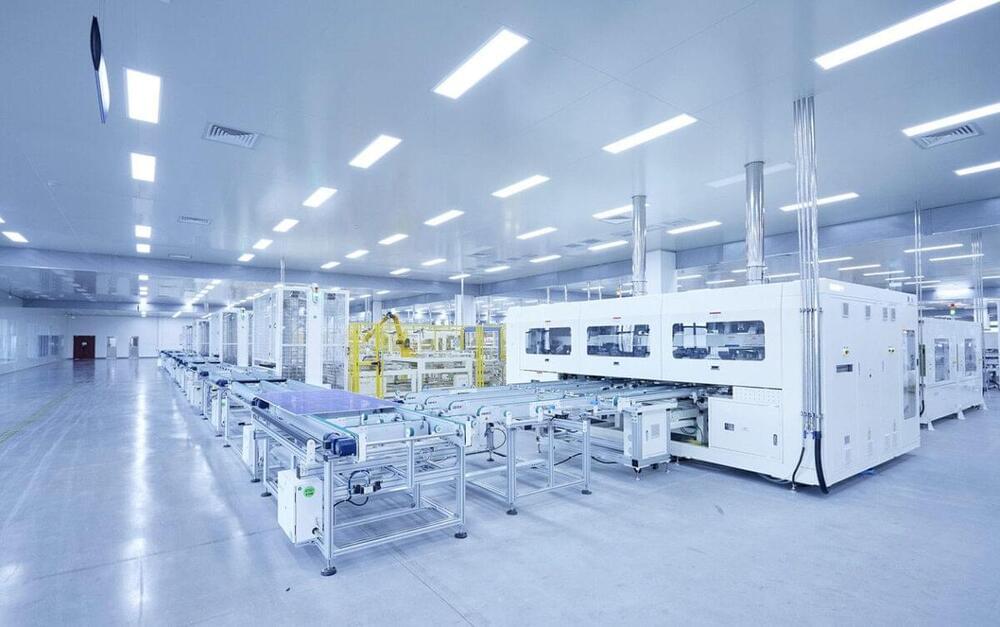
Laboratory testing has revealed that some negatively-doped, ‘n-type’ tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) and heterojunction (HJT) solar modules are susceptible to ultraviolet (UV) light-related damage and degradation. That could mean trouble down the line, if modules in the field begin to show UV-related performance loss. Manufacturers are implementing solutions at cell and module level.
Page 189
Oct 20, 2024
Discover the V-Score: The Secret Weapon in Quantum Problem Solving
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: chemistry, computing, information science, particle physics, quantum physics
Predicting the behavior of many interacting quantum particles is a complex task, but it’s essential for unlocking the potential of quantum computing in real-world applications. A team of researchers, led by EPFL, has developed a new method to compare quantum algorithms and identify the most challenging quantum problems to solve.
Quantum systems, from subatomic particles to complex molecules, hold the key to understanding the workings of the universe. However, modeling these systems quickly becomes overwhelming due to their immense complexity. It’s like trying to predict the behavior of a massive crowd where everyone constantly influences everyone else. When you replace the crowd with quantum particles, you encounter what’s known as the “quantum many-body problem.”
Quantum many-body problems involve predicting the behavior of numerous interacting quantum particles. Solving these problems could lead to major breakthroughs in fields like chemistry and materials science, and even accelerate the development of technologies like quantum computers.
Oct 20, 2024
Quantum Breakthrough: Unmasking Hidden Magnetic Marvels in Kagome Lattices
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, quantum physics
Researchers have achieved a breakthrough in observing intrinsic magnetic structures in kagome lattices, which may significantly influence future quantum computing and superconductivity applications.
A research team led by Prof. Qingyou Lu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. Yimin Xiong from Anhui University, has achieved a groundbreaking discovery. Using advanced techniques such as magnetic force microscopy (MFM), electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, and micromagnetic simulations, they have made the first-ever observation of intrinsic magnetic structures within a kagome lattice.
These findings, published recently in Advanced Science, shed new light on the behavior of materials, which is largely determined by the interaction between their internal electrons and lattice structure. Kagome lattices, known for their unique properties like Dirac points and flat bands, display extraordinary phenomena such as topological magnetism and unconventional superconductivity. These lattices are of great interest because of their potential to unlock new insights into high-temperature superconductivity and quantum computing. Despite this, the intrinsic spin patterns that define these materials have remained elusive—until now.
Oct 20, 2024
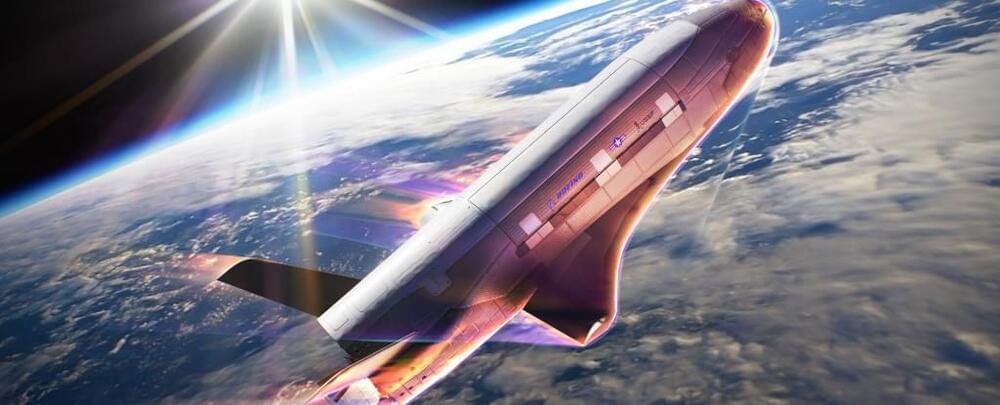
Mysterious Space Plane X-37B to Try ‘First of a Kind’ Maneuvers in Orbit
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: space
The X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV) has been shrouded in mystery since its maiden flight in 2011.
Designed by Boeing and operated by the US Space Force (USSF), this remotely operated, reusable space plane is designed to operate in Low-Earth Orbit (LEO), 240 to 800 kilometers (150 to 500 miles) above the Earth, and test reusable vehicle technologies that support long-term space objectives.
On December 29th, 2023, the X-37B began its seventh mission (OTV-7) and has reportedly been conducting experiments on the effects of space radiation and testing Space Domain Awareness (SDA) technologies.
Oct 20, 2024
Google Pivots to Nuclear Reactors to Power Its Artificial Intelligence
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: climatology, nuclear energy, robotics/AI
Google on Monday signed a deal to get electricity from small nuclear reactors to help power artificial intelligence.
The agreement to buy energy from reactors built by Kairos Power came just weeks after word that Three Mile Island, the site of America’s worst nuclear accident, will restart operations to provide energy to Microsoft.
“We believe that nuclear energy has a critical role to play in supporting our clean growth and helping to deliver on the progress of AI,” Google senior director of energy and climate said during a briefing.
Oct 20, 2024
Dreams as Portals to Parallel Realities and Reflections of Self
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: cosmology, neuroscience
Your consciousness could travel multiverse when you dream, claim scientists https://interestingengineering.com/science/alternate-reality-in-dreams
Oct 20, 2024
From $8,000 to $3: OpenAI’s Revolutionary Impact on Legal Work
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: law, robotics/AI
OpenAI CPO Kevin Weil says their o1 model can now write legal briefs that previously were the domain of $1000/hour associates: “what does it mean when you can suddenly do $8000 of work in 5 minutes for $3 of API credits?” pic.twitter.com/MotT9Oo9rv
Oct 20, 2024
ESA: First piece of great cosmic map features 100 mn celestial objects
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: cosmology
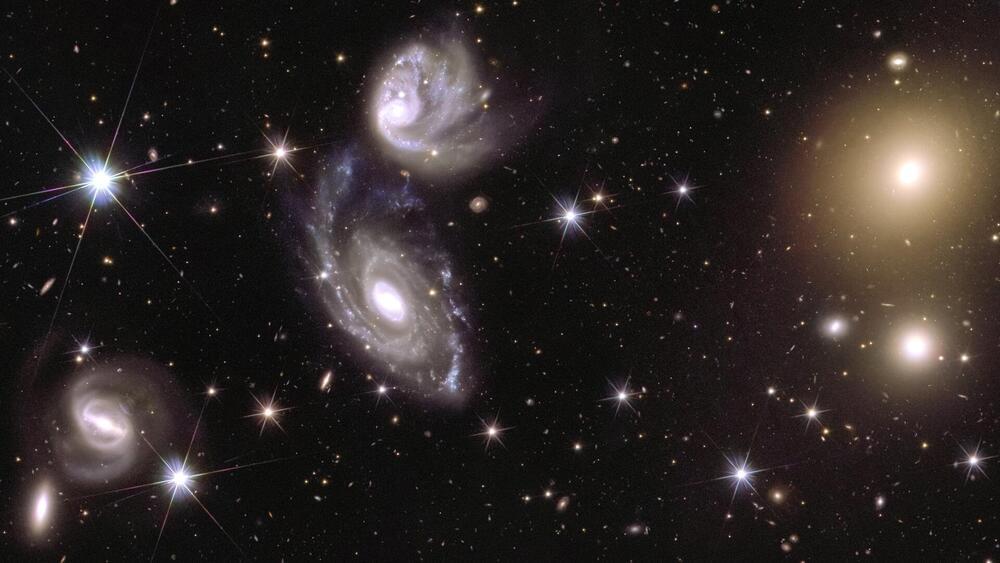

The universe’s structure spans a vast network 500 times the size of the moon.
According to ESA, “This first piece of the map already contains around 100 million sources: stars in our Milky Way and galaxies beyond. Some 14 million of these galaxies could be used to study the hidden influence of dark matter and dark energy on the Universe.”
Continue reading “ESA: First piece of great cosmic map features 100 mn celestial objects” »
Oct 20, 2024
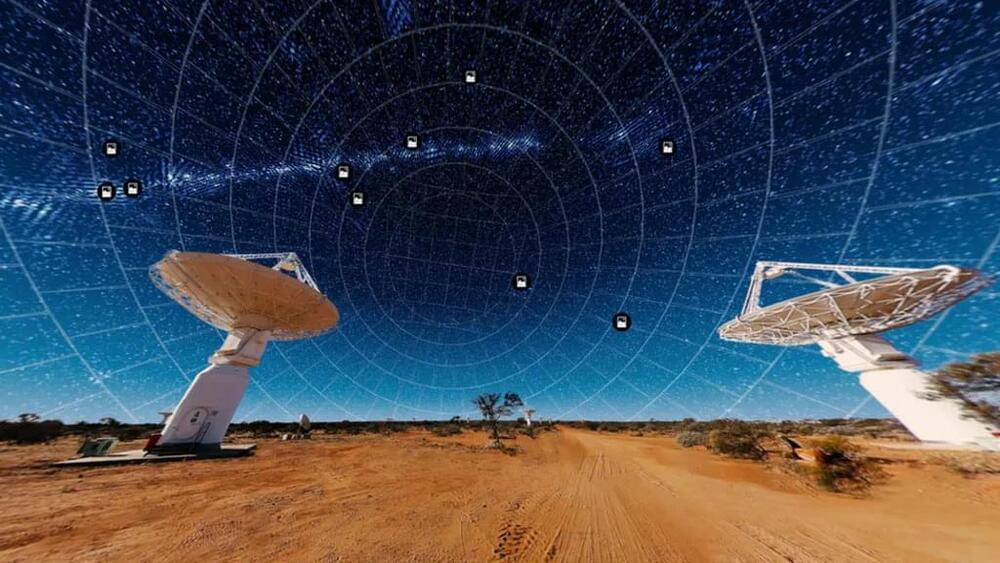
Scientists Have Mapped 1 Million New Galaxies In Just 300 Hours
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: space
Australian scientists say they have mapped a million new galaxies using an advanced telescope in the desert.
Astronomers mapped 83% of the sky and discovered 1 million new galaxies in just 300 hours.
The CSIRO, the national science agency, said its new telescope had created “a new atlas of the Universe” in record time – showing unprecedented detail.