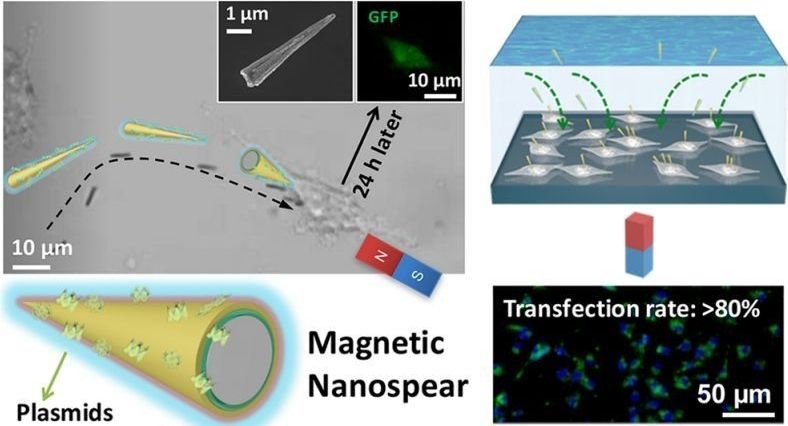
UCLA scientists have developed a new method that utilizes microscopic splinter-like structures called “nanospears” for the targeted delivery of biomolecules such as genes straight to patient cells. These magnetically guided nanostructures could enable gene therapies that are safer, faster and more cost-effective.
The research was published in the journal ACS Nano by senior author Paul Weiss, UC Presidential Chair and distinguished professor of chemistry and biochemistry, materials science and engineering, and member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA.
Gene therapy, the process of adding or replacing missing or defective genes in patient cells, has shown great promise as a treatment for a host of diseases, including hemophilia, muscular dystrophy, immune deficiencies and certain types of cancer.








Comments are closed.