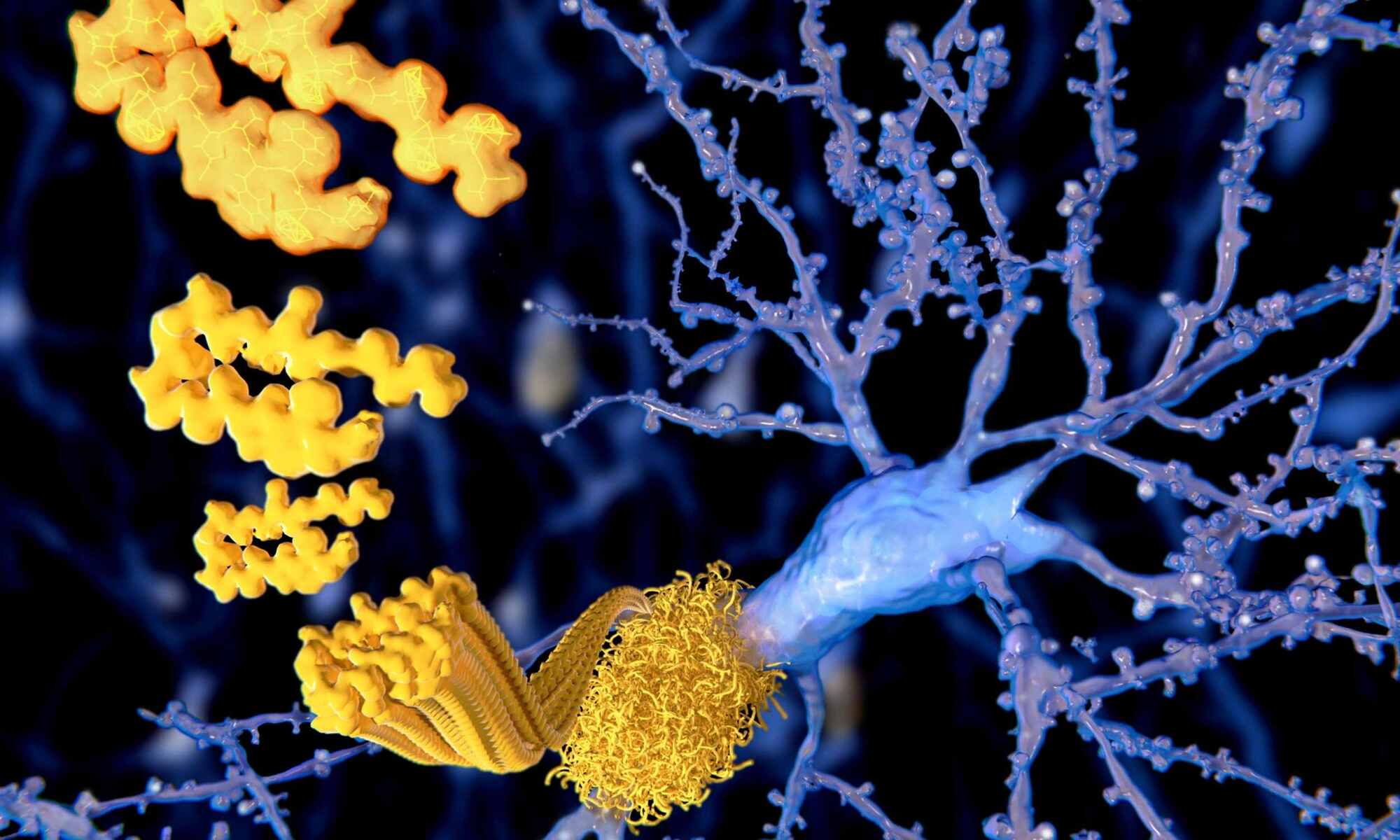
A young Chinese man diagnosed with Alzheimer’s at the age of 19 is demanding that the early causes of the disease be investigated.


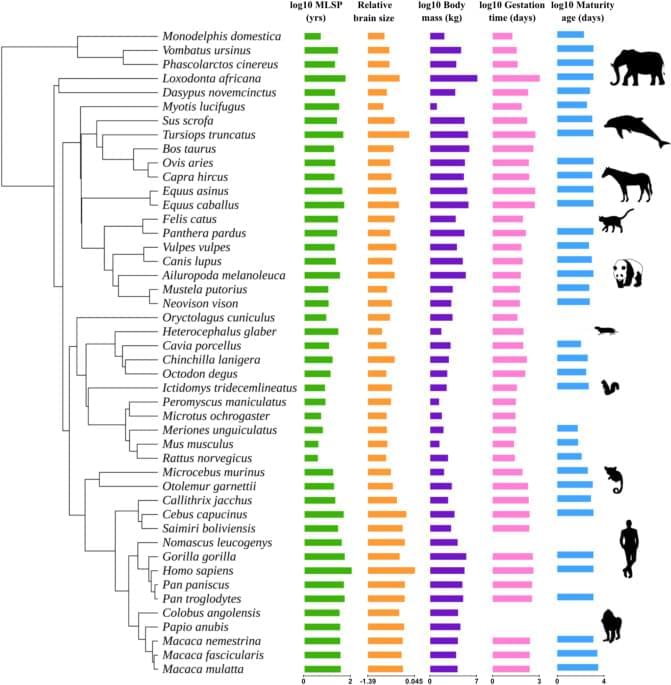
Kilili, H., Padilla-Morales, B., Castillo-Morales, A. et al. Sci Rep 15, 15,087 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98786-3
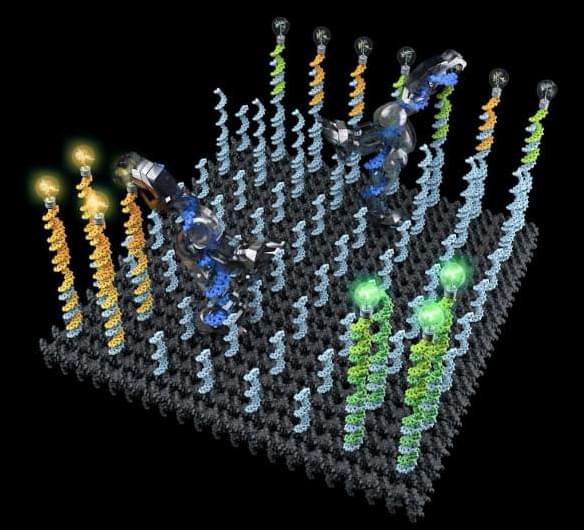
The field of nanotechnology is still in its nascent stages, but recent innovations are increasingly making this science fiction world of tiny robots into a reality. New breakthrough research from a team at Caltech has demonstrated the ability of a robot made of a single strand of DNA to explore a molecular surface, pick up targeted molecules, and move them to another designated location.
“Just like electromechanical robots are sent off to faraway places, like Mars, we would like to send molecular robots to minuscule places where humans can’t go, such as the bloodstream,” says Lulu Qian, co-author on the paper. “Our goal was to design and build a molecular robot that could perform a sophisticated nanomechanical task: cargo sorting.”
Previous work by a variety of researchers has successfully demonstrated the creation of such DNA robots, but this is the first time they have been shown to pick up and transport specific molecules.
In this profound and thought-provoking clip from the Quantum Convergence documentary, tech pioneer and physicist Federico Faggin delves into his transformative experience of consciousness — the moment he felt himself as the universe observing itself. Faggin, best known for his work in developing the first microprocessor, explores the fundamental nature of consciousness, its relationship with matter, and the deeper purpose of the universe.
🌐 About Quantum Convergence:
Quantum Convergence is a groundbreaking documentary that explores the intersection of science, technology, and consciousness. Featuring leading thinkers and visionaries, the film examines how our understanding of reality is evolving in the age of AI and quantum physics.
🔔 Subscribe for more transformative content:
📍 Stay updated with more clips and insights from Quantum Convergence by hitting the notification bell.
👍 Like, share, and comment if you believe in the power of consciousness.
#QuantumConvergence #Consciousness #FedericoFaggin #AI #Philosophy #Science #QuantumPhysics.
Learn more — https://www.infinitepotential.com/


Researchers have developed two unique energy-efficient and cost-effective systems that use urea found in urine and wastewater to generate hydrogen.
The unique systems reveal pathways to economically generate “green” hydrogen, a sustainable and renewable energy source, and the potential to remediate nitrogenous waste in aquatic environments.
Typically, we generate hydrogen through the electrolysis of water where water is split into oxygen and hydrogen. It is a promising technology to help solve the global energy crisis, but the process is energy intensive, which renders it cost-prohibitive when compared to extracting hydrogen from fossil fuels (gray hydrogen), itself an undesirable process because of the carbon emissions it generates.
Researchers at TUM and TUMint. Energy Research have taken a significant step towards improving solid-state batteries. They developed a new material made of lithium, antimony and scandium that conducts lithium ions more than 30% faster than any previously known material. The work is published in the journal Advanced Energy Materials.
The team led by Prof. Thomas F. Fässler from the Chair of Inorganic Chemistry with a Focus on Novel Materials partially replaced lithium in a lithium antimonide compound with the metal scandium. This creates specific gaps, so-called vacancies, in the crystal lattice of the conductor material. These gaps help the lithium ions to move more easily and faster, resulting in a new world record for ion conductivity.
Since the measured conductivity far exceeded that of existing materials, the team collaborated with the Chair of Technical Electrochemistry under Prof. Hubert Gasteiger at TUM to confirm the result.
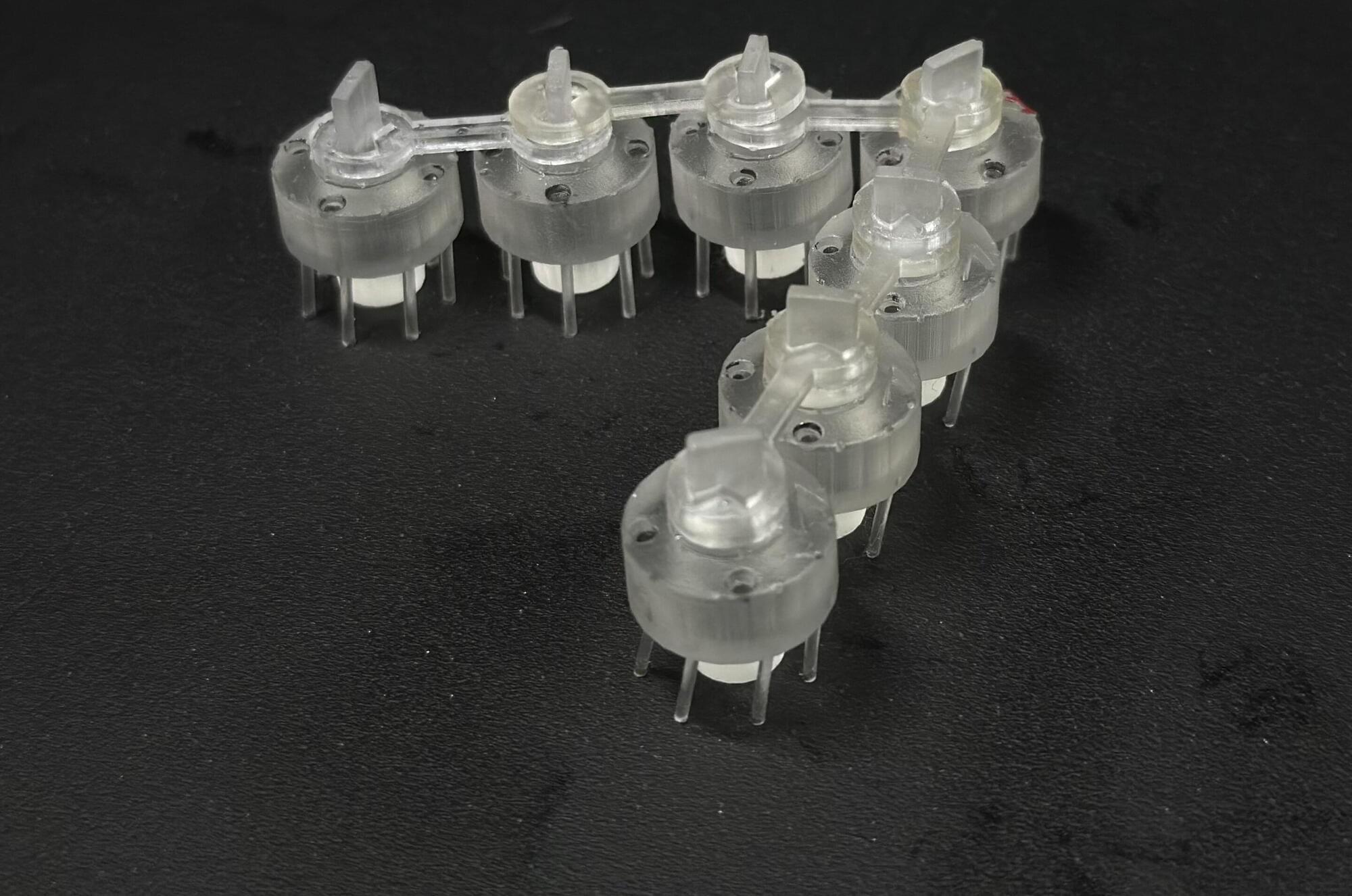
A joint research team from Seoul National University and Harvard University has developed a next-generation swarm robot system inspired by nature—capable of movement, exploration, transport, and cooperation, all without the need for precise sensors or centralized control.
The study was led by Professor Ho-Young Kim, Dr. Kyungmin Son, and master’s student Kwanwoo Kim at SNU’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor L. Mahadevan and Dr. Kimberly Bowal at Harvard.
Their approach connects simple, active particles into chain-like structures that can carry out complex tasks without any advanced programming or artificial intelligence. The research is published in Science Advances.