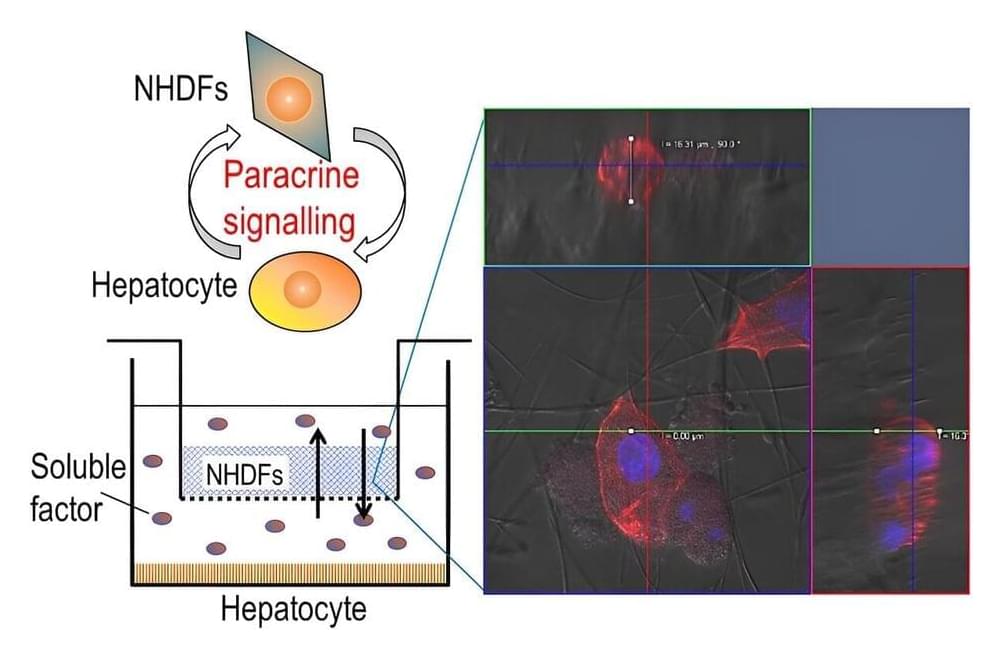
Communication and coordination among different cells are fundamental aspects that regulate many functions in our body. This process, known as paracrine signaling, involves the release of signaling molecules by a cell into its extracellular matrix (ECM) or surroundings to communicate changes in its cellular processes or the local environment. These signaling molecules are then detected by neighboring cells, leading to various cellular responses.
For instance, during cell/tissue injury, the paracrine signaling process releases growth factors that signal nearby stem cells to assist in tissue repair in the form of scar tissue formation or blood clotting. Similar processes occur in the regulation of other vital functions, such as digestion, respiration, and reproduction. Additionally, paracrine signals influence the expression and activity of enzymes involved in drug metabolism and play a role in drug–drug interactions.
The signaling molecules, which may contain proteins and genetic material, are transported within tiny vesicles called exosomes. These vesicles serve as valuable biomarkers for various diseases and can even be engineered to carry drugs, making them a highly effective targeted drug delivery system. Notably, the hormone oxytocin and the neurotransmitter dopamine are paracrine messengers.









Leave a reply