Apr 30, 2015
Should We Arm the International Space Station With Lasers to Destroy Space Junk?
Posted by Seb in category: space
By Jason Dorrier — SingularityHub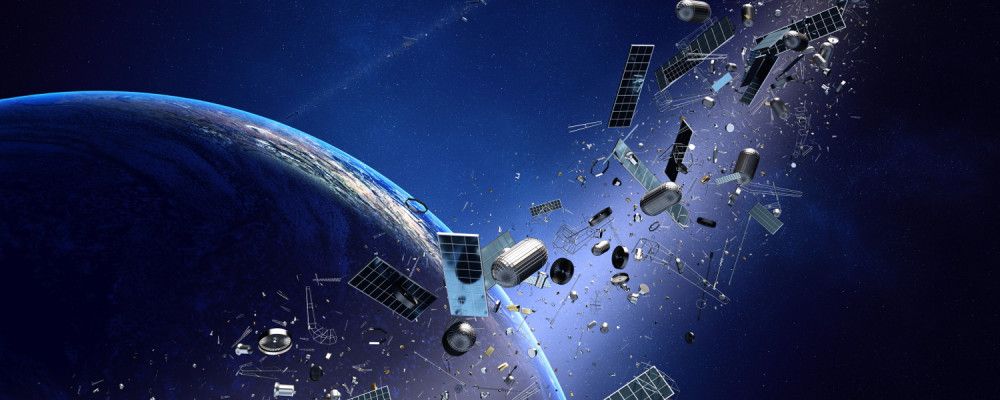
If you look closely enough, Earth has rings. NASA estimates there are some 500,000 pieces of space debris in orbit. Space junk, traveling up to ten times the speed of a bullet, endangers satellites and spacecraft—and it is very, very hard to remove. A team of scientists, however, think they have a way: Lasers.
A recent paper by Tokyo’s Riken institute proposes using a telescope on the International Space Station (ISS) to track small bits of space junk. A laser on the telescope would target and zap the junk, sending it crashing into the atmosphere, where it would vaporize—no longer a threat to humans or satellites. Read more

 Quoted: “I recall reading somewhere that “Ethereum is to Bitcoin as an iPhone is to a calculator”, which is a pretty good analogy. Bitcoin proved to us that it was possible to keep a tamper-proof system synchronised across the globe. There really is no reason the same system can’t be applied to other problems in the same way we apply normal computers to them.
Quoted: “I recall reading somewhere that “Ethereum is to Bitcoin as an iPhone is to a calculator”, which is a pretty good analogy. Bitcoin proved to us that it was possible to keep a tamper-proof system synchronised across the globe. There really is no reason the same system can’t be applied to other problems in the same way we apply normal computers to them.