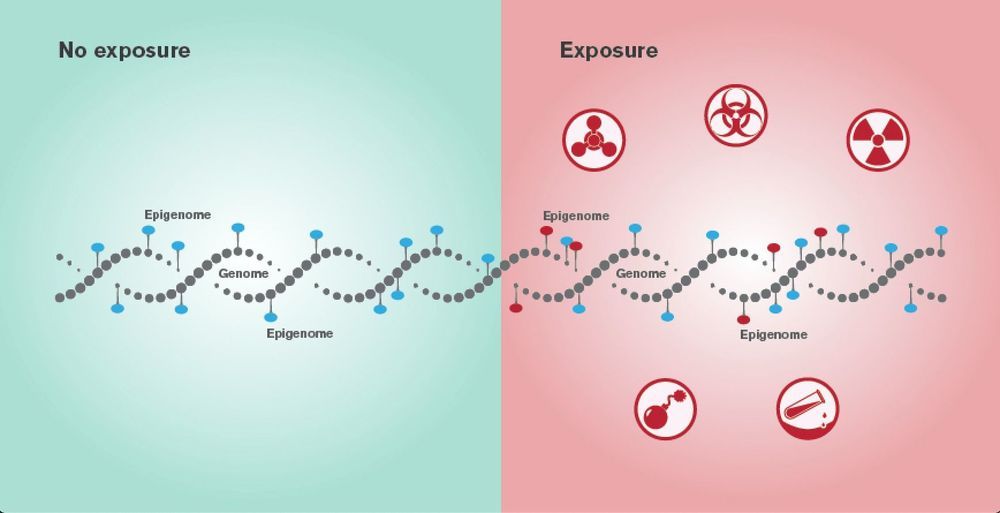
Arizona State University has been selected to participate in DARPA’s Epigenetic CHaracterization and Observation (ECHO) program. According to DARPA, the “ECHO program has two primary challenges: to identify and discriminate epigenetic signatures created by exposure to threat agents; and to create technology that performs highly specific forensic and diagnostic analyses to reveal the exact type and time of exposure.” (Epigenetic changes are chemical modifications that affect genes, altering their expression while leaving the genetic code intact. Epigenetic changes can occur as natural responses to the environment but can also signal exposure to toxic agents or disease pathogens.)
Epigenetics is coming into its own in the 21st century. DARPA describes the epigenome as “biology’s record keeper,” explaining that “though DNA does not change over a single lifetime, a person’s environment may leave marks on the DNA that modify how that individual’s genes are expressed. This is one way that people can adapt and survive in changing conditions, and the epigenome is the combination of all of these modifications. Though modifications can register within seconds to minutes, they imprint the epigenome for decades, leaving a time-stamped biography of an individual’s exposures that is difficult to deliberately alter.”
Sethuraman Panchanathan, ASU Knowledge Enterprise executive vice president and chief research and innovation officer, said the project fits with the university’s mission.








Comments are closed.