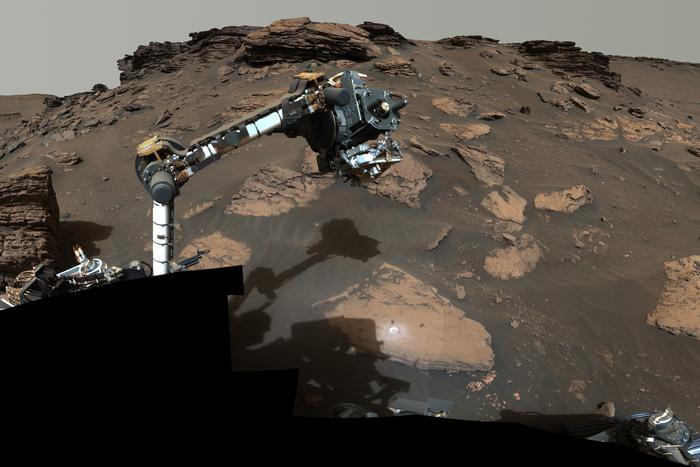
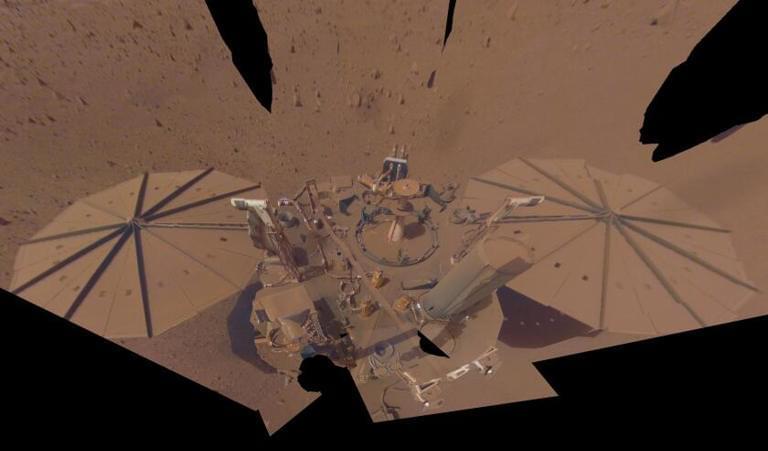
“These are the oldest rocks that may have been deposited by water, that we’ve ever laid hands or rover arms on,” said Dr. Benjamin Weiss. “That’s exciting, because it means these are the most promising rocks that may have preserved fossils, and signatures of life.”
Did life once exist on Mars, and if so, where will we find it? This is what a recent study published in AGU Advances hopes to address as a team of several dozen international researchers led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) investigated rocks samples obtained by NASA’s Perseverance (Percy) rover obtained in Jezero Crater on Mars, and which allegedly contain minerals only found in water. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions for life to have emerged on the Red Planet long ago, along with identifying what evidence could be used to find life elsewhere in the solar system.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data obtained from seven rock samples collected by Percy along Jezero’s western slope, which scientists have hypothesized was an ancient lake long ago. After examining Percy’s images of the surrounding area and the chemical analyses from the rock samples, the team determined that the rocks contain evidence of water, meaning this location likely contained a lake long ago. However, the potential for this lake having life is still unknown since the team did not identify evidence of organic matter within the samples. Despite this, the team determined that the rocks were created more than 3.5 billion years ago, long before life emerged on the Earth.
Continue reading “NASA’s Perseverance Rover Uncovers Water-Borne Minerals in Mars’ Jezero Crater” »