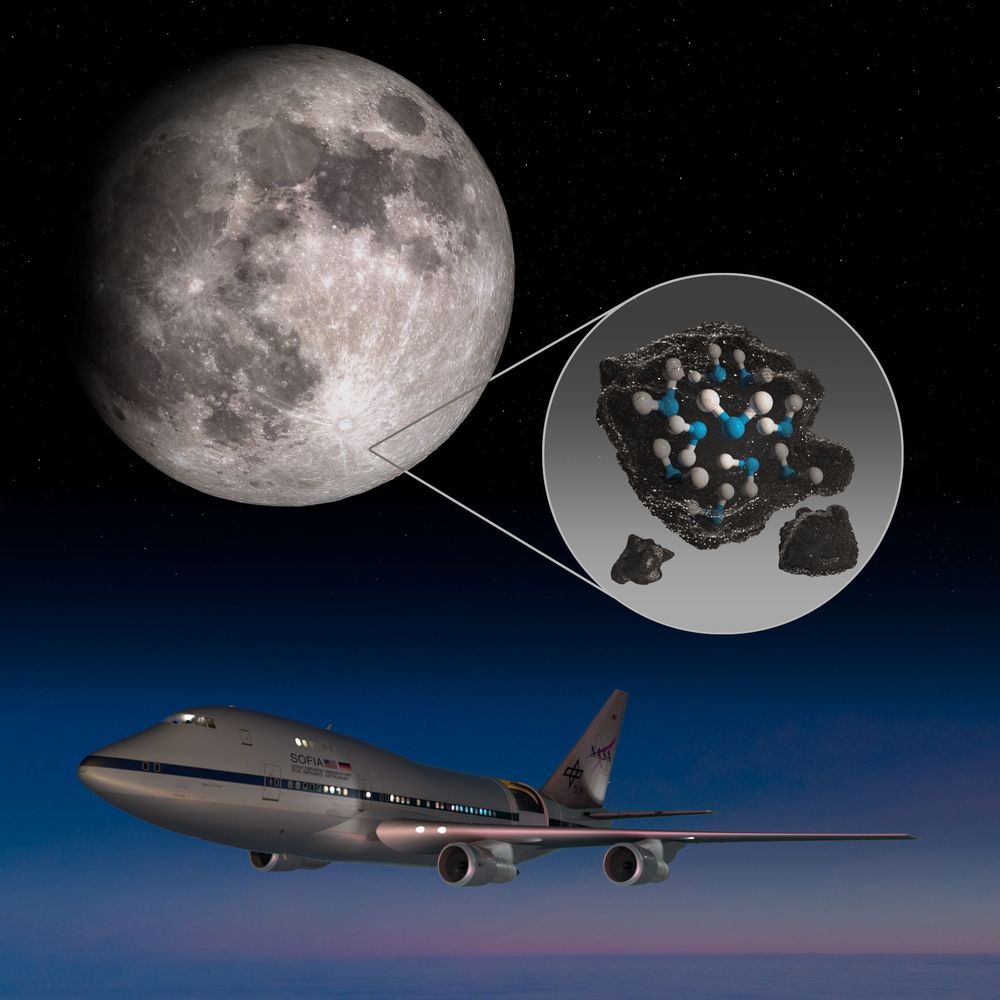
NASA’s Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) has confirmed, for the first time, water on the sunlit surface of the Moon. This discovery indicates that water may be distributed across the lunar surface, and not limited to cold, shadowed places.
SOFIA has detected water molecules (H2O) in Clavius Crater, one of the largest craters visible from Earth, located in the Moon’s southern hemisphere. Previous observations of the Moon’s surface detected some form of hydrogen, but were unable to distinguish between water and its close chemical relative, hydroxyl (OH). Data from this location reveal water in concentrations of 100 to 412 parts per million – roughly equivalent to a 12-ounce bottle of water – trapped in a cubic meter of soil spread across the lunar surface. The results are published in the latest issue of Nature Astronomy.
“We had indications that H2O – the familiar water we know – might be present on the sunlit side of the Moon,” said Paul Hertz, director of the Astrophysics Division in the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Now we know it is there. This discovery challenges our understanding of the lunar surface and raises intriguing questions about resources relevant for deep space exploration.”