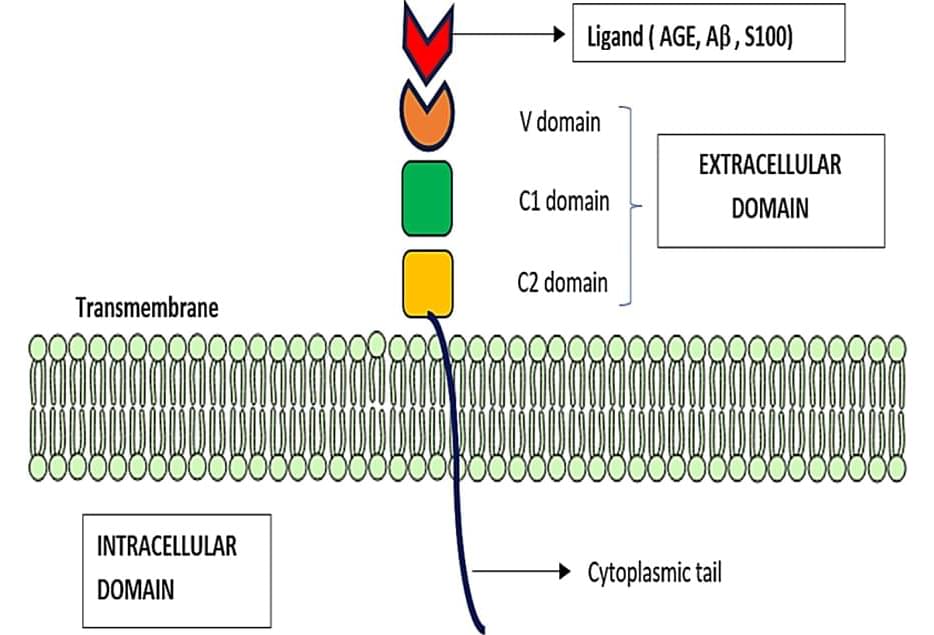
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) accumulate in the brain, leading to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The pathophysiology of AD is influenced by receptors for AGEs and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Protein glycation results in irreversible AGEs through a complicated series of reactions involving the formation of Schiff’s base, the Amadori reaction, followed by the Maillard reaction, which causes abnormal brain glucose metabolism, oxidative stress, malfunctioning mitochondria, plaque deposition, and neuronal death. Amyloid plaque and other stimuli activate macrophages, which are crucial immune cells in AD development, triggering the production of inflammatory molecules and contributing to the disease’s pathogenesis. The risk of AD is doubled by risk factors for atherosclerosis, dementia, advanced age, and type 2 diabetic mellitus (DM). As individuals age, the prevalence of neurological illnesses such as AD increases due to a decrease in glyoxalase levels and an increase in AGE accumulation. Insulin’s role in proteostasis influences hallmarks of AD-like tau phosphorylation and amyloid β peptide clearance, affecting lipid metabolism, inflammation, vasoreactivity, and vascular function. The high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein, a key initiator and activator of a neuroinflammatory response, has been linked to the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD. The TLR4 inhibitor was found to improve memory and learning impairment and decrease Aβ build-up. Therapeutic research into anti-glycation agents, receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) inhibitors, and AGE breakers offers hope for intervention strategies. Dietary and lifestyle modifications can also slow AD progression. Newer therapeutic approaches targeting AGE-related pathways are needed.