Dec 15, 2024
AI Medical Imagery Model Offers Fast, Cost-Efficient Expert Analysis
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI
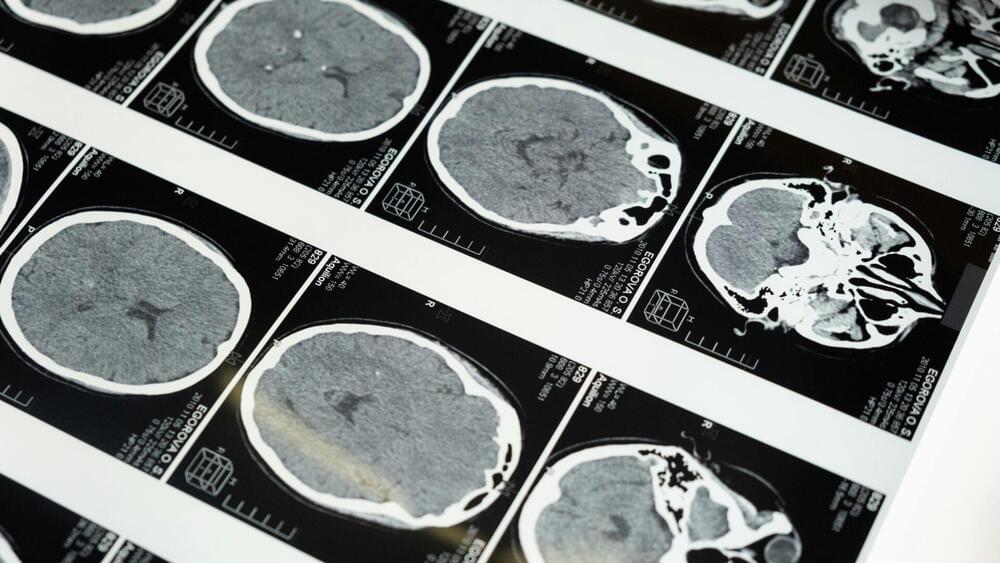
Researchers at UCLA have developed a new AI model that can expertly analyze 3D medical images of diseases in a fraction of the time it would otherwise take a human clinical specialist.
The deep-learning framework, named SLIViT (SLice Integration by Vision Transformer), analyzes images from different imagery modalities, including retinal scans, ultrasound videos, CTs, MRIs, and others, identifying potential disease-risk biomarkers.
Dr. Eran Halperin, a computational medicine expert and professor at UCLA who led the study, said the model is highly accurate across a wide variety of diseases, outperforming many existing, disease-specific foundation models. It uses a novel pre-training and fine-tuning method that relies on large, accessible public data sets. As a result, Halperin believes that the model can be deployed—at relatively low costs—to identify different disease biomarkers, democratizing expert-level medical imaging analysis.