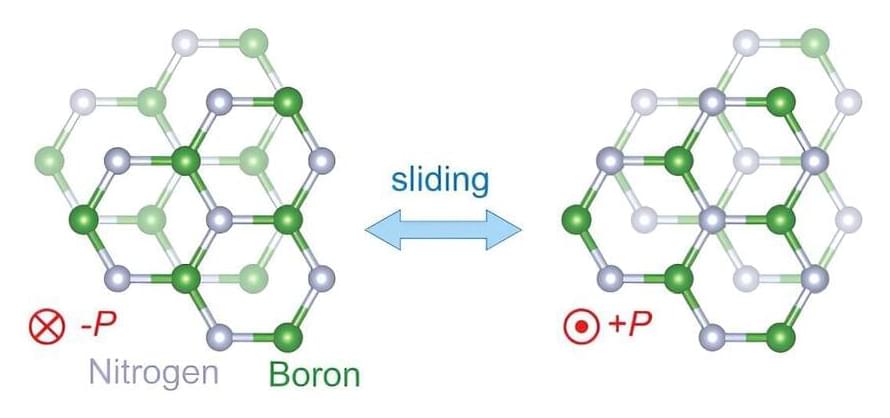
In 2021, a team led by MIT physicists reported creating a new ultrathin ferroelectric material, or one where positive and negative charges separate into different layers. At the time, they noted the material’s potential for applications in computer memory and much more. Now the same core team and colleagues—including two from the lab next door—have built a transistor with that material and shown that its properties are so useful that it could change the world of electronics.
Although the team’s results are based on a single transistor in the lab, “in several aspects its properties already meet or exceed industry standards” for the ferroelectric transistors produced today, says Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, the Cecil and Ida Green Professor of Physics, who led the work with professor of physics Raymond Ashoori. Both are also affiliated with the Materials Research Laboratory.
“In my lab we primarily do fundamental physics. This is one of the first, and perhaps most dramatic, examples of how very basic science has led to something that could have a major impact on applications,” Jarillo-Herrero says.