Washington state leads the nation in apple production, and in 2022, the industry contributed more than two billion dollars to the U.S. gross domestic product. Throughout Washington, farms employ anywhere from a dozen to hundreds of workers each year for orchard operations, including for pollination, pruning, flower thinning and fruit harvesting. With an aging population and a decrease in migrant farm workers, however, farmers have struggled to meet their needs for workers during harvest season.
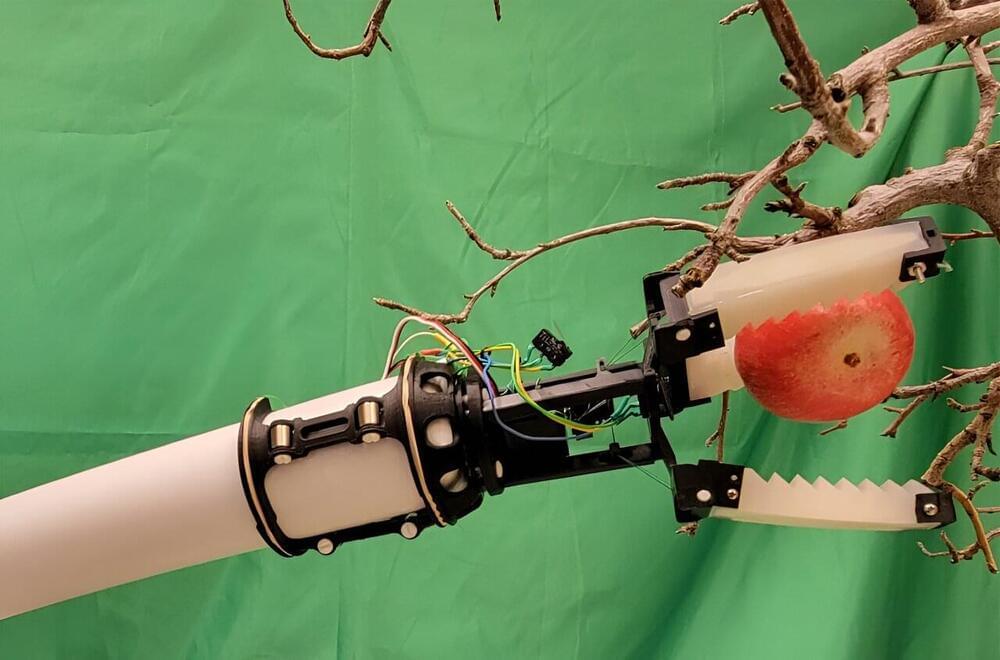
In recent years, researchers have started developing robotic apple harvesting systems, but the ones that have been developed are expensive and complex to use in orchards.
Ninatanta, who grew up in Yakima, Washington, picked fruit alongside his parents during his childhood. When he began his work with Luo on a robotic apple gripper, he had his parents videotape their work, so he could model his gripper on their handiwork.