Page 54
Dec 14, 2024
Artificial Intelligence for Cell Analysis in Biologics Development
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biological, mapping, robotics/AI
There’s No Turning Back
Not long ago, solving the crystal structure of a protein required an entire PhD.
Growing crystals, collecting X-ray diffraction data, and interpreting electron density maps often took years of optimization and expensive instruments. Even then, solving all protein structures was a challenge, further compounding the “protein folding problem” in biology.
Dec 14, 2024
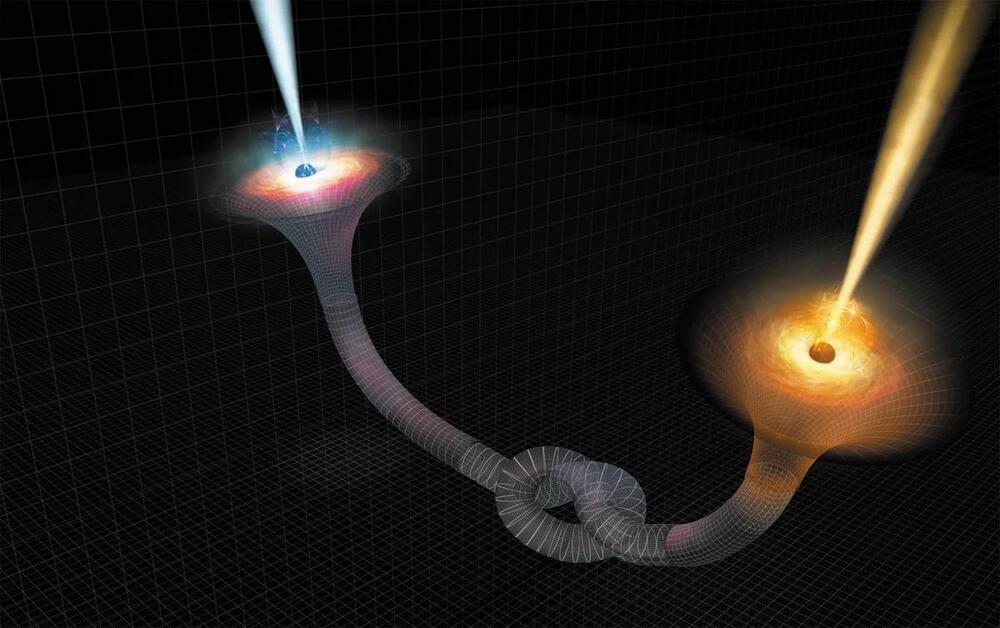
Objects previously thought as black holes may actually be wormholes, scientists say
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: cosmology, particle physics
A team of physicists from Sofia University in Bulgaria has proposed a fascinating theory that wormholes, hypothetical tunnels linking different parts of the universe, could be hiding in plain sight. These wormholes may resemble black holes so closely that current technology cannot distinguish between the two, according to a new study reported by New Scientist.
Black holes have long been a source of mystery. They absorb everything, even light, leaving no trace of what falls into them. But where does the swallowed matter go? Some physicists have speculated that black holes might connect to “white holes,” which would spew out particles and radiation on the other end. Together, these phenomena could form a wormhole, or more specifically, an Einstein-Rosen bridge, connecting distant regions of space and time.
Dec 14, 2024
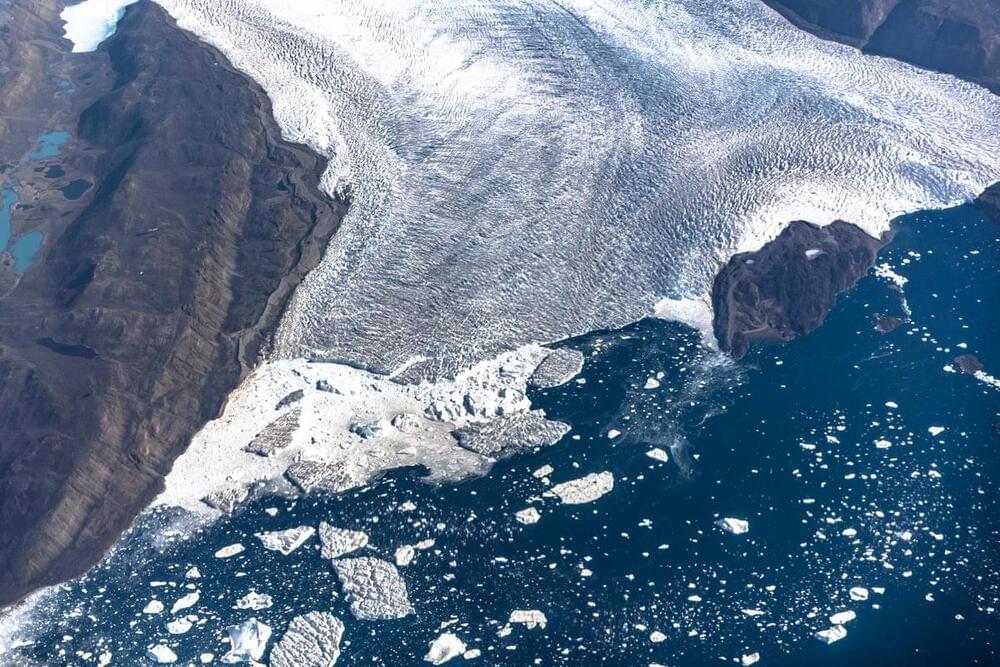
A Rapidly Warming Arctic Looks Dramatically Different Now Than 20 Years Ago
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: futurism
Rising temperatures, increasing precipitation, thawing permafrost and melting ice are pushing the Arctic outside its historical norms.
By Chelsea Harvey & E&E News
Dec 14, 2024
Brain organoids and assembloids are new models for elucidating, treating neurodevelopmental disorders
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
But Kelby, who was training to become an operating room nurse, realized Holden’s episodes reminded him of what he was learning about warning signs for stroke. JJ called Holden’s cardiologist in Utah and asked for a detailed neurologic evaluation, which enabled the mysterious episodes to be diagnosed as seizures. Holden began taking anti-seizure medication, which helped, to his parents’ great relief.
A few months after Holden was born, Sergiu Pasca, MD, arrived at Stanford Medicine to pursue a postdoctoral fellowship in the lab of Ricardo Dolmetsch, PhD, then an assistant professor of neurobiology, who was redirecting his research to autism spectrum disorder. At the time, Pasca did not know the Hulet family. But his work soon became focused on the disorder that has shaped Holden’s life.
Dec 14, 2024
Breakthrough film converts body heat into electricity for wearables
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: entertainment, wearables
QUT researchers develop a film that converts body heat into electricity, potentially eliminating the need for batteries in wearable tech.
Dec 14, 2024
Perplexity, Google, and the battle for AI search supremacy
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: business, robotics/AI
AIs that generate answers to user queries could transform search, but only if someone can get the tech and the business model right.
Dec 14, 2024
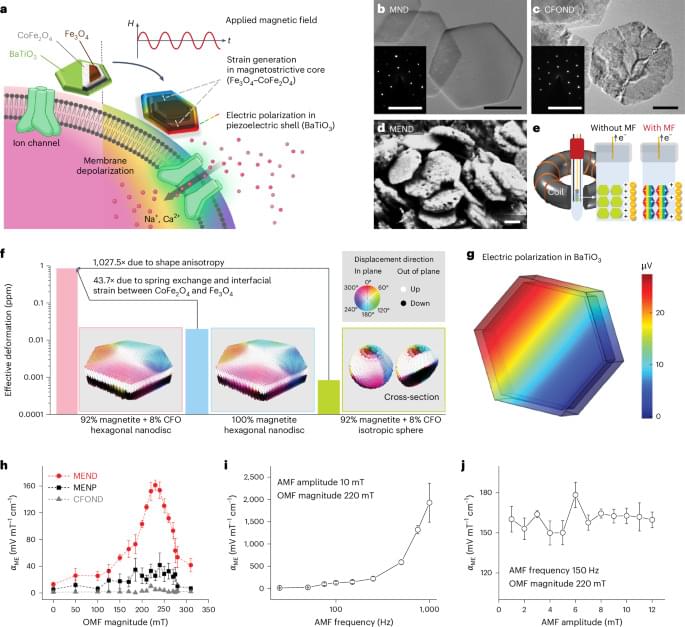
Magnetoelectric nanodiscs enable wireless transgene-free neuromodulation
Posted by Logan Thrasher Collins in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
In this study, the authors present magnetoelectric nanodiscs that enable minimally invasive, remote magnetic neuromodulation with subsecond precision to drive reward and motor behaviours in genetically intact mice.
Dec 14, 2024
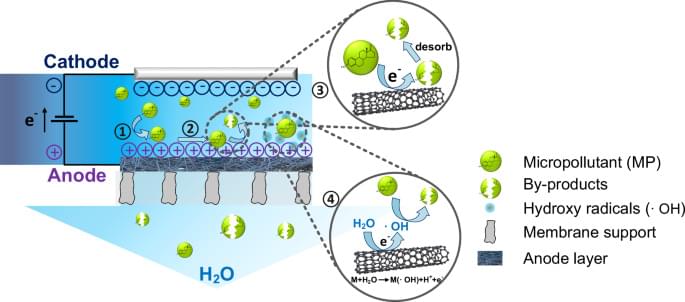
Differentiation of adsorption and degradation in steroid hormone micropollutants removal using electrochemical carbon nanotube membrane
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: chemistry, nanotechnology
Pervasive micropollutants in aquatic environments pose significant threats to global water supply safety. Here, authors achieved permeate concentrations below the detection limit (2.5 ng/L) using a CNT-based electrochemical membrane, with the contributions of adsorption and degradation distinguished.
Dec 14, 2024
New graphene ink enables the smart wearables of the future
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: materials, wearables

’The world’s best’ graphene ink, which can be used for printed electronics—such as an intelligent t-shirt that measures your pulse—has been developed in collaboration with the Danish Technological Institute in a MADE demonstration project. The newly developed ink has already opened new markets for the company Danish Graphene.
Imagine a super-strong spider web that can bend and stretch without breaking.
Continue reading “New graphene ink enables the smart wearables of the future” »