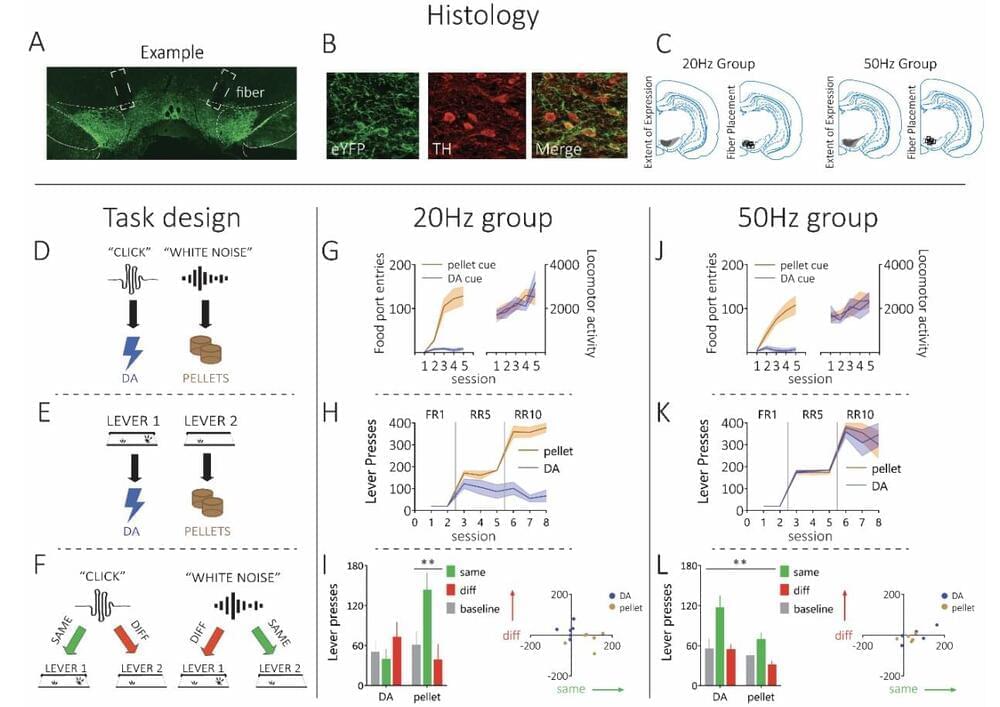
Nanoscale materials offer remarkable chemical and physical properties that transform theoretical applications, like single-molecule sensing and minimally invasive photothermal therapy, into practical realities.
The unparalleled features of nanoparticles make them promising for various research and industrial uses. However, effectively using these materials is challenging due to the absence of a rapid and consistent method to transfer a uniform monolayer of nanoparticles, a crucial step in device manufacturing.
One potential solution to this challenge lies in electrostatic assembly processes, where oppositely charged nanoparticles adhere to a surface, forming a monolayer that repels other similarly charged particles from attaching further. While effective, this process is often slow. Nature provides an innovative model to address this limitation through underwater adhesion strategies, which have evolved to circumvent similar problems.