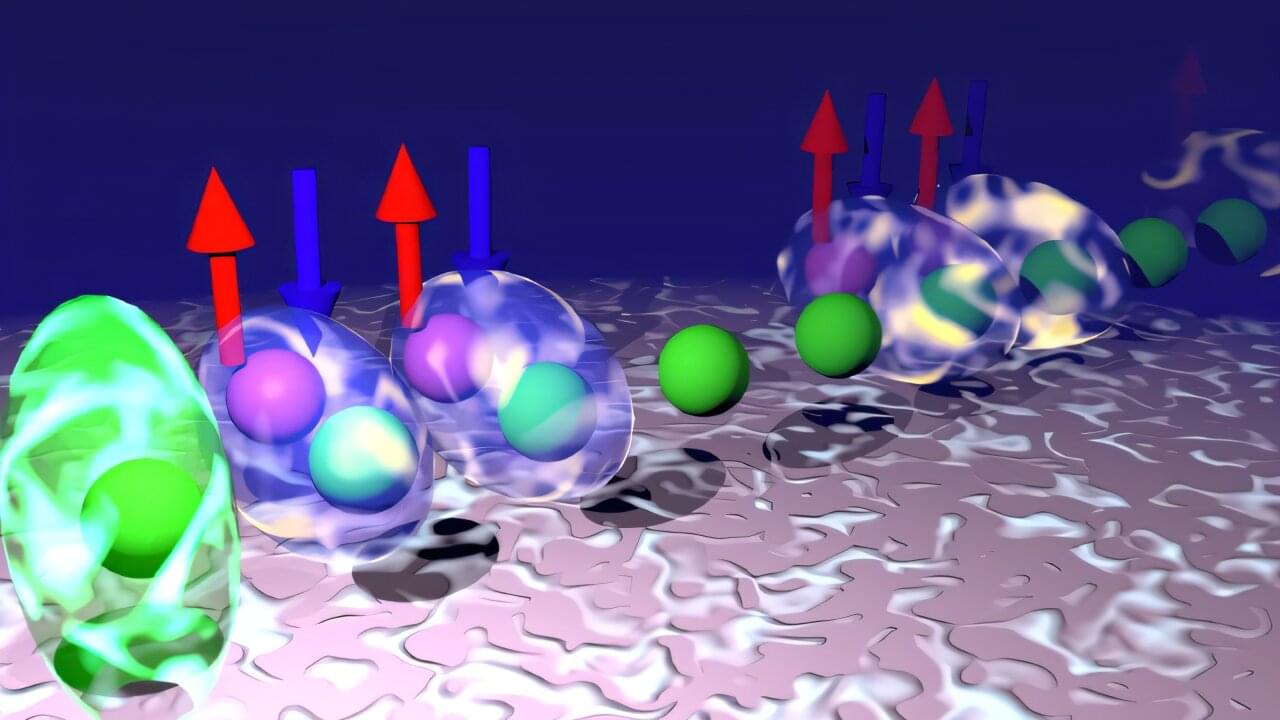
The entry of quantum computers into society is currently hindered by their sensitivity to disturbances in the environment. Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, and Aalto University and the University of Helsinki in Finland, now present a new type of exotic quantum material, and a method that uses magnetism to create stability.
This breakthrough can make quantum computers significantly more resilient—paving the way for them to be robust enough to tackle quantum calculations in practice.
The paper, “Topological Zero Modes and Correlation Pumping in an Engineered Kondo Lattice,” is published in Physical Review Letters.