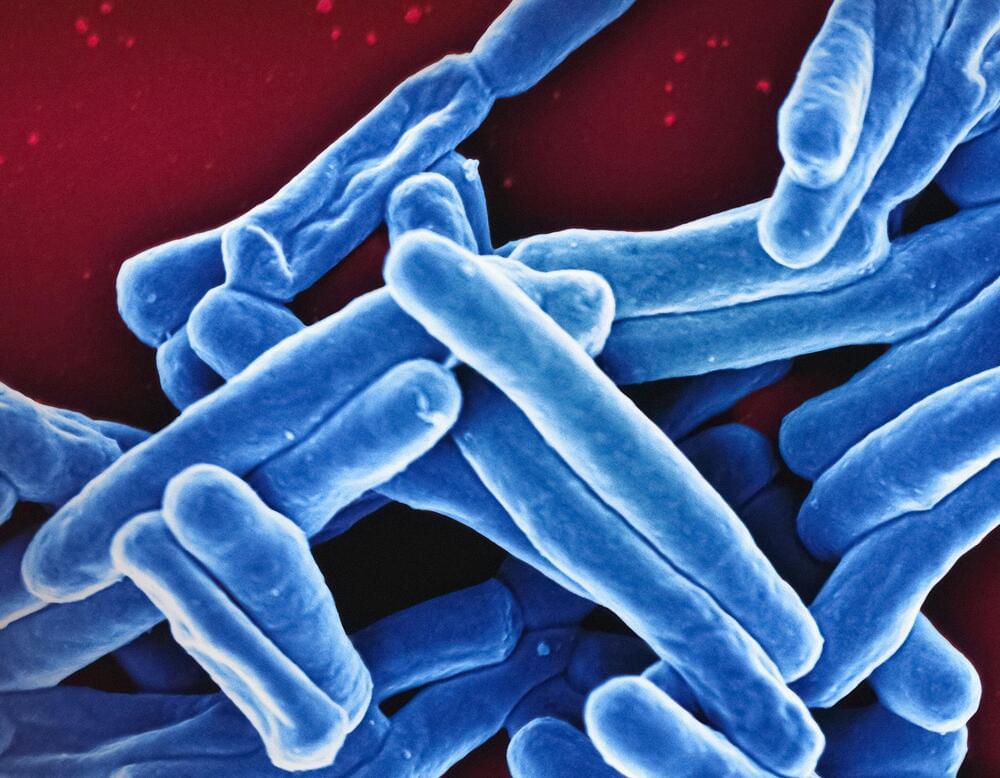
The rod-shaped tuberculosis (TB) bacterium, which the World Health Organization has once again ranked as the top infectious disease killer globally, is the first single-celled organism ever observed to maintain a consistent growth rate throughout its life cycle. These findings, reported by Tufts University School of Medicine researchers on November 15 in the journal Nature Microbiology, overturn core beliefs of bacterial cell biology and hint at why the deadly pathogen so readily outmaneuvers our immune system and antibiotics.
“The most basic thing you can study in bacteria is how they grow and divide, yet our study reveals that the TB pathogen is playing by a completely different set of rules compared to easier-to-study model organisms,” said Bree Aldridge, a professor of molecular biology and microbiology at the School of Medicine and a professor of biomedical engineering at the School of Engineering, as well as one of the paper’s co-senior authors along with Ariel Amir of the Weizmann Institute of Science.
TB bacteria are successful at surviving in humans because some parts of the infection can quickly evolve within their host, allowing these outliers to avoid detection or resist treatment. If someone has TB, it takes months of various antibiotics to be cured, and even then, this approach is only successful in 85% of patients. Aldridge and her colleagues hypothesize that gaps in our understanding of the basic biology behind this phenomenon have been holding back the development of more effective treatments.