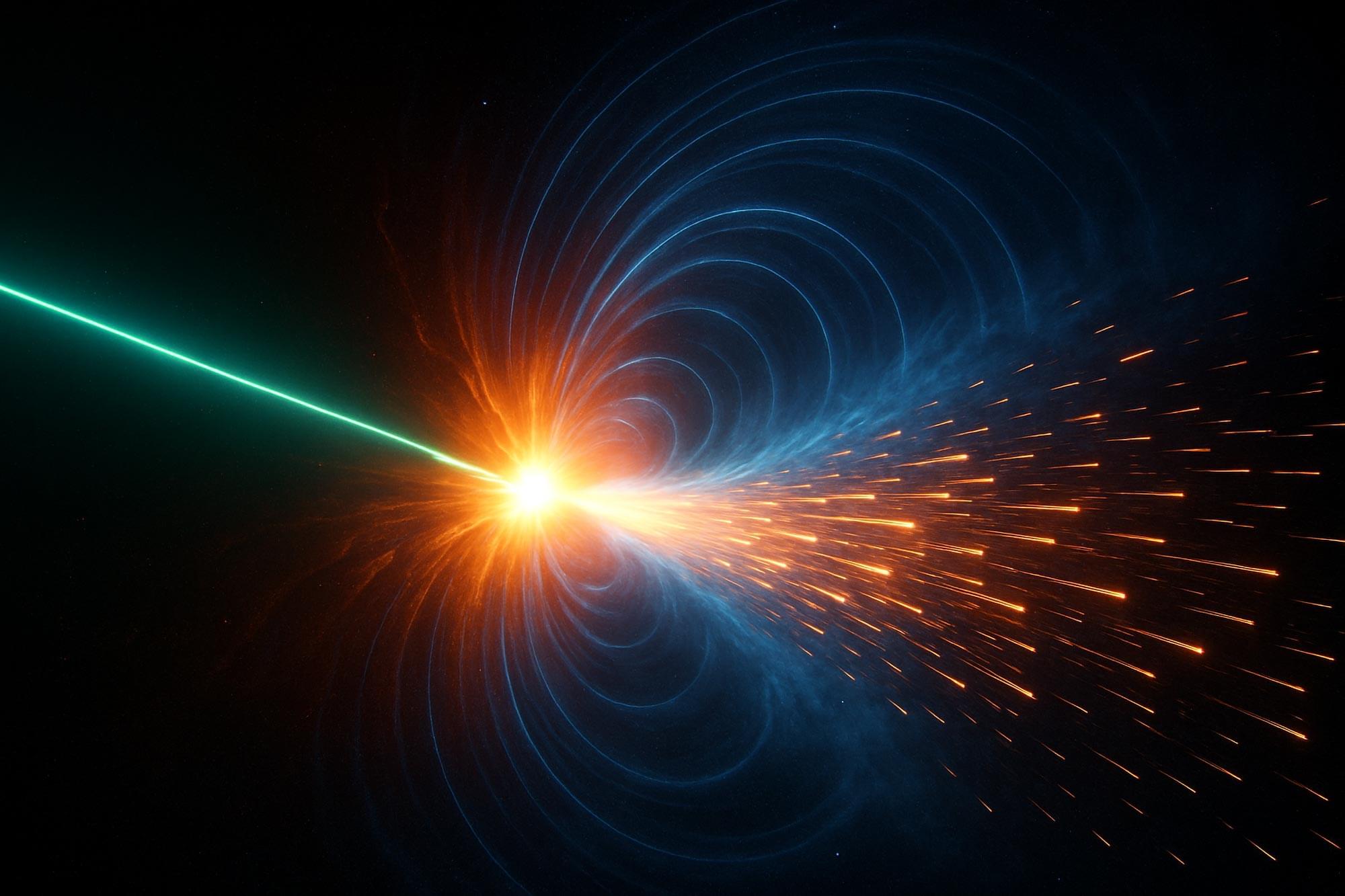
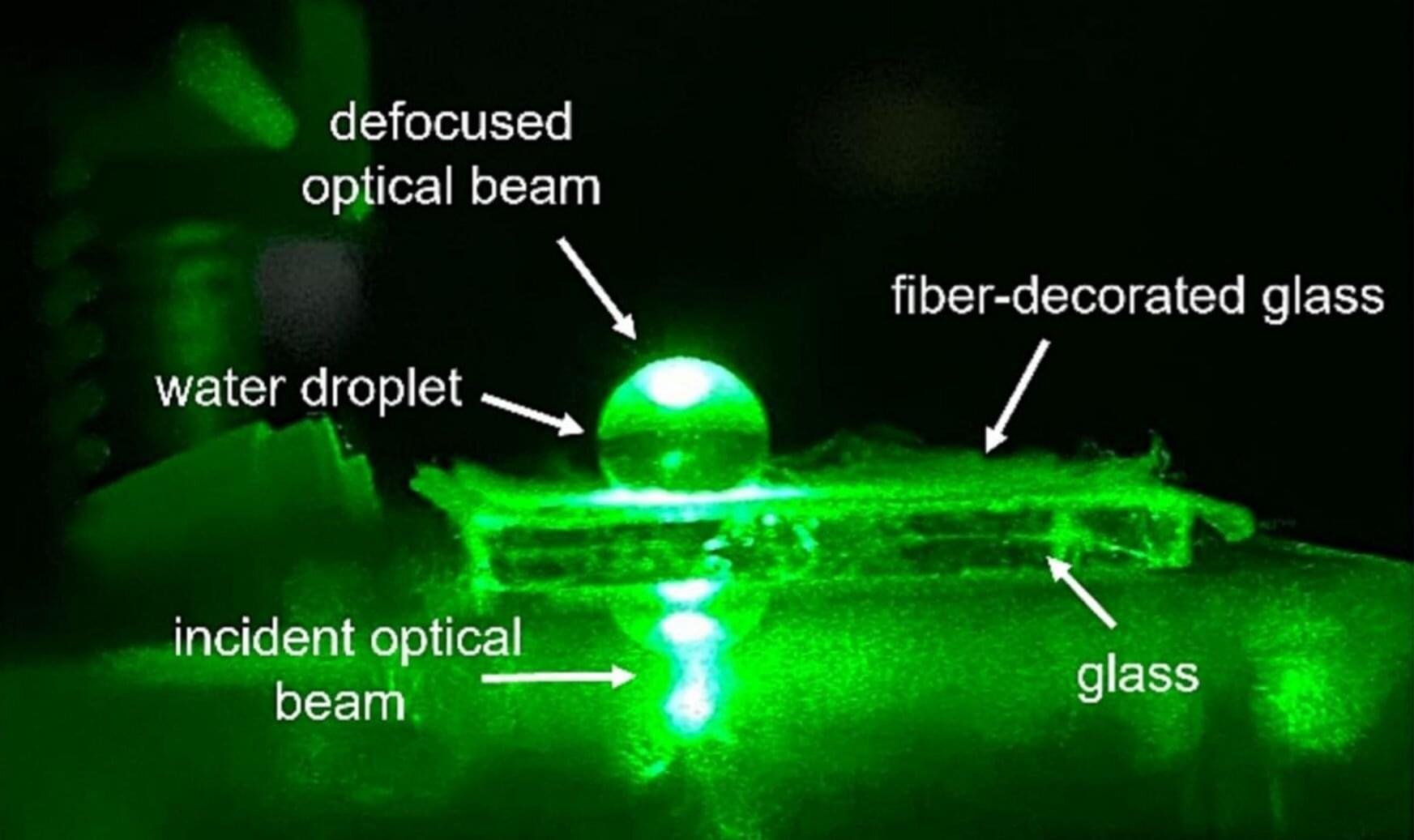
In a dramatic leap for astrophysics, Chinese researchers have recreated a key cosmic process in the lab: the acceleration of ions by powerful collisionless shocks.
By using intense lasers to simulate space-like conditions, they captured high-speed ion beams and confirmed the decades-old theory that shock drift acceleration, not shock surfing, is the main driver behind these energy gains. This discovery connects lab physics with deep-space phenomena like cosmic rays and supernova remnants, paving the way for breakthroughs in both fusion energy and space science.
Breakthrough in particle acceleration observed in lab.