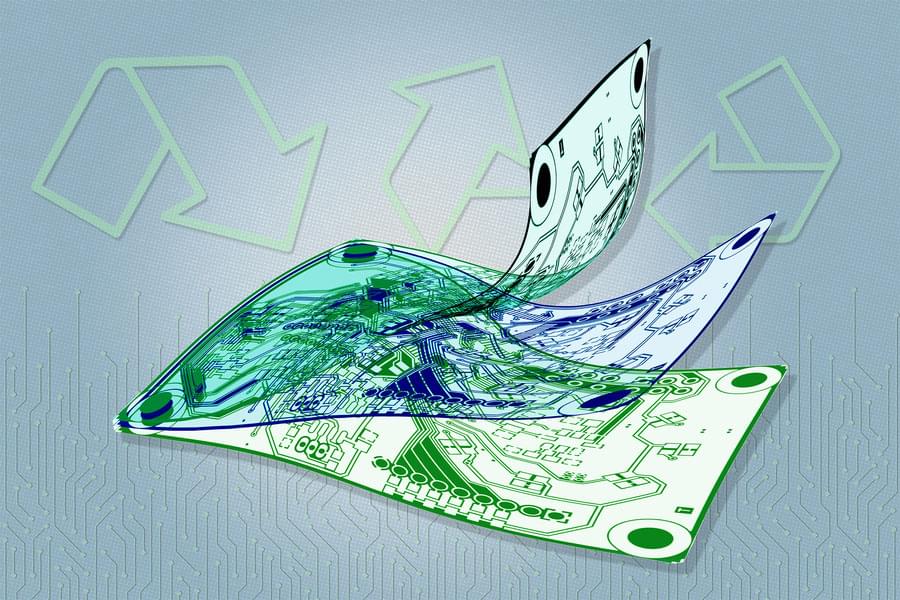
Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a rapidly growing global problem, and it’s expected to worsen with the production of new kinds of flexible electronics for robotics, wearable devices, health monitors, and other new applications, including single-use devices.
A new kind of flexible substrate material developed at MIT, the University of Utah, and Meta has the potential to enable not only the recycling of materials and components at the end of a device’s useful life, but also the scalable manufacture of more complex multilayered circuits than existing substrates provide.
The development of this new material is described in the journal RSC Applied Polymers (“Photopatternable, Degradable, and Performant Polyimide Network Substrates for E-Waste Mitigation”), in a paper by MIT Professor Thomas J. Wallin, University of Utah Professor Chen Wang, and seven others.