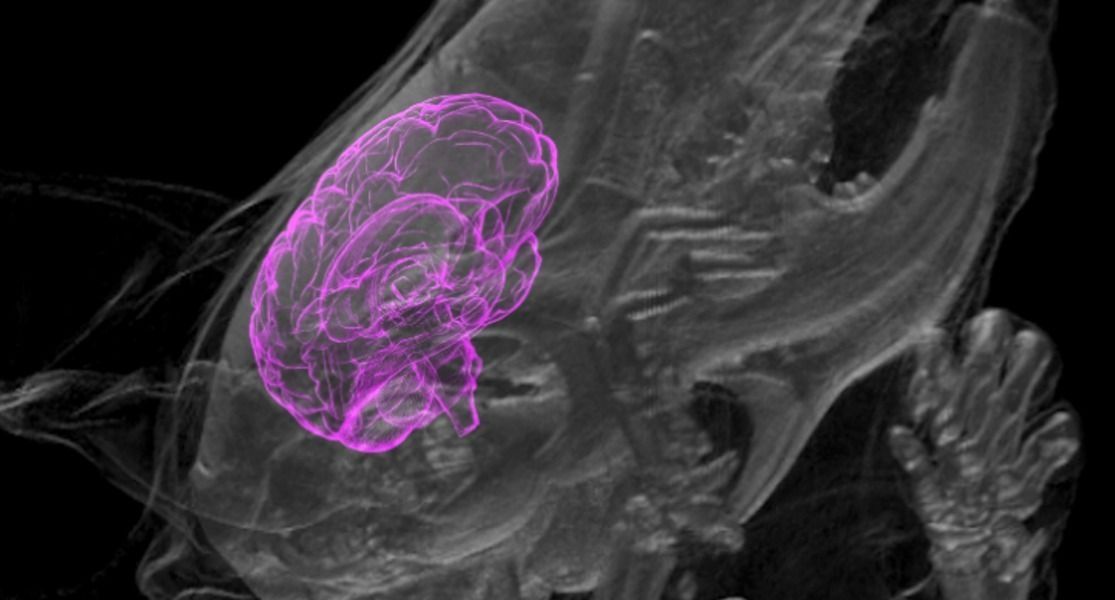
Stem cell technology has advanced so much that scientists can grow miniature versions of human brains — called organoids, or mini-brains if you want to be cute about it — in the lab, but medical ethicists are concerned about recent developments in this field involving the growth of these tiny brains in other animals. Those concerns are bound to become more serious after the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience starting November 11 in Washington, D.C., where two teams of scientists plan to present previously unpublished research on the unexpected interaction between human mini-brains and their rat and mouse hosts.
In the new papers, according to STAT, scientists will report that the organoids survived for extended periods of time — two months in one case — and even connected to lab animals’ circulatory and nervous systems, transferring blood and nerve signals between the host animal and the implanted human cells. This is an unprecedented advancement for mini-brain research.
“We are entering totally new ground here,” Christof Koch, president of the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle, told STAT. “The science is advancing so rapidly, the ethics can’t keep up.”








Comments are closed.