Jun 2, 2022
Using laser technology to measure the rotational cooling of molecular ions colliding with electrons
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: particle physics, quantum physics, space
When it is free in cold space, a molecule will spontaneously cool down by slowing its rotation and losing rotational energy in quantum transitions. Physicists have shown that this rotational cooling process can be accelerated, slowed down and even inverted by the molecule’s collisions with surrounding particles.
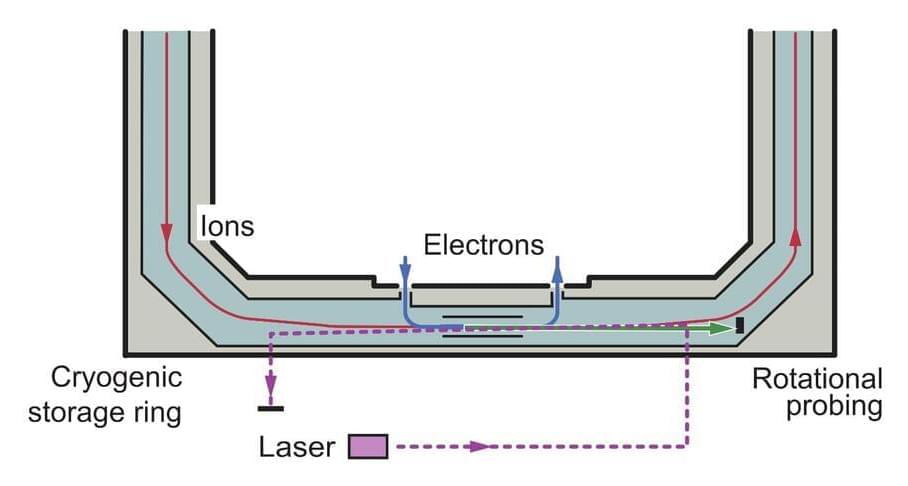
Researchers at the Max-Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics in Germany and the Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory have recently carried out an experiment aimed at measuring the rate of quantum transitions caused by collisions between molecules and electrons. Their findings, published in Physical Review Letters, offer the first experimental evidence of this rate, which had previously only been theoretically estimated.
“When electrons and molecular ions are present in tenuous, ionized gases, the lowest quantum level populations of the molecules can be changed in a collision process,” Ábel Kálosi, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “One example of this process is in interstellar clouds, where observations reveal molecules predominantly in their lowest quantum states. The attractive force between the negatively charged electrons and the positively charged molecular ions makes the process of electronic collisions particularly efficient.”