Jun 6, 2018
Genomic Approach to Understand the Association of DNA Repair with Longevity and Healthy Aging Using Genomic Databases of Oldest-Old Population
Posted by Alexander Rodionov in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
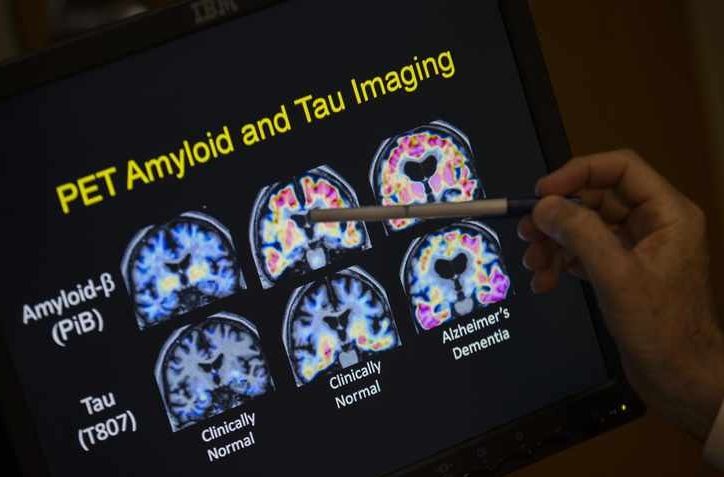
Aged population is increasing worldwide due to the aging process that is inevitable. Accordingly, longevity and healthy aging have been spotlighted to promote social contribution of aged population. Many studies in the past few decades have reported the process of aging and longevity, emphasizing the importance of maintaining genomic stability in exceptionally long-lived population. Underlying reason of longevity remains unclear due to its complexity involving multiple factors. With advances in sequencing technology and human genome-associated approaches, studies based on population-based genomic studies are increasing. In this review, we summarize recent longevity and healthy aging studies of human population focusing on DNA repair as a major factor in maintaining genome integrity. To keep pace with recent growth in genomic research, aging- and longevity-associated genomic databases are also briefly introduced. To suggest novel approaches to investigate longevity-associated genetic variants related to DNA repair using genomic databases, gene set analysis was conducted, focusing on DNA repair- and longevity-associated genes. Their biological networks were additionally analyzed to grasp major factors containing genetic variants of human longevity and healthy aging in DNA repair mechanisms. In summary, this review emphasizes DNA repair activity in human longevity and suggests approach to conduct DNA repair-associated genomic study on human healthy aging.
Aging is an inevitable process in human life. Many countries are rapidly transitioning to an aging society due to increasing life expectancy and advanced medical supports [1–3]. Over the last few decades, the advent of aging society is considered a crucial issue that may cause future decline in productivity of community [1, 4]. Many researchers have recently warned that urban environmental pollutants can cause physiological weakness and increase the risk of premature aging or chronic diseases in the elderly population [5–9]. Thus, interest in antiaging and healthy longevity is constantly increasing. “Active aging” or “successful aging” has been spotlighted as a strategy to promote social contribution of the elderly [10]. The definition of successful aging remains controversial.





 Keith’s note: China is getting ready to launch a new space station which, when complete, will be on par with Mir with many capabilities similar to those offered by the ISS. China is openly seeking governmental and commercial participation. Meanwhile they are about to land a rover on the far side of the Moon as part of a methodical plan to land humans there.
Keith’s note: China is getting ready to launch a new space station which, when complete, will be on par with Mir with many capabilities similar to those offered by the ISS. China is openly seeking governmental and commercial participation. Meanwhile they are about to land a rover on the far side of the Moon as part of a methodical plan to land humans there.