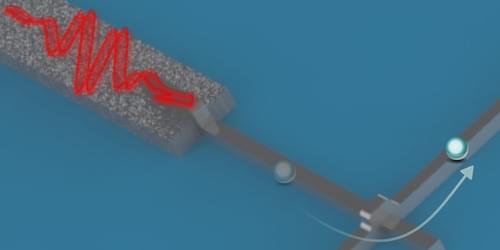
A new device converts a stream of microwave photons into an electric current with high efficiency, which will benefit quantum information technologies.
Technologies for quantum computing, sensing, and communication process information stored in quantum bits (qubits) by using microwave photons. But detecting such photons accurately and at high rates—to read out the changing states of a quantum computer, for example—is a challenge, since they have much less energy than visible or infrared photons. Now researchers have demonstrated a detection method based on the fact that a photon can assist in the quantum tunneling of an electron through a superconducting junction [1]. The technique converts a stream of microwave photons into a flow of electrons far more effectively than other methods, showing an efficiency of 83%, and it will be of immediate use in quantum technologies.
Building good detectors of microwave photons is inherently difficult, says Julien Basset of the University of Paris-Saclay, because such photons lack the energy needed to excite electrons in semiconductors into the conduction band, thereby generating a current that can be measured. Researchers have been pursuing several techniques, but none works well for a continuous stream of photons, in which multiple photons may arrive simultaneously. For such continuous operation, as would likely be required in many practical quantum information devices, the best efficiency demonstrated so far has been only a few percent, Basset says.