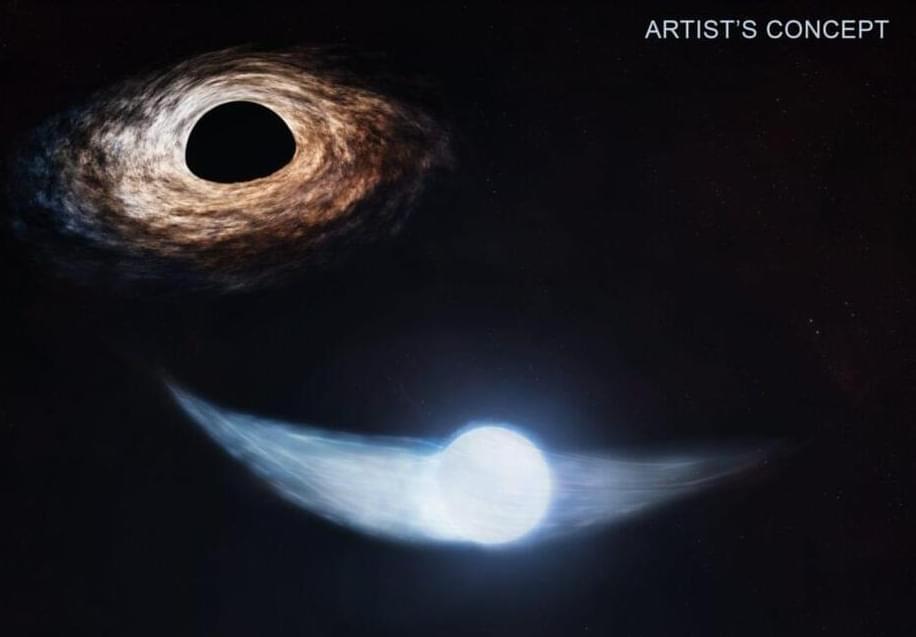
Astronomers have found a supermassive black hole ejecting a jet of energy at nearly the speed of light. This event, called AT2022cmc, is the most distant tidal disruption event (TDE) ever recorded, taking place 12.4 billion light years away from Earth. The international team of researchers shared their findings in papers published on November 30 in Nature and Nature Astronomy, noting that this TDE was observable due to the intense brightness of its jet and the direction it pointed—right toward Earth.
Igon Andreoni, an astronomer at the University of Maryland and co-leader of the study, emphasized how unusual it is to witness such a jet, as it must be aimed almost directly at Earth for detection. The light from AT2022cmc reached Earth after traveling across space for approximately 8.5 billion years, implying that this event happened when the universe was just a third of its current age.
The observation has led researchers to propose that the black hole involved was spinning at a high rate, which likely contributed to the formation of the jet. Despite its classification as “supermassive,” this black hole’s mass, estimated at a few hundred million times that of the Sun, is typical for black holes at the centers of galaxies.