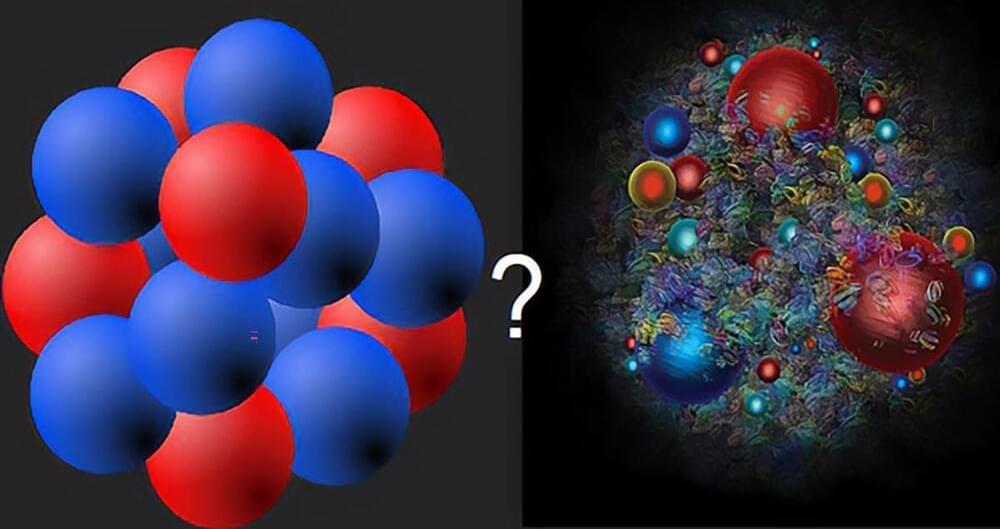
Matter inside neutron stars can have different forms: a dense liquid of nucleons or a dense liquid of quarks.
Recent studies reveal that in neutron stars, quark liquids are fundamentally different from nucleon liquids, as evidenced by the unique color-magnetic field in their vortices. This finding challenges previous beliefs in quantum chromodynamics and offers new insights into the nature of confinement.
The science of neutron star matter.