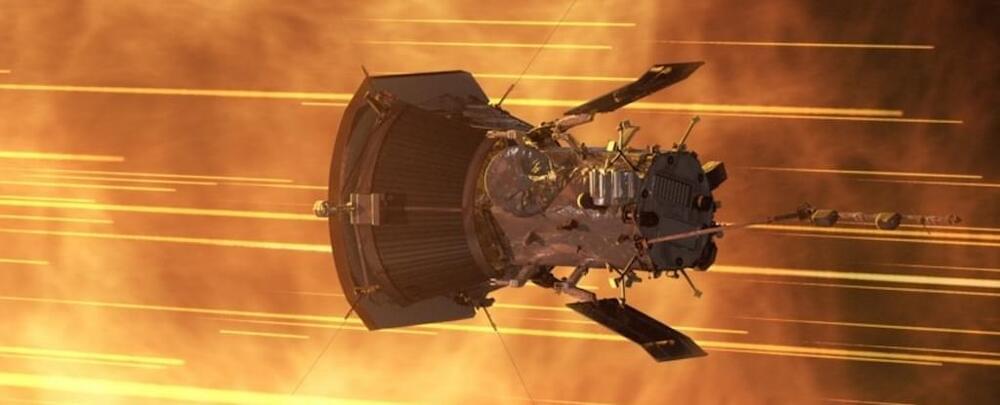
Falling through the Solar System at an astonishing 635,266 kilometers (394,736 miles) per hour, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has just smashed the record for fastest object ever to be created by human hands.
The event on September 27 marks the turning point of the mission’s 17th loop around the Sun as it collects data on the heated winds of charged particles and violent magnetism that surround our closest star, and comes just under three years after its previous record of 586,863.4 kilometers (364,660 miles) per hour.
At these speeds, it’d be possible for an aircraft to circumnavigate our planet roughly 15 times in a single hour, or zoom from New York to Los Angeles in just over 20 seconds.