Nov 21, 2023
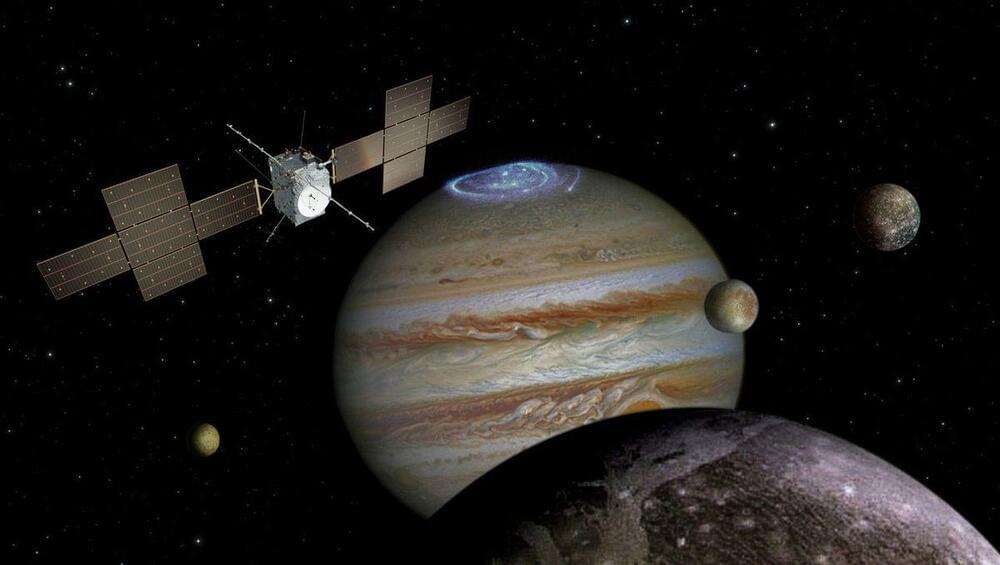
Europe’s JUICE probe will be 1st to use gravity of Earth and moon to slingshot to Jupiter
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: space
On Nov. 17, JUICE performed a 43-minute burn to get into position for its upcoming Earth-moon flyby, the first-ever double gravity assist.