Sep 30, 2023
Striking rare gold: Researchers unveil new material infused with gold in an exotic chemical state
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: chemistry, particle physics, solar power, sustainability
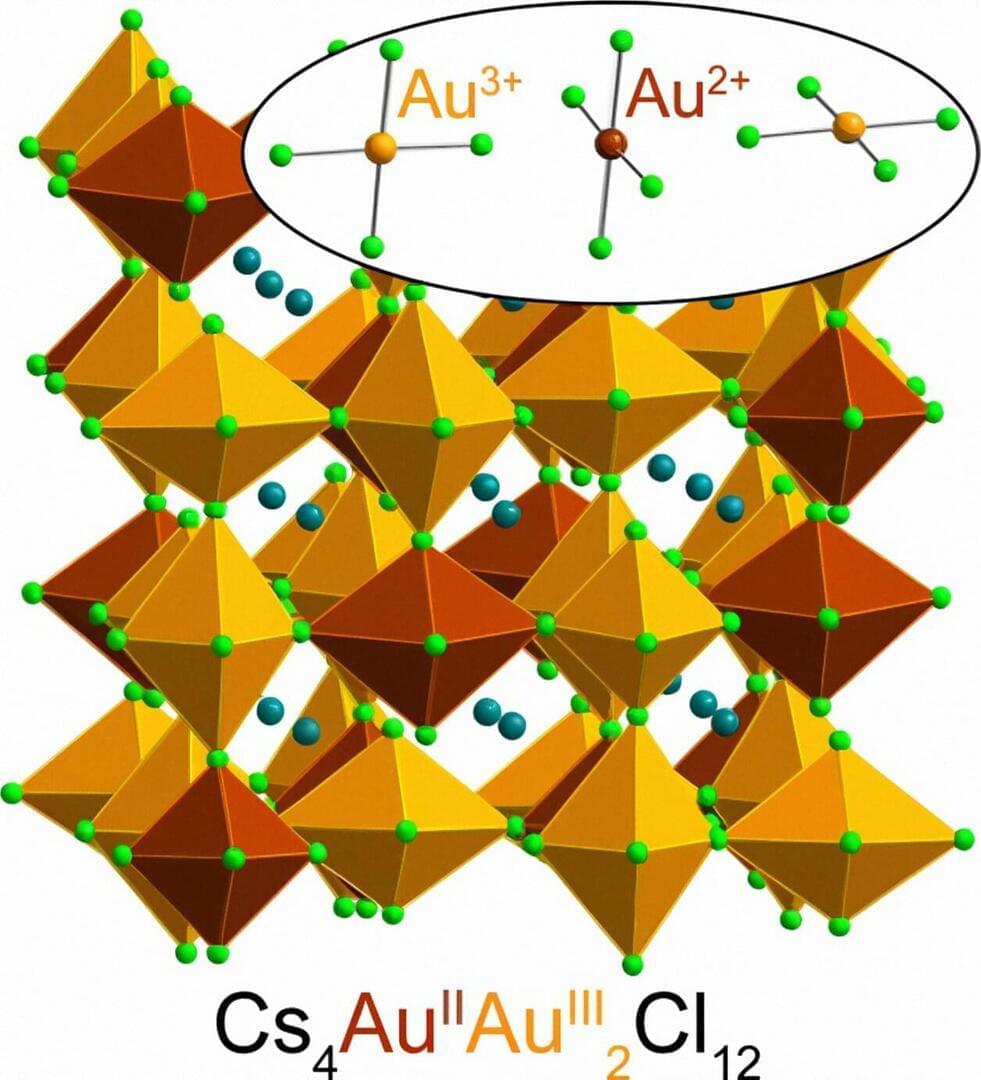
For the first time, Stanford researchers have found a way to create and stabilize an extremely rare form of gold that has lost two negatively charged electrons, denoted Au2+. The material stabilizing this elusive version of the valued element is a halide perovskite—a class of crystalline materials that holds great promise for various applications including more-efficient solar cells, light sources, and electronics components.
Surprisingly, the Au2+ perovskite is also quick and simple to make using off-the-shelf ingredients at room temperature.
“It was a real surprise that we were able to synthesize a stable material containing Au2+ —I didn’t even believe it at first,” said Hemamala Karunadasa, associate professor of chemistry at the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences and senior author of the study published Aug. 28 in Nature Chemistry. “Creating this first-of-its-kind Au2+ perovskite is exciting. The gold atoms in the perovskite bear strong similarities to the copper atoms in high-temperature superconductors, and heavy atoms with unpaired electrons, like Au2+, show cool magnetic effects not seen in lighter atoms.”