A new study highlights a potential role for immune system dysfunction in the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.


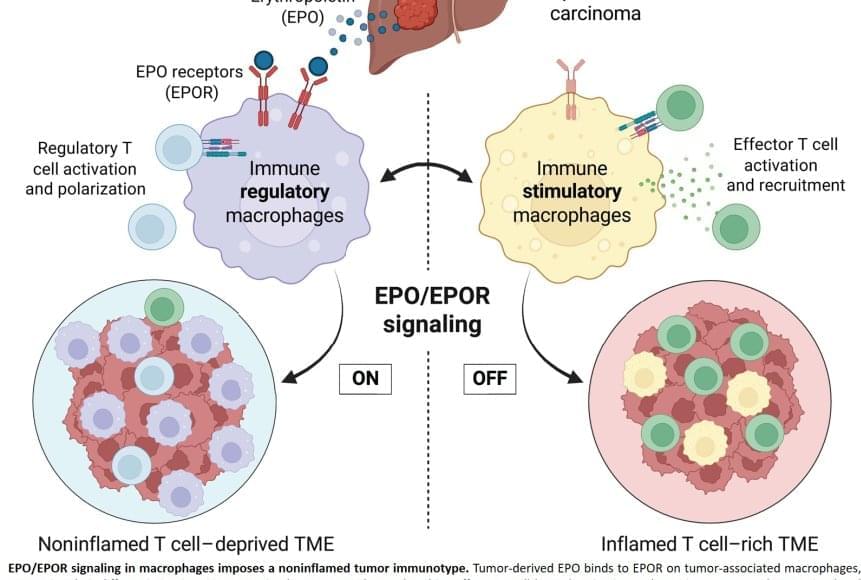
A protein identified nearly 40 years ago for its ability to stimulate the production of red blood cells plays a surprising, critical role in dampening the immune system’s response to cancer.
Blocking the activity of the protein turns formerly “cold,” or immune-resistant, liver tumors in mice into “hot” tumors teeming with cancer-fighting immune cells. When combined with an immunotherapy that further activates these immune cells against the cancer, the treatment led to complete regression of existing liver tumors in most mice. Treated animals lived for the duration of the experiment. In contrast, control animals survived only a few weeks.
“This is a fundamental breakthrough in our understanding of how the immune system is turned off and on in cancer,” said the senior author published the work in Science. “I could not be more excited about this discovery, and I hope treatments that target the mechanism we uncovered will quickly move forward to human trials.”
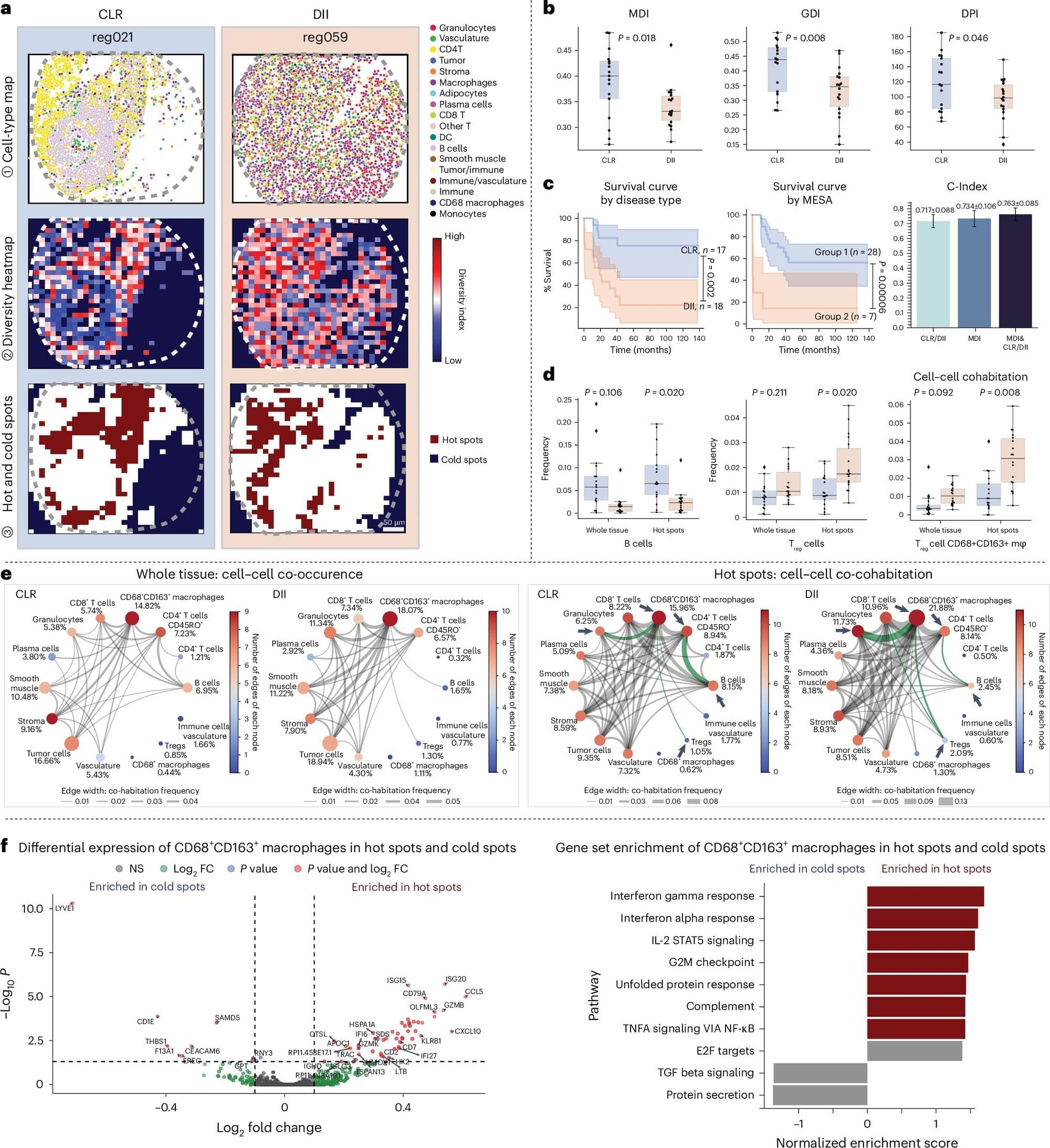
To understand what drives disease progression in tissues, scientists need more than just a snapshot of cells in isolation—they need to see where the cells are, how they interact, and how that spatial organization shifts across disease states. A computational method called MESA (Multiomics and Ecological Spatial Analysis), detailed in a study published in Nature Genetics, is helping researchers study diseased tissues in more meaningful ways.
The work details the results of a collaboration among researchers from MIT, Stanford University, Weill Cornell Medicine, the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard, and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and was led by the Stanford team.
MESA brings an ecology-inspired lens to tissue analysis. It offers a pipeline to interpret spatial omics data—the product of cutting-edge technology that captures molecular information along with the location of cells in tissue samples. This data provides a high-resolution map of tissue “neighborhoods,” and MESA helps make sense of the structure of that map.
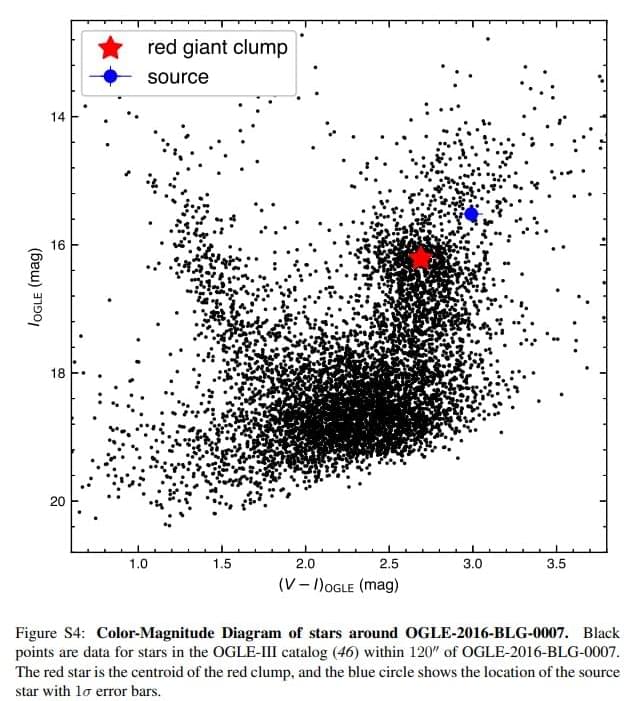
A new study of light anomalies combined with results from a Korea Microlensing Telescope Network microlensing survey show that super-Earths exist as far from their host star as our gas giants are from the sun. Which means that Earth-like exoplanets are a lot more common NASA press releases over every new statistical wobble suggest.
In a demographically diverse sample of healthy people, Cornell researchers found dramatic changes over the human lifespan in the brain’s “blue spot”—a tiny region involved in cognition and believed to be the first affected by neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease.
Using specialized MRI scans to measure the intensity of neuromelanin, a pigment that gives the locus coeruleus (LC) its blue color, the research team observed an inverted U-shaped curve that peaked in later middle age before dropping off sharply, a finding that helps characterize healthy aging patterns.
Maintaining a stronger blue signal after age 60 was associated with better cognitive performance, according to the study involving 134 participants aged 19 to 86. Because of the participants’ diversity, including about 40% who were non-white, the researchers also discovered higher peaks among Black participants and women, groups known to be more susceptible to Alzheimer’s.

On this day, April 25, in 1929, the world learned how astronomer Edwin Hubble had discovered that the universe was much larger than we had believed. On this day in 2025, you can preorder a book and on the 29th learn about this and four other Astrophysics discoveries that changed how we see the universe — and ourselves — in The Story of Astrophysics in Five Revolutions.
By Ersilia Vaudo, translated by Vanessa Di Stefano. If you use this link we get a penny or something.
He had published his seminal paper in the March issue of Astrophysical Journal but on April 25th in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences he published the how, and people began to think about what it meant. He had discovered that the collection of gas and dust we call Andromeda was actually another galaxy.
Researchers have created a light-powered soft robot that can carry loads through the air along established tracks, similar to cable cars or aerial trams. The soft robot operates autonomously, can climb slopes at angles of up to 80 degrees, and can carry loads up to 12 times its weight.
“We’ve previously created soft robots that can move quickly through the water and across solid ground, but wanted to explore a design that can carry objects through the air across open space,” says Jie Yin, associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work published in Advanced Science.
“The simplest way to do this is to follow an established track—similar to the aerial trams you see in the mountains. And we’ve now demonstrated that this is possible.”
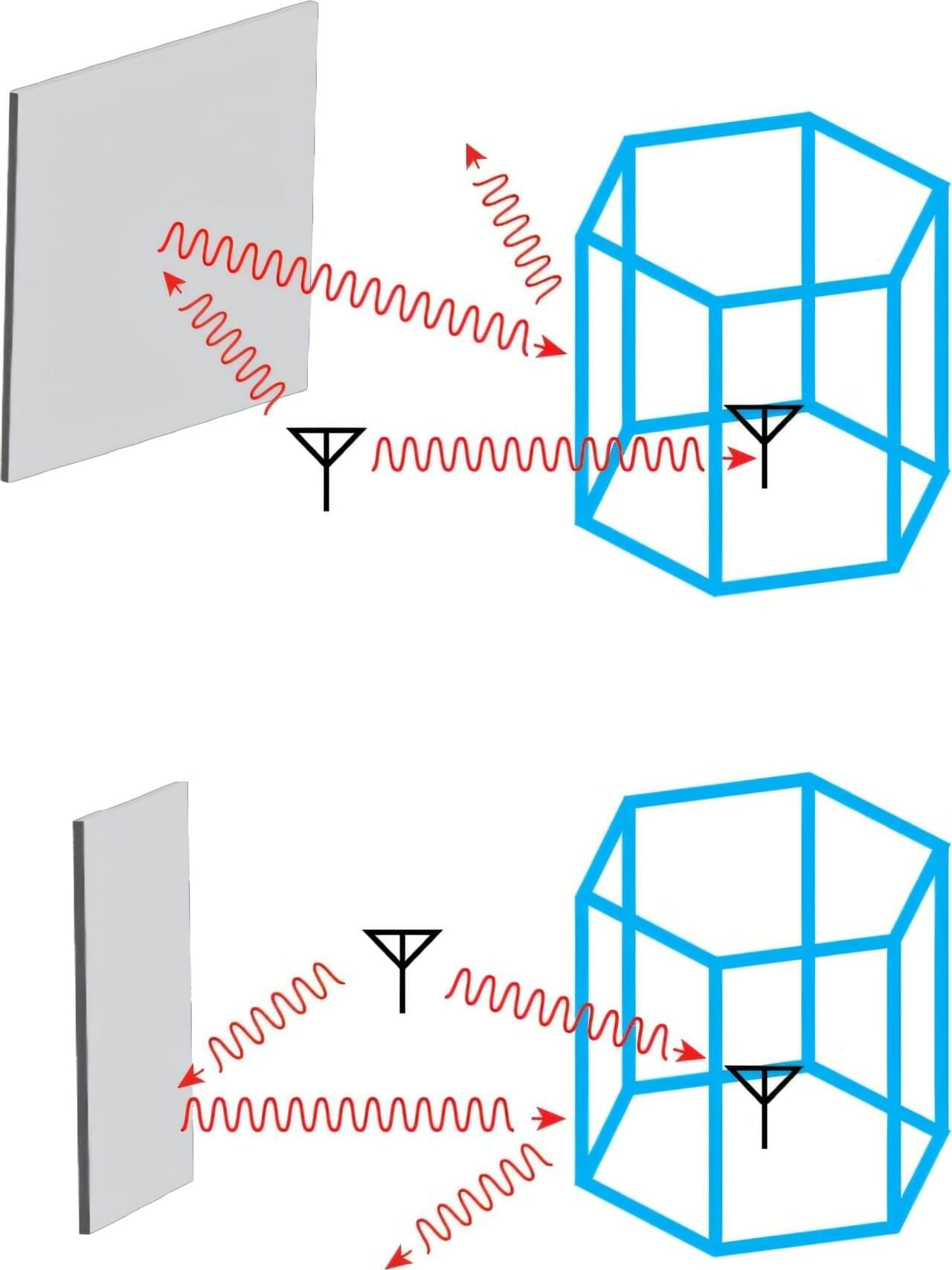
The evolution of wireless communications and the miniaturization of electrical circuits have fundamentally reshaped our lives and the digital landscape. However, as we push toward higher-frequency communications in an increasingly connected world, engineers face growing challenges from multipath propagation—a phenomenon where the same radio signal reaches receiving antennas through multiple routes, usually with time delays and altered amplitudes.
Multipath interference leads to many reliability issues, ranging from “ghosting” in television broadcasts to signal fading in wireless communications.
Addressing multipath interference has long presented two fundamental physical challenges. First, multipath signals share the same frequency with the main (leading) signal, rendering conventional frequency-based filtering techniques ineffective. Second, the incident angles of these signals are variable and unpredictable. These limitations have made passive solutions particularly difficult to implement, as traditional materials bound by linear time-invariant (LTI) responses maintain the same scattering profile for a given frequency, regardless of when the signal arrives.
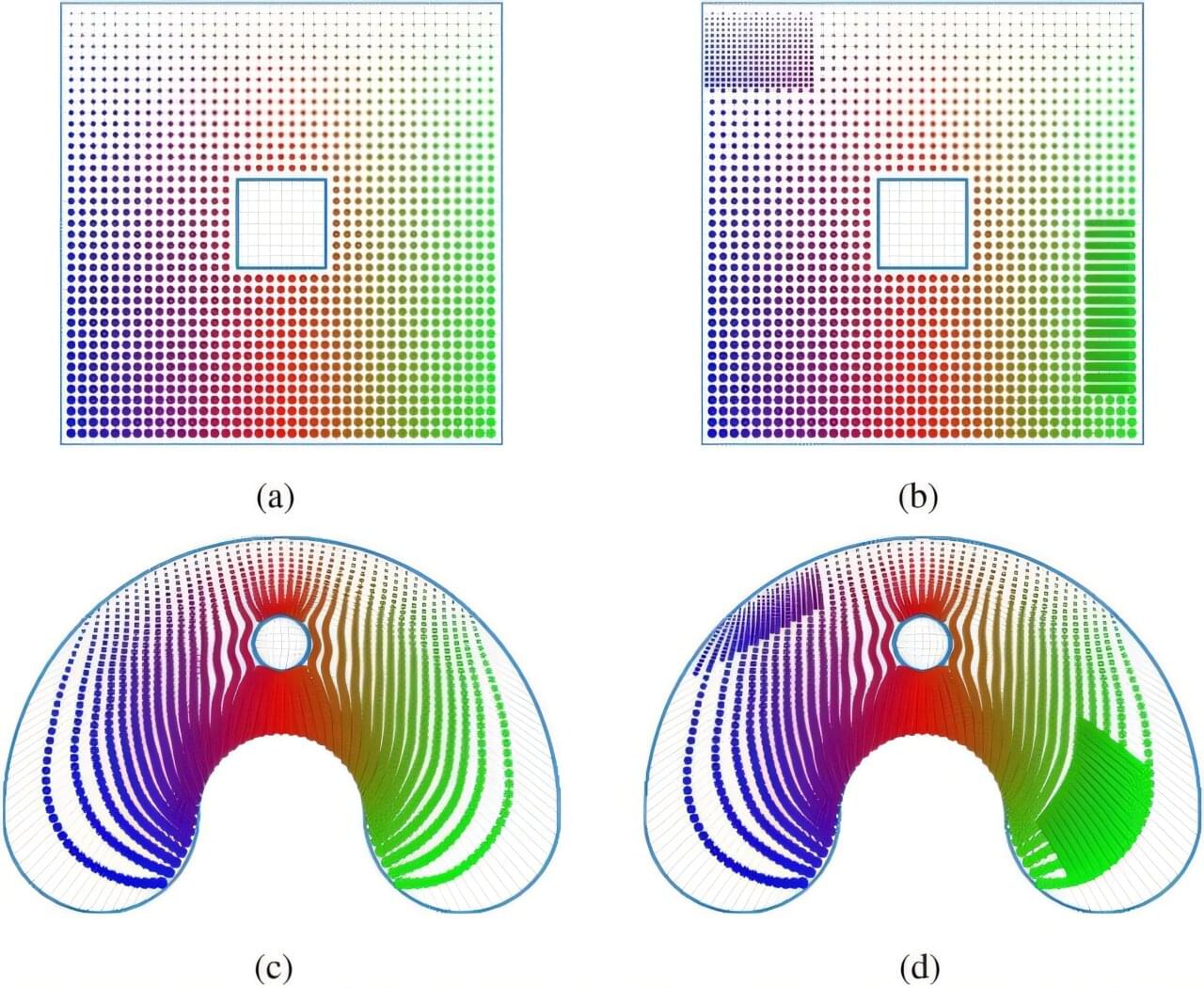
A research team from the Skoltech AI Center proposed a new neural network architecture for generating structured curved coordinate grids, an important tool for calculations in physics, biology, and even finance. The study is published in the Scientific Reports journal.
“Building a coordinate grid is a key task for modeling. Breaking down a complex space into manageable pieces is necessary, as it allows you to accurately determine the changes in different quantities—temperature, speed, pressure, and so on,” commented the lead author of the paper, Bari Khairullin, a Ph.D. student from the Computational and Data Science and Engineering program at Skoltech.
“Without a good grid, calculations become either inaccurate or impossible. In physics, they help model the movement of liquids and gases, in biology, tissue growth and drug distribution, and in finance, they predict market fluctuations. The proposed approach opens up new possibilities in building grids using artificial intelligence.”
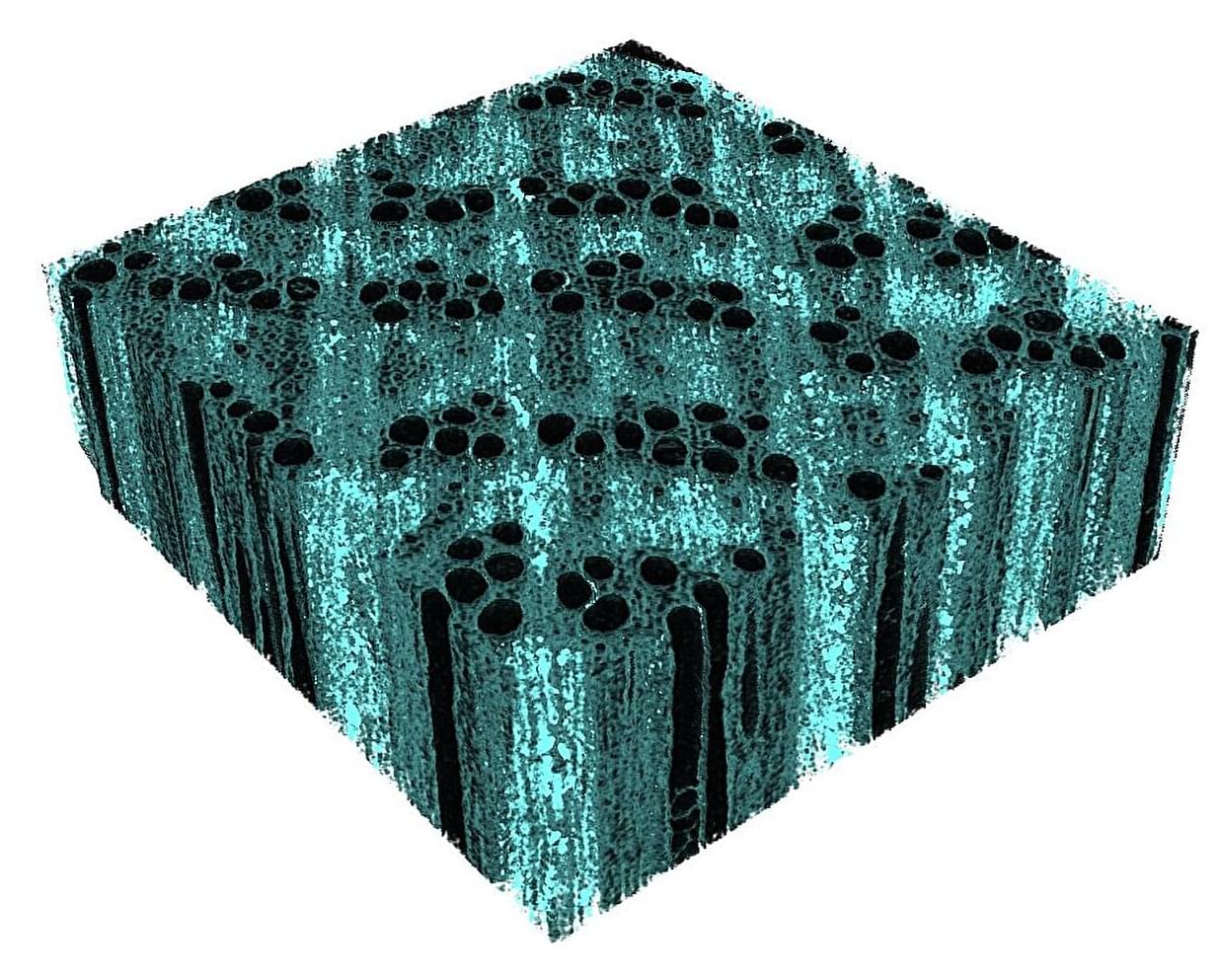
Scientists and engineers are developing high-performance materials from eco-friendly sources like plant waste. A key component, lignocellulose—found in wood and many plants—can be easily collected and chemically modified to improve its properties.
By using these kinds of chemical changes, researchers are creating advanced materials and new ways to design and build sustainably. With about 181.5 billion tons of wood produced globally each year, it’s one of the largest renewable material sources.