Apr 14, 2015
Here’s why humans are so obsessed with colonizing Mars
Posted by Seb in categories: space, space travel
Vivian Giang | Quartz
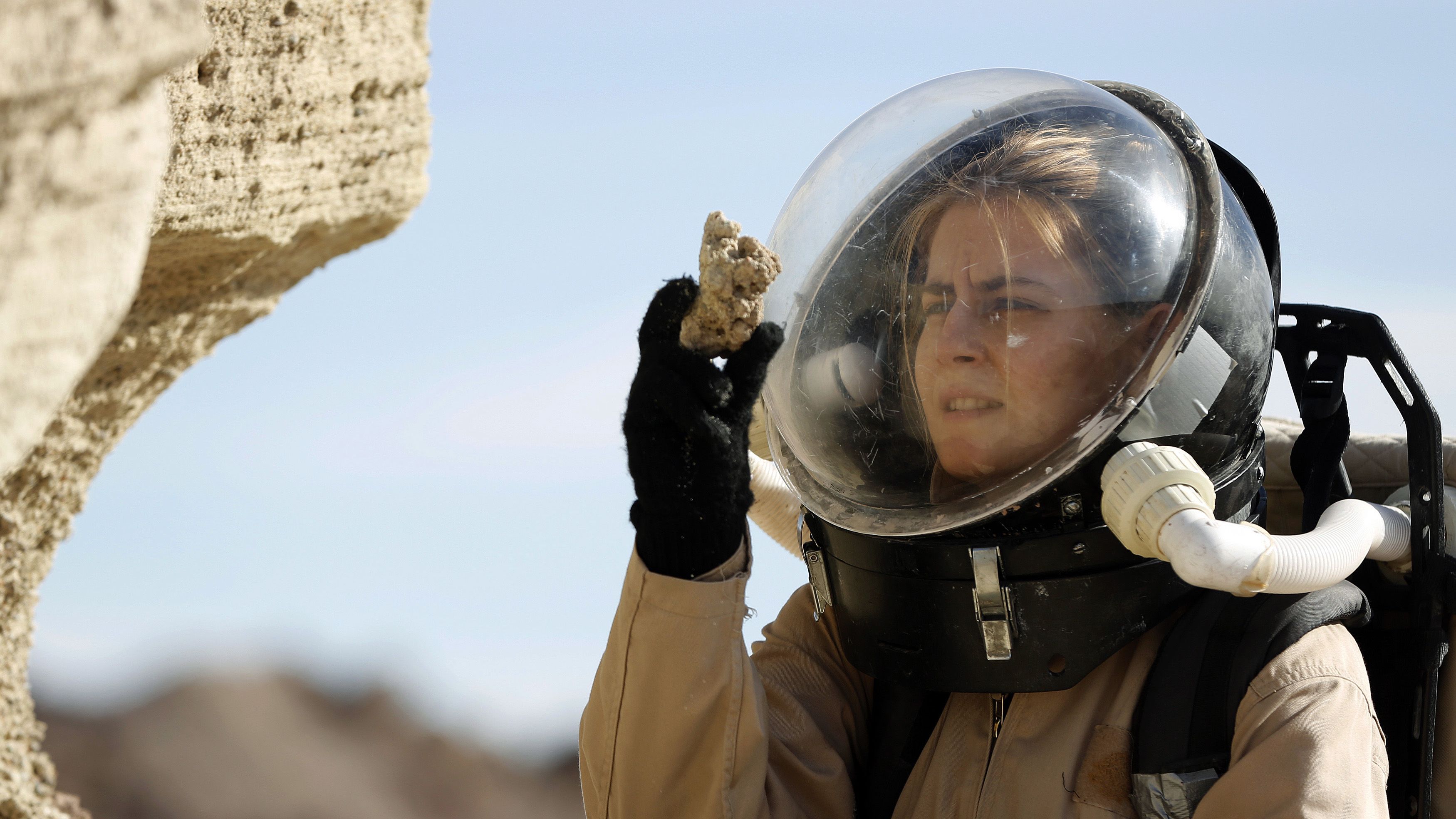

“‘Mars has been unanimously agreed upon by the world’s space agencies as the ‘horizon goal’ for human spaceflight,’ said Do, part of the MIT research group responsible for a widely read report debunking Mars One’s mission as unfeasible. ‘It is widely agreed that Mars is the most promising destination for near term colonization.’” Read more




 Scientists have been working
Scientists have been working 









