Thalamic regions drive conscious perception by syncing with the prefrontal cortex, acting as a gateway to awareness. Using direct intracranial brain recordings in humans, a new study has identified the thalamus, a small, deeply situated brain structure, as a key player in conscious perception. Th
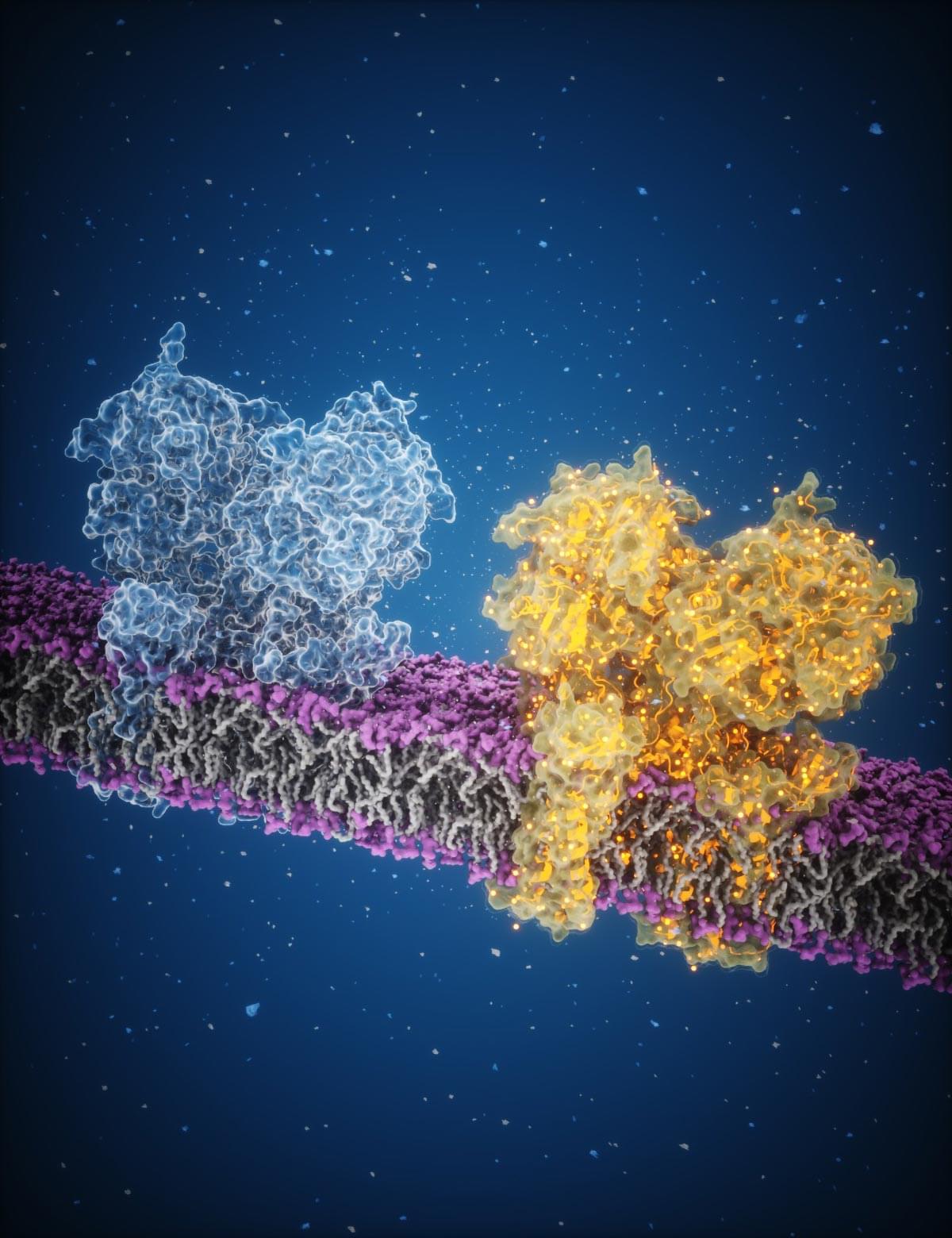
Scientists used advanced cryo-EM imaging to reveal how glutamate activates brain receptors, paving the way for new neurological treatments. To better understand how brain cells communicate using chemical signals, scientists have used a highly specialized microscope to capture detailed images of h
Every star that hangs upon the evening firmament will one day die, its lights snuffed and its fires cooling in the dwindling cosmic end times.
We don’t always know when, but for a binary star system around 150 light-years from Earth, a precise time of death has now been discovered. Some 23 billion years from now, the two white dwarf stars are destined to smash together.
At least, they would, if not for the fact both will be taken out before this fated merger by a spectacular explosion – a Type Ia supernova, one of the measuring sticks against which we gauge distance in the Universe.
On April 1, 2025, the Taiwanese manufacturer TSMC introduced the world’s most advanced microchip: the 2 nanometre (2nm) chip.
Mass production is expected for the second half of the year, and TSMC promises it will represent a major step forward in performance and efficiency – potentially reshaping the technological landscape.
Microchips are the foundation of modern technology, found in nearly all electronic devices, from electric toothbrushes and smartphones to laptops and household appliances. They are made by layering and etching materials like silicon to create microscopic circuits containing billions of transistors.
Noticing somebody fidgeting can be distracting. Vexing. Even excruciating. But why?
According to research, the stressful sensations caused by seeing others fidget are an incredibly common psychological phenomenon, affecting as many as one in three people.
Called misokinesia – meaning ‘hatred of movements’ – this strange phenomenon had been little studied by scientists until recent years, but was noted in the context of a related condition, misophonia: a disorder where people become irritated upon hearing certain repetitious sounds.
If you go walking in the wild, you might expect that what you’re seeing is natural. All around you are trees, shrubs and grasses growing in their natural habitat.
But there’s something here that doesn’t add up. Across the world, there are large areas of habitat which would suit native plant species just fine. But very often, they’re simply absent.
Our new research gauges the scale of this problem, known as “dark diversity”. Our international team of 200 scientists examined plant species in thousands of sites worldwide.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Neuroscience are two fields, but they are closely related to each other. Artificial intelligence can provide powerful tools for neuroscience research, and its application in neurological diseases is of great importance. The convergence of AI and neuroscience has sparked a paradigm shift in our understanding of the brain and its intricate mechanisms.
Here, Creative Biolabs explores the remarkable impact of AI in neuroscience research, highlighting its potential to unlock new frontiers in our quest to unravel the mysteries of the brain.
Neuroscience research generates vast amounts of complex data, ranging from molecular and cellular information to data generated by large-scale brain activity. For researchers, analyzing and decoding this wealth of data is a major challenge. AI technology steps in to address just this problem.
Researchers have used a mind-reading brain implant to continuously play a paralyzed person’s thoughts through a speaker, allowing them to talk again.
In this episode, we welcome Prof. Dr.-Ing. Maurits Ortmanns, a leading expert in ASIC design and professor at the University of Ulm, Germany. With a distinguished career in microelectronics, Dr. Ortmanns has contributed extensively to the development of integrated circuits for biomedical applications. He shares insights into the critical role of ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) design in advancing neurotech implants, focusing on low-power, high-speed circuits that are essential for optimizing the performance and reliability of these devices. Dr. Ortmanns also discusses the challenges and future of circuit integration in neurotechnology.
Top 3 Takeaways:
“Each ASIC is very low in cost because the development cost is spread across millions of units. The actual production cost is minimal; the primary expense lies in the development time until the first chips are produced and ready for manufacturing.” “For an inexperienced engineer, it typically takes about six months to a year to design the blueprint for the chip. Then, depending on the manufacturer, it takes an additional four to six months for the actual fabrication of the ASIC. Finally, you would need another one to two months for testing, so the total turnaround time for a small chip is approximately one and a half years.” “Let’s take the example of a neuromodulator. You need recordings or data from neurons and stimulation data going to the neurons, so you essentially have these two components. Then, you encounter challenges like stimulation artifacts. One person might focus on eliminating the stimulation artifact in the recording channel. That requires additional algorithms or hardware, and the data needs to be digitized, which is another task. You may also have someone working on a compression algorithm and building digital circuitry to compress the raw input data. Then, there’s the data interface, power management, and wireless energy delivery. Each person works on their specific innovation, and if everything is well-planned and lucky, all these pieces can come together to create a complete system. However, sometimes you simply don’t have a breakthrough idea for power management or communication.” 0:45 Do you want to introduce yourself better than I just did?
3:15 What is integrated circuit design?
7:30 What are ASIC’s? How are they used in neurotech?
10:15 How does the million dollar fab cost get split into each chip?