Jun 10, 2018
Berkeley’s desert water extractor is taking us one step closer to harvesting water out of thin air
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, sustainability
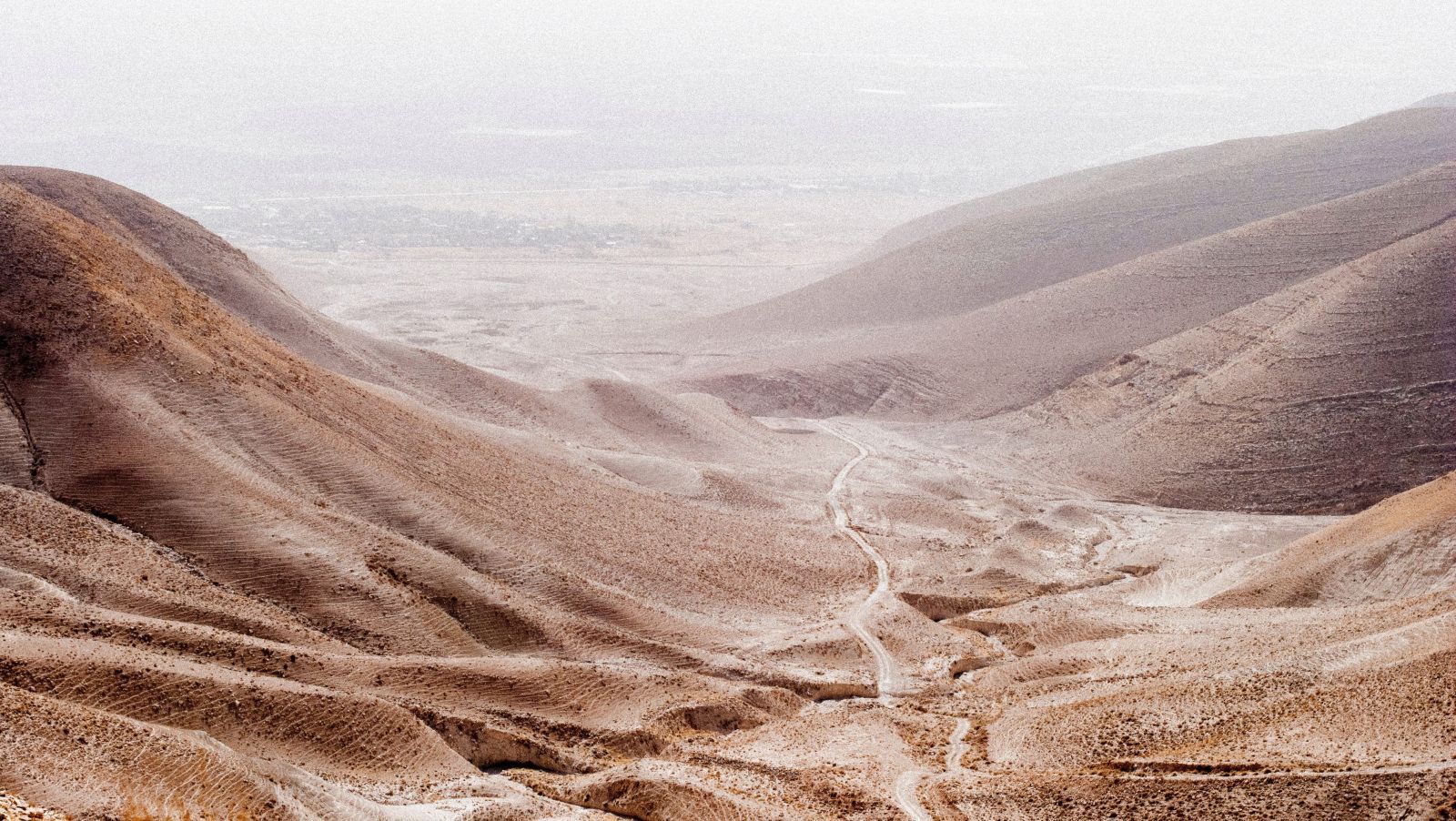
Right now, there are roughly 16 sextillion liters of water suspended in the atmosphere. The air around you is a river, you just can’t see it.
Harvesting water from air would be a game-changing solution to tackling freshwater scarcity, which is increasing as the world warms. It would be especially vital in places with very little humidity in the air, like the desert. But while it’s technically possible—you just need to get the water content in the air to condense around something—doing so efficiently has been difficult, until now.
The challenge with this technology is cooling. Water vapor will only condense into a liquid if the material it condenses on is cooler than the surrounding air. That’s why droplets of condensation will appear on a soda can the moment you take it out of the fridge. But how do you leave a piece of machinery in the desert sun all day and keep it cooler than the surrounding air? One way would be to install a cooling system. But it takes a a lot of energy to perpetually cool an object in a hot place, and isn’t feasible in places where energy is expensive. We also don’t want to increase the amount of energy demand in a world already struggling to reduce emissions.