Do you have a telescope? Would you like to see some of the same night sky objects from the ground that Hubble has from space? We invite you to commemorate Hubble’s 35th anniversary by accepting our year-long stargazing challenge. On a clear night, find a safe location with a dark sky away from bright lights, point your telescope skyward, and with the help of star and finder charts, gaze upon some of the same iconic nebulae and galaxies Hubble has observed. How many of them can you find?
Page 21
Nov 19, 2024
Quantum time crystals could be used to store energy
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, quantum physics
The weird thermodynamics found in time crystals could be harnessed to store energy in a quantum battery-like device.
Nov 19, 2024
Caltech Astrophysicists Flip Black Hole Theories With Stunning New Simulations
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: cosmology, evolution, physics
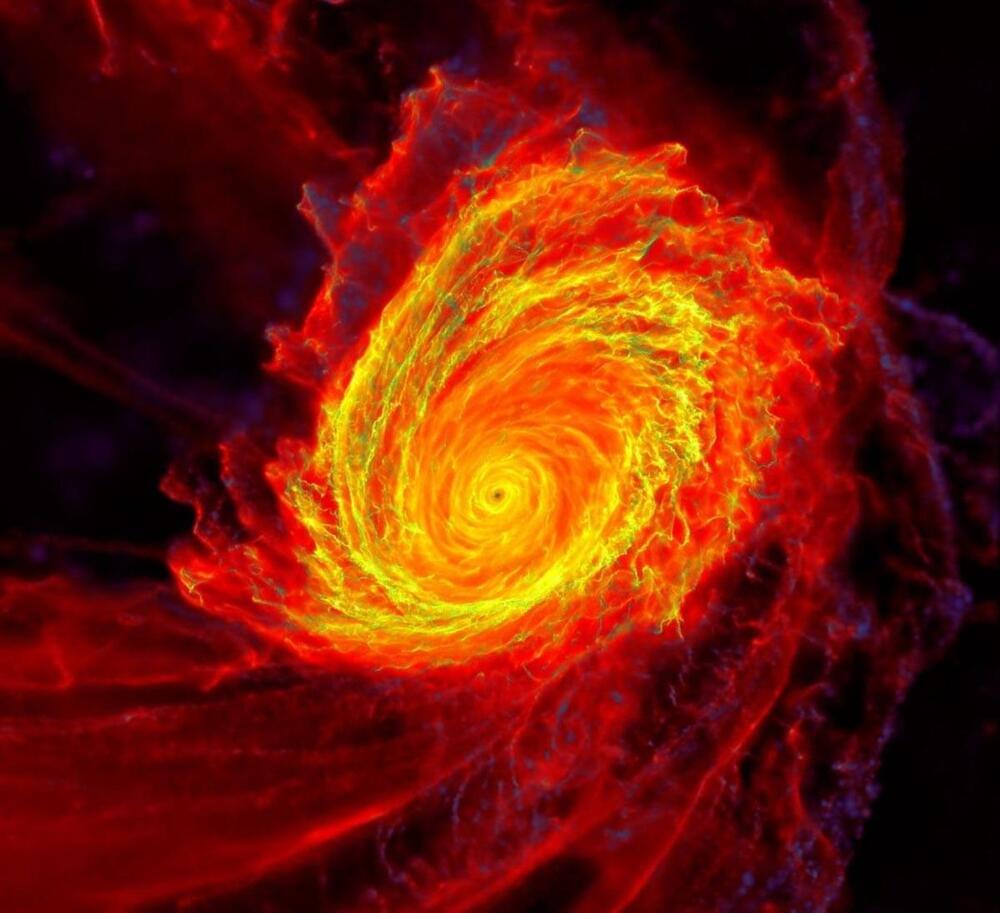

Astounding simulation shows magnetic fields create fluffy, not flat, accretion disks around supermassive black holes, altering our understanding of black hole dynamics.
A team of astrophysicists from Caltech has achieved a groundbreaking milestone by simulating the journey of primordial gas from the early universe to its incorporation into a disk of material feeding a supermassive black hole. This innovative simulation challenges theories about these disks that have persisted since the 1970s and opens new doors for understanding the growth and evolution of black holes and galaxies.
Continue reading “Caltech Astrophysicists Flip Black Hole Theories With Stunning New Simulations” »
Nov 19, 2024
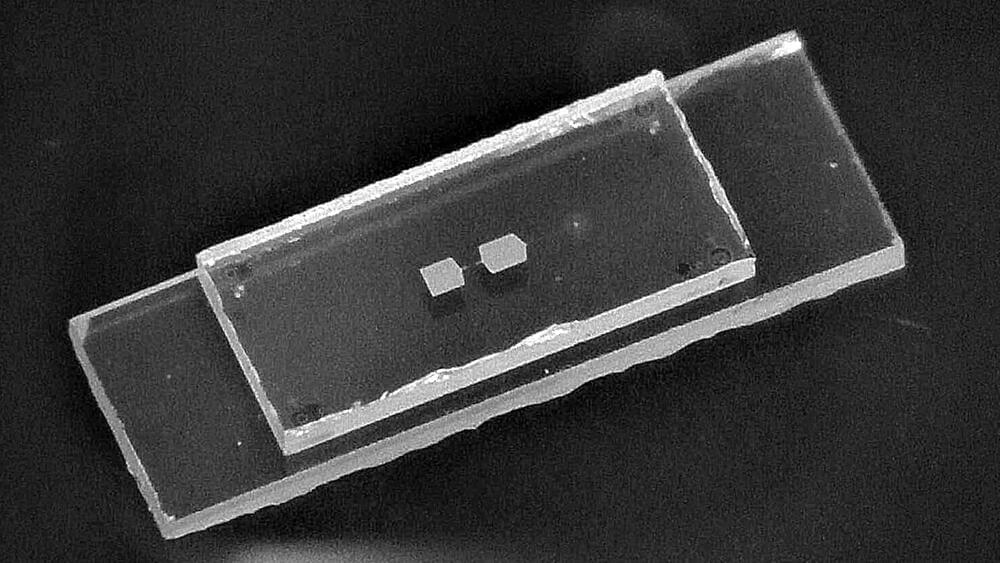
Quantum miracle: Scientists create world’s first mechanical qubit
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: innovation, quantum physics
Researchers at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich have developed the first-ever fully functional mechanical qubit. This incredible quantum innovation is a two-in-one system combining the abilities of a mechanical oscillator and a superconducting qubit.
Compared to the traditional virtual qubits that are created using multiple physical qubits and error-correcting codes to protect quantum information, mechanical qubits are real, physical systems that don’t need this extra layer of protection.
Nov 19, 2024
Ion Engines could take us to the Solar Gravitational Lens in less than 13 years, suggests paper
Posted by Natalie Chan in categories: materials, space travel
Sending an object to another star is still the stuff of science fiction. But some concrete missions could get us at least part way there. These “interstellar precursor missions” include a trip to the solar gravitational lens point at 550 AU from the sun—farther than any artificial object has ever been, including Voyager.
To get there, we’ll need plenty of new technologies, and a recent paper presented at the 75th International Astronautical Congress in Milan this month looks at one of those potential technologies—electric propulsion systems, otherwise known as ion drives.
The paper aimed to assess when any existing ion drive technology could port a large payload on one of several trajectories, including a trip around Jupiter, one visiting Pluto, and even one reaching that fabled solar gravitational lens. To do so, they specified an “ideal” ion drive with characteristics that enabled optimal values for some of the system’s physical characteristics.
Nov 19, 2024
Humans are walking ecosystems and microbes rule their evolution
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biological, genetics, health, robotics/AI
We might like to think of ourselves as autonomous entities but, in reality, we’re more like walking ecosystems, teeming with bacteria, viruses, and other microbes. It turns out that differences in these microbes might be as crucial to evolution and natural variation as genetic mutations are.
This novel perspective was discussed in a recent publication by Seth Bordenstein, director of Penn State’s One Health Microbiome Center, who is a professor of biology and entomology and holds the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Endowed Chair in Microbiome Sciences.
He, along with 21 colleagues from around the globe, collectively known as the Holobiont Biology Network, propose that understanding the relationships between microbes and their hosts will lead to a more profound understanding of biological variation.
Nov 19, 2024
Nvidia Is Helping Google Design Quantum Computing Processors
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: quantum physics, robotics/AI
Nvidia Corp., the chipmaker at the center of a boom in artificial intelligence use, is teaming up with Alphabet Inc.’s Google to pursue another technology once relegated to science fiction: quantum computing.
Nov 19, 2024
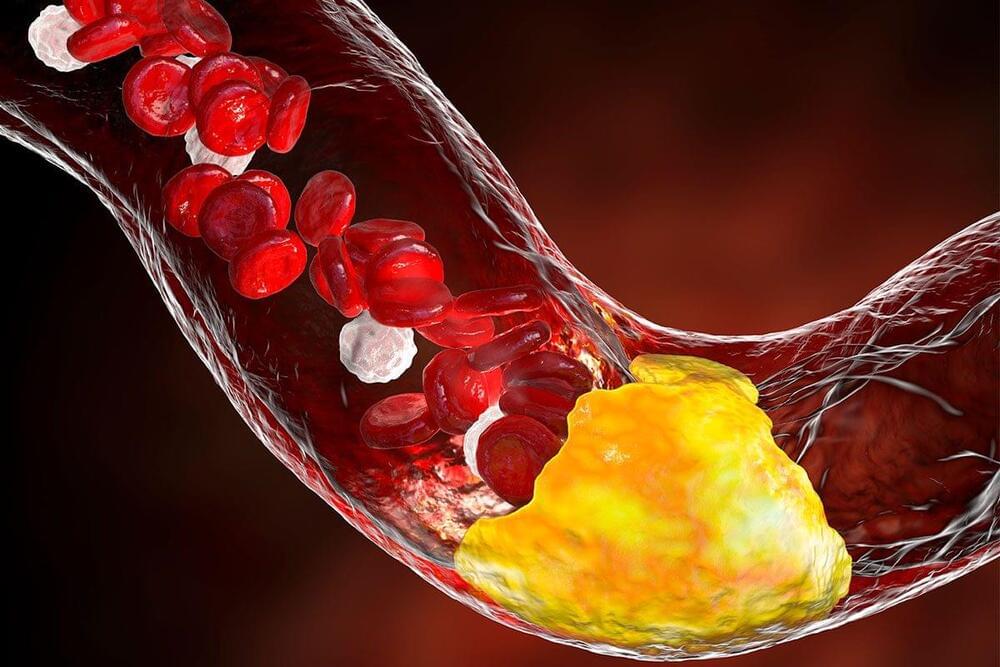
Here’s how your cholesterol level shapes your dementia risk
Posted by Arthur Brown in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Scientists have discovered your cholesterol levels could be significantly linked to your risk of developing dementia. And it’s not just high cholesterol that matters: fluctuating levels over several years could increase your chances of the disease by 60 per cent, suggests a new study of 10,000 people.
The research also suggests that, even if you don’t develop dementia, a large cholesterol variability – swinging from high to low levels – is linked to an increased risk of general cognitive decline by 23 per cent.
Nov 19, 2024
A New Formula Reveals That Alien Life Might Form in Unlikely Realities
Posted by Arthur Brown in category: alien life
Nov 19, 2024
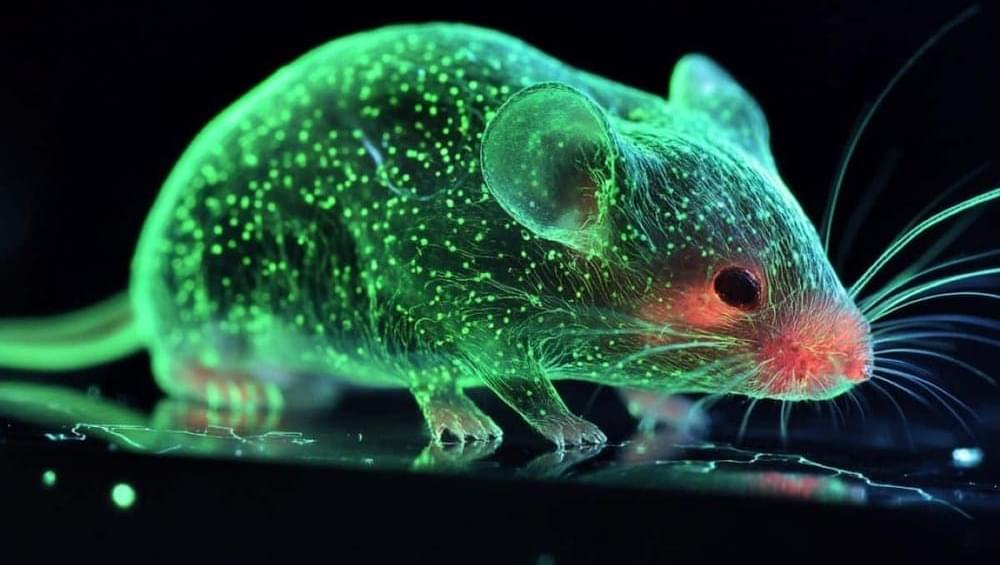
Ancient Gene Reprograms Stem Cells to Create a Living Mouse
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
Summary: Scientists have reprogrammed mouse cells into pluripotent stem cells using a gene from choanoflagellates, single-celled organisms related to animals. This breakthrough demonstrates that key genes driving stem cell formation existed in unicellular ancestors nearly a billion years ago.
The resulting stem cells were used to create a chimeric mouse, showcasing how ancient genetic tools can integrate with modern mammalian biology. This discovery redefines the evolutionary origins of stem cells and may inform regenerative medicine advancements.