Apr 16, 2018
Scientists decipher the magma bodies under Yellowstone
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: energy, supercomputing
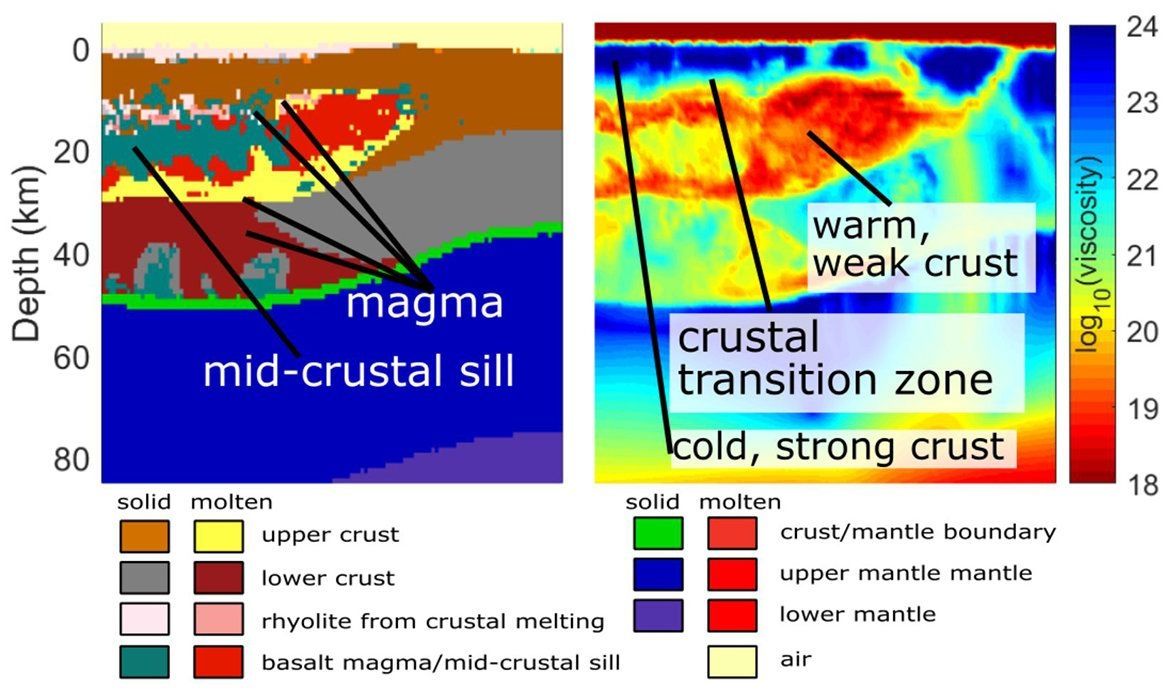
Using supercomputer modeling, University of Oregon scientists have unveiled a new explanation for the geology underlying recent seismic imaging of magma bodies below Yellowstone National Park.
Yellowstone, a supervolcano famous for explosive eruptions, large calderas and extensive lava flows, has for years attracted the attention of scientists trying to understand the location and size of magma chambers below it. The last caldera forming eruption occurred 630,000 years ago; the last large volume of lava surfaced 70,000 years ago.
Crust below the park is heated and softened by continuous infusions of magma that rise from an anomaly called a mantle plume, similar to the source of the magma at Hawaii’s Kilauea volcano. Huge amounts of water that fuel the dramatic geysers and hot springs at Yellowstone cool the crust and prevent it from becoming too hot.
Continue reading “Scientists decipher the magma bodies under Yellowstone” »