Sep 4, 2019
A biocompatible magnetic skin that could enable new wearable systems
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biotech/medical, cyborgs, wearables
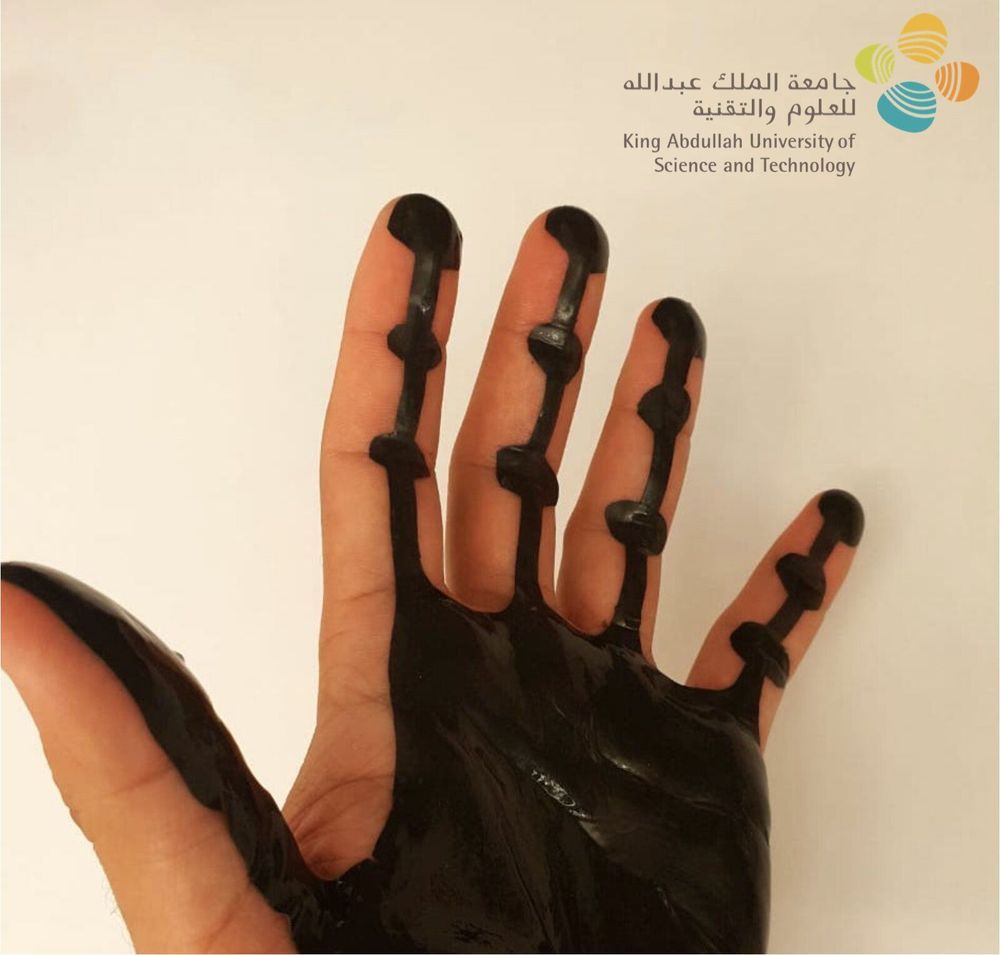
Researchers at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology have recently developed a flexible and imperceptible magnetic skin that adds permanent magnetic properties to all surfaces to which it is applied. This artificial skin, presented in a paper published in Wiley’s Advanced Materials Technologies journal, could have numerous interesting applications. For instance, it could enable the development of more effective tools to aid people with disabilities, help biomedical professionals to monitor their patients’ vital signs, and pave the way for new consumer tech.
“Artificial skins are all about extending our senses or abilities,” Adbullah Almansouri, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “A great challenge in their development, however, is that they should be imperceptible and comfortable to wear. This is very difficult to achieve reliably and durably, if we need stretchable electronics, batteries, substrates, antennas, sensors, wires, etc. We decided to remove all these delicate components from the skin itself and place them in a comfortable nearby location (i.e., inside of eye glasses or hidden in a fabric).”
The artificial skin, developed under the supervision of Prof. Jürgen Kosel, is magnetic, thin and highly flexible. When it is worn by a human user, it can be easily tracked by a nearby magnetic sensor. For instance, if a user wears it on his eyelid, it allows for his eye movements to be tracked; if worn on fingers, it can help to monitor a person’s physiological responses or even to control switches without touching them.