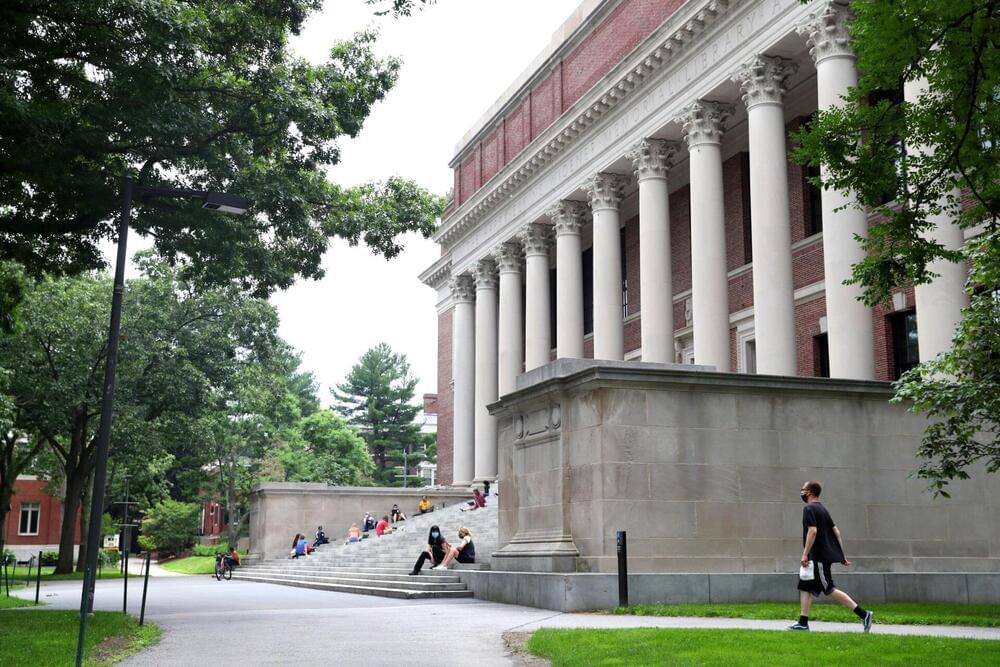
Data is the new oil, as they say, and perhaps that makes Harvard University the new Exxon. The school announced Thursday the launch of a dataset containing nearly one million public domain books that can be used for training AI models. Under the newly formed Institutional Data Initiative, the project has received funding from both Microsoft and OpenAI, and contains books scanned by Google Books that are old enough that their copyright protection has expired.
Wired in a piece on the new project says the dataset includes a wide variety of books with “classics from Shakespeare, Charles Dickens, and Dante included alongside obscure Czech math textbooks and Welsh pocket dictionaries.” As a general rule, copyright protections last for the lifetime of the author plus an additional 70 years.
Foundational language models, like ChatGPT, that behave like a verisimilitude of a real human require an immense amount of high-quality text for their training—generally the more information they ingest, the better the models perform at imitating humans and serving up knowledge. But that thirst for data has caused problems as the likes of OpenAI have hit walls on how much new information they can find—without stealing it, at least.