An investigational drug for glioblastoma more than doubled survival and progression-free time compared to standard rates. | Drug Discovery And Development
To compete in an increasingly complex market, companies will need to unleash distinctive capabilities, reduce low-value work, speed up decision-making, and harness AI and digital.
Biological systems, once thought too chaotic for quantum effects, may be quietly leveraging quantum mechanics to process information faster than anything man-made.
New research suggests this isn’t just happening in brains, but across all life, including bacteria and plants.
Schrödinger’s legacy inspires a quantum leap.
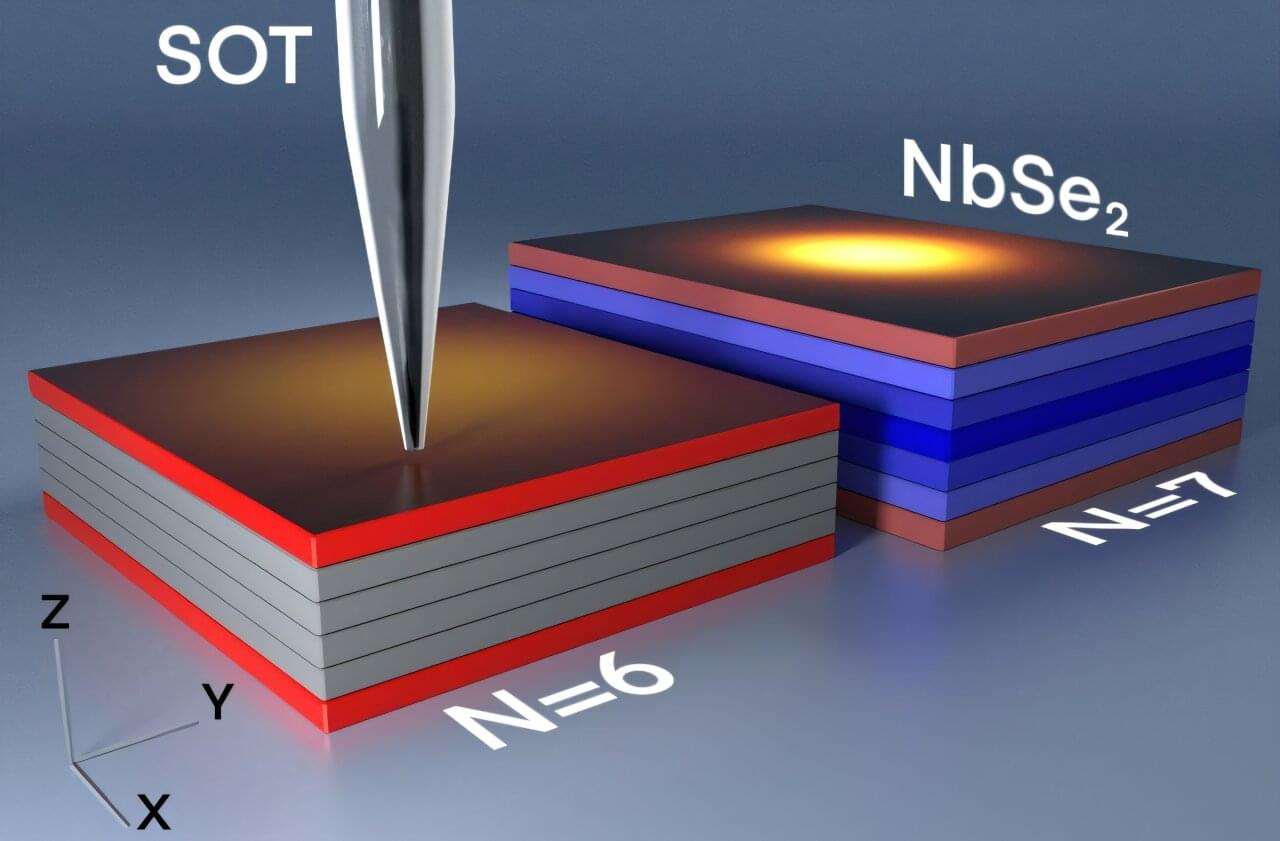
Researchers have discovered an unexpected superconducting transition in extremely thin films of niobium diselenide (NbSe2). Publishing in Nature Communications, they found that when these films become thinner than six atomic layers, superconductivity no longer spreads evenly throughout the material, but instead becomes confined to its surface.
This discovery challenges previous assumptions and could have important implications for understanding superconductivity and developing advanced quantum technologies.
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have made a surprising discovery about how superconductivity behaves in extremely thin materials. Superconductors are materials that allow electric current to flow without resistance, which makes them incredibly valuable for technology. Usually, the properties of superconductors change predictably when the materials become thinner; however, this study found something unexpected.
Randomness is essential to some research, but it’s always been prohibitively complicated to achieve. Now, we can use “pseudorandomness” instead.
A quantum algorithm for solving mathematical problems related to knots could give us the first example of a quantum computer tackling a genuinely useful problem that would otherwise be impossible for a classical computer
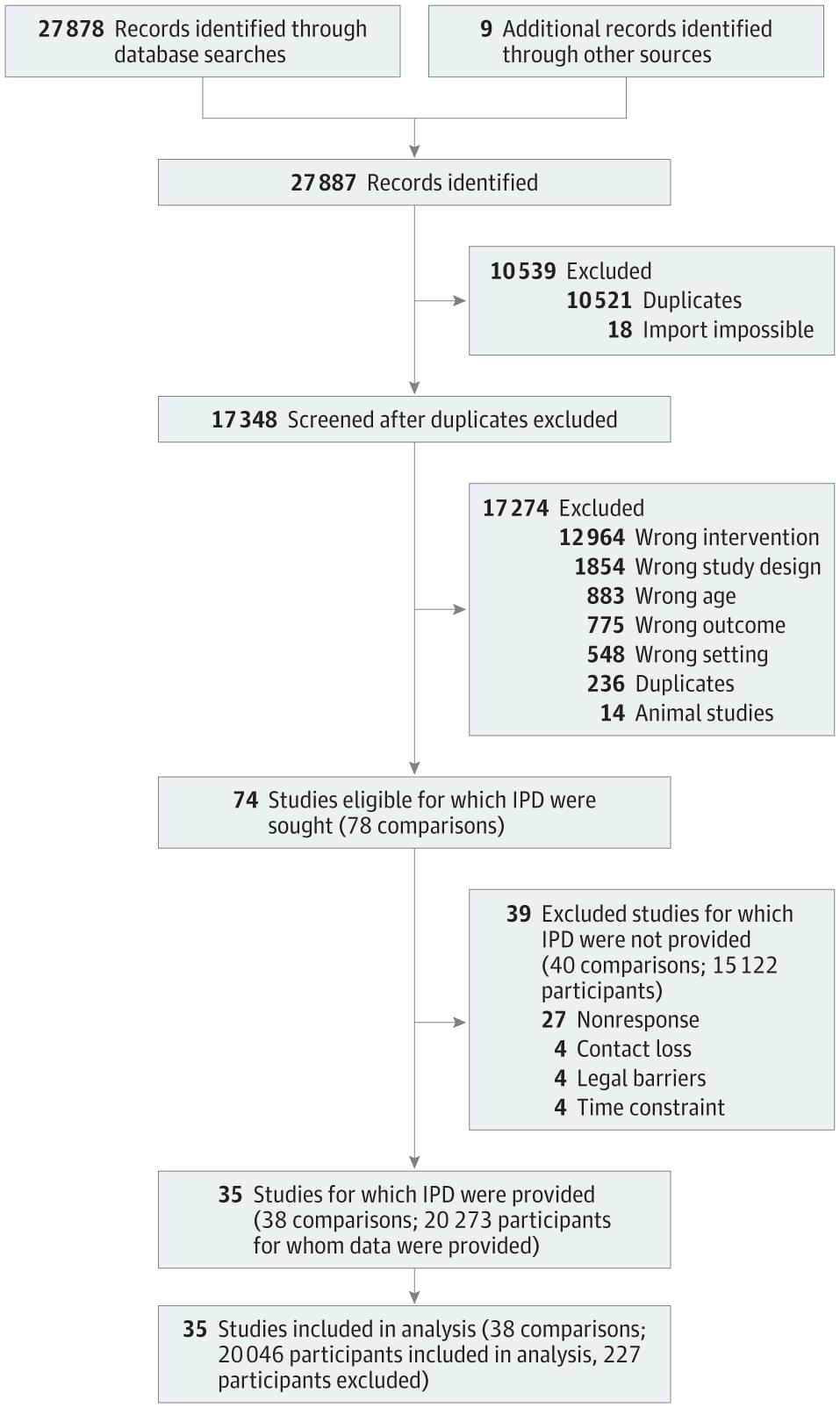
Effective Components of Collaborative Care for Depression in Primary Care: An Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis
Posted in biotech/medical, neuroscience | Leave a Comment on Effective Components of Collaborative Care for Depression in Primary Care: An Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis
This meta-analysis using individual patient data assesses which components of collaborative care are most effective in reducing symptoms of depression in primary care.
A team from the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) has revived algae that lay dormant in Baltic Sea sediment for nearly 7,000 years.
As our bodies grow, cells proliferate to form tissues, and cells frequently have to be repaired or replaced throughout life. But the genome can also become less stable over time, or may pick up mutations that can lead to disease; these and other processes can cause cells to enter a state in which they stop dividing, known as senescence. Senescent cells become more common as we age. There also tends to be more inflammation as we age, but the link between increasing instability in the genome and inflammation is not well understood. Now scientists have reported a direct connection between DNA instability and inflammation in senescent cells. The findings have been reported in Nature Communications.
“In addition to no longer growing and proliferating, the other hallmark of senescent cells is that they have this inflammatory program causing them to secrete inflammatory molecules,” noted senior study author Peter Adams, Ph.D., director and professor of the Cancer Genome and Epigenetics Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys.