Dec 4, 2024
Hackers claim major breakthrough in Windows and Office license fraud
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, innovation
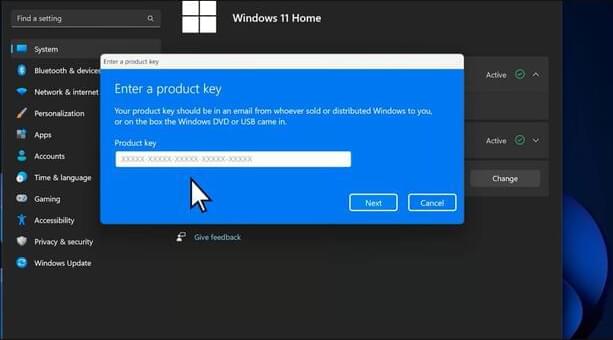
Massgrave, a piracy group developing activation scripts for Microsoft products, claims to have discovered a new method to permanently activate “almost any version of Windows and Office.”
This group is behind the MAS (Microsoft Activation Scripts) project, which develops piracy tools to activate various versions of Microsoft Windows operating systems and Office products. Unauthorized software license manipulation is illegal in most jurisdictions.
Continue reading “Hackers claim major breakthrough in Windows and Office license fraud” »