This essay briefly introduces and contextualizes the extant work on aesthetic snobbery, and identifies some areas for further inquiry. Currently four kinds of snobbery have been identified—social con…


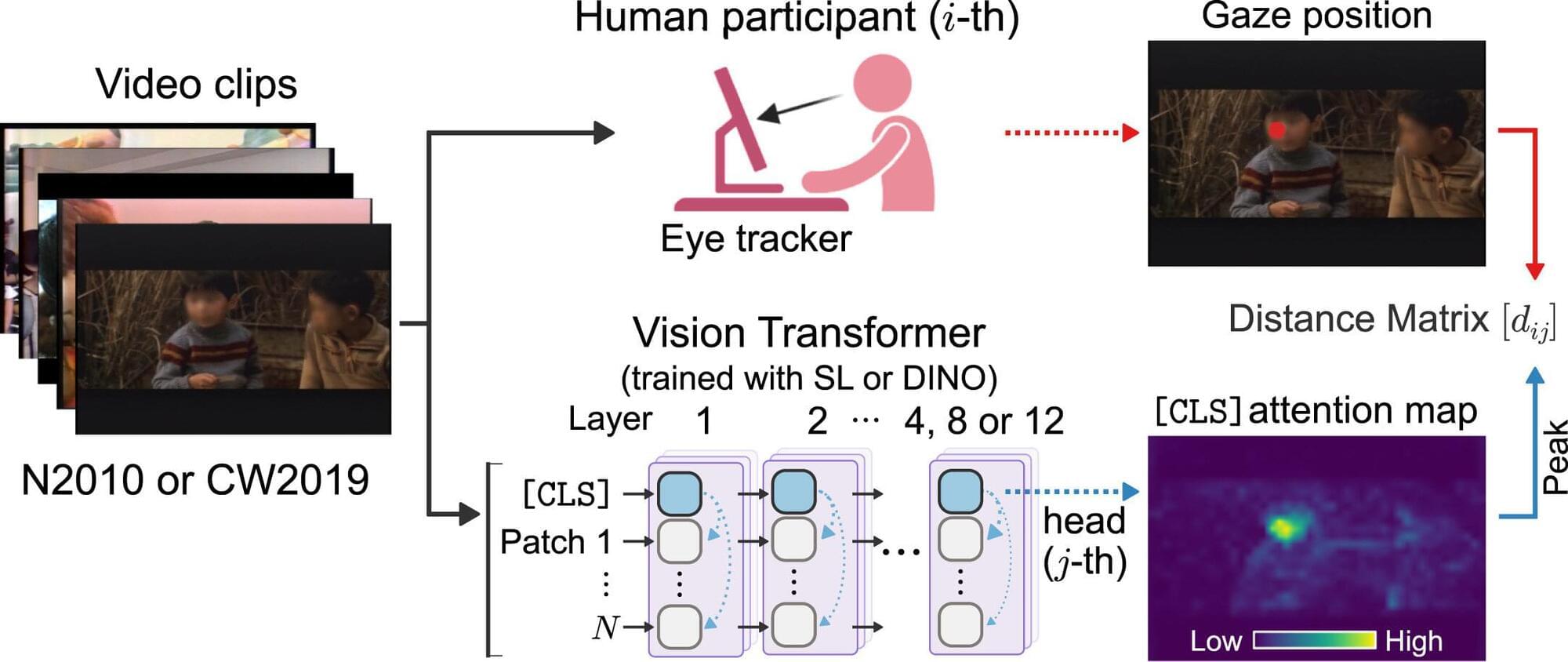
Can machines ever see the world as we see it? Researchers have uncovered compelling evidence that vision transformers (ViTs), a type of deep-learning model that specializes in image analysis, can spontaneously develop human-like visual attention patterns when trained without labeled instructions.
Visual attention is the mechanism by which organisms, or artificial intelligence (AI), filter out “visual noise” to focus on the most relevant parts of an image or view. While natural for humans, spontaneous learning has proven difficult for AI.
However, researchers have revealed, in their recent publication in Neural Networks, that with the right training experience, AI can spontaneously acquire human-like visual attention without being explicitly taught to do so.
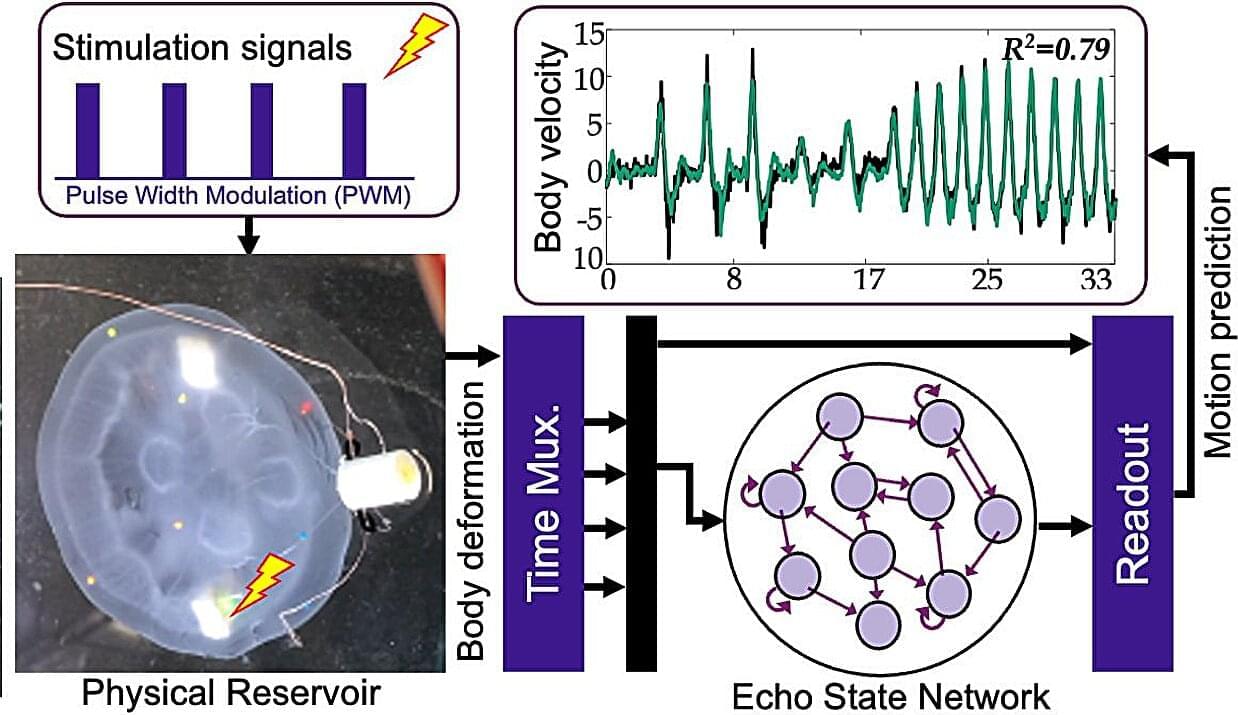
Unlike fish, jellyfish lack bones and possess a sole rudimentary nerve net, yet they can travel considerable distances with minimal energy expenditure. A jellyfish’s seemingly effortless glide through the water is thanks to a ring of muscle within its soft belly, which creates a simple jet that propels it forward. Scientists refer to this intrinsic capability as “embodied intelligence,” which suggests that the organism’s physical structure plays a role in problem-solving.
When harnessed, this locomotion provides an efficient means to monitor coral reefs, track oil spills, and observe climate trends. “Jellyfish cyborgs” require minimal power and operate without engines, limiting the environmental impact associated with current methods of studying the vast expanse of the ocean.
In a new study, a research team, led by Dai Owaki, an associate professor in the Department of Robotics at Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Engineering, successfully modulated the swimming behavior of jellyfish using gentle electric pulses. Moreover, they utilized a lightweight artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict the swimming speed of each jellyfish.
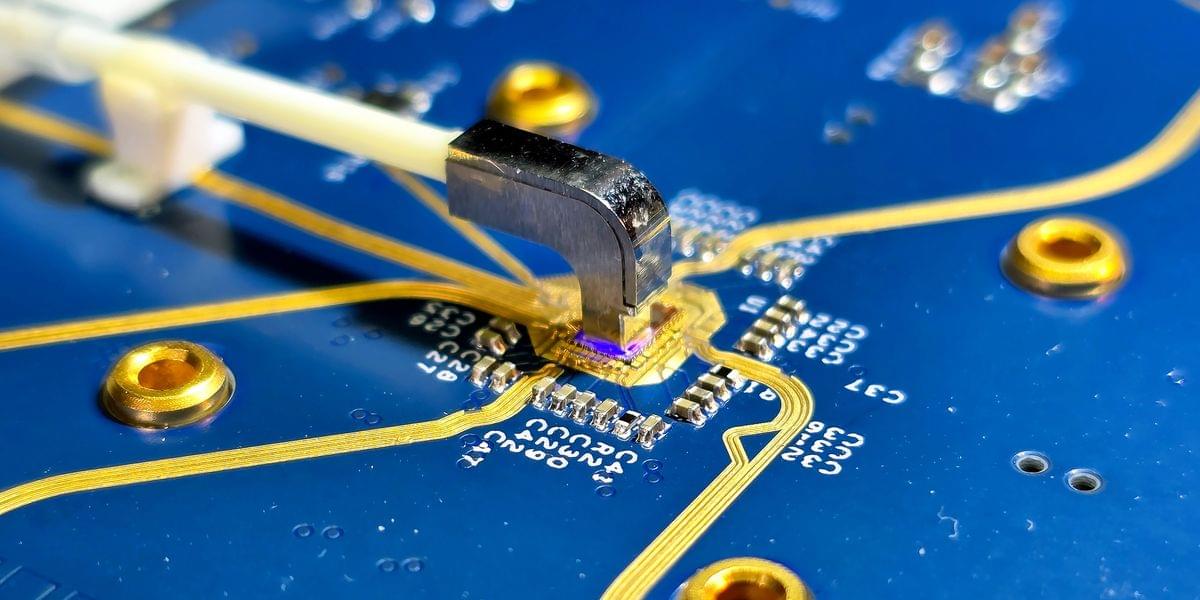


A team of scientists has unveiled a breakthrough that could one day propel computers to operate at speeds millions of times faster than today’s most advanced processors.
The discovery, led by researchers at the University of Arizona and their international collaborators, centers on harnessing ultrafast pulses of light to control the movement of electrons in graphene – a material just one atom thick.
The research, recently published in Nature Communications, demonstrates that electrons can be made to bypass barriers almost instantaneously by firing laser pulses lasting less than a trillionth of a second at graphene. This phenomenon, known as quantum tunneling, has long intrigued physicists, but the team’s ability to observe and manipulate it in real time marks a significant milestone.
Penguin guano helps clouds form in coastal Antarctica, making these birds an important factor in the region’s climate.
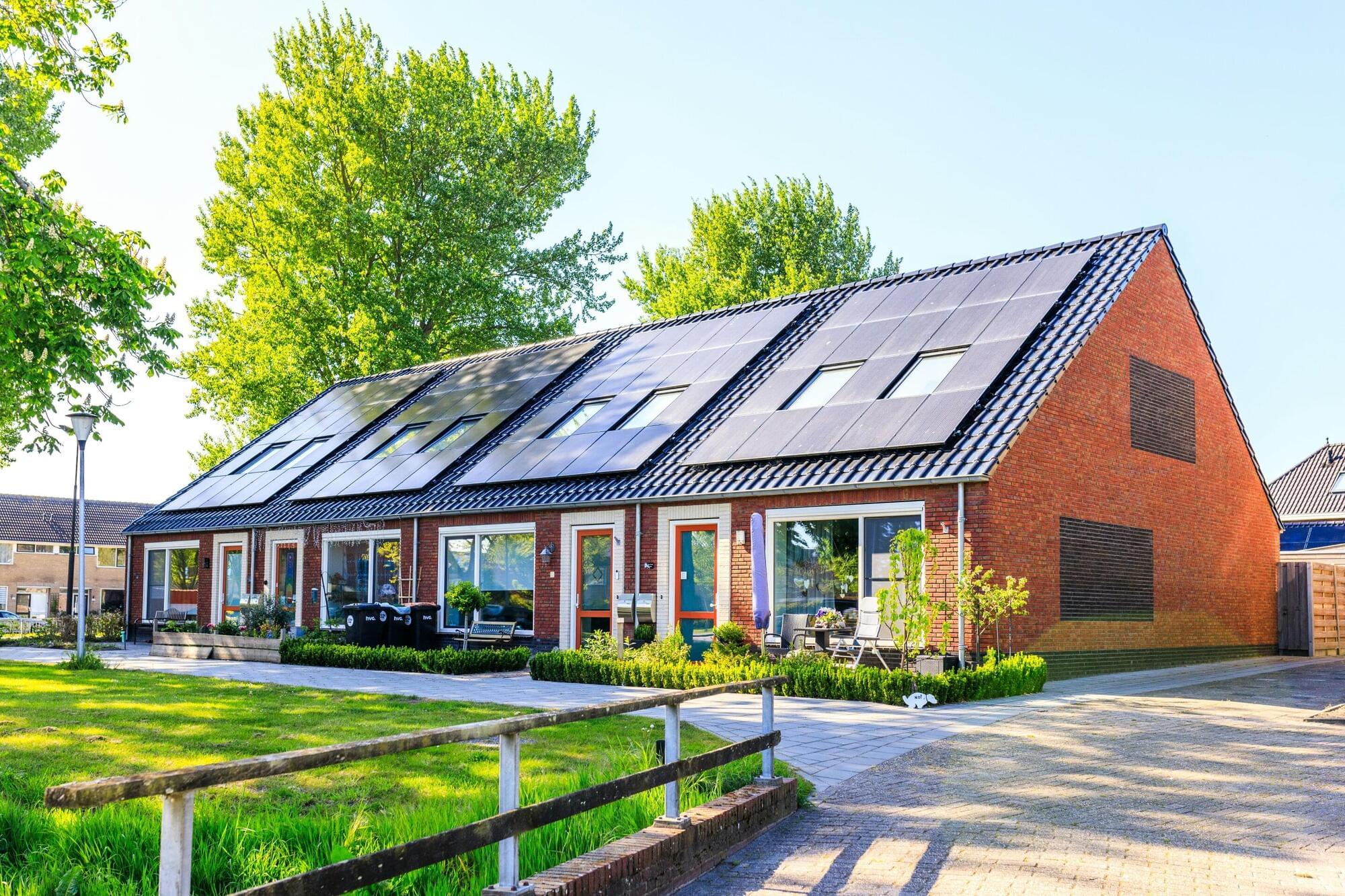


A new study led by Tohoku University has revealed that rooftop solar panels, when combined with electric vehicles (EVs) as batteries, could supply 85% of Japan’s electricity demand and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 87%. The research provides a promising pathway for Japan’s local governments to achieve carbon neutrality by taking advantage of existing infrastructure—rooftops and vehicles—rather than relying solely on large-scale energy systems.