Hailstones are formed during thunderstorms, when raindrops are propelled into very cold parts of a cloud, where they freeze. Once the particles are heavy enough, gravity pulls them back towards Earth. As they plummet, they grow into hailstones, which can cause injury to people and significant damage to homes and cars.
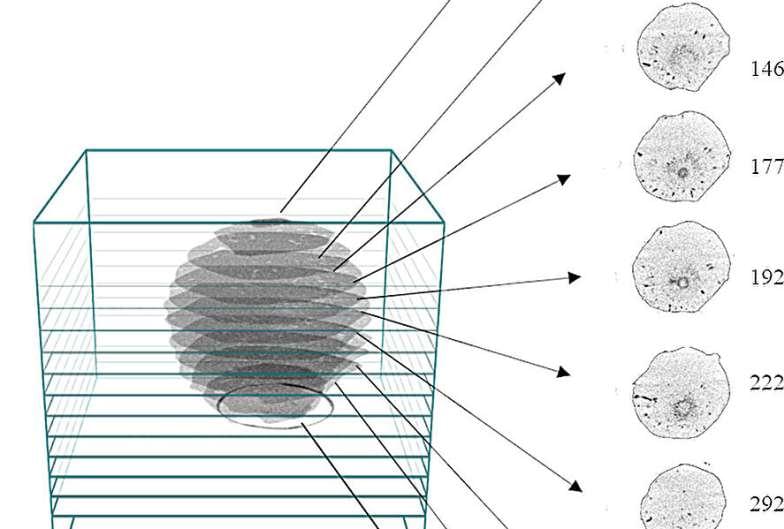
Scientists have been studying how hailstones grow since the 1960s but doing so meant breaking them in the process. To better understand the anatomy and growth of hailstones, researchers in Catalonia have used computed tomography (CT) scans to examine the giant hailstones that hit the north-east of the Iberian Peninsula during an exceptionally strong thunderstorm in the summer of 2022.
“We show that the CT scanning technique enables the observation of the internal structure of the hailstones without breaking the samples,” said Carme Farnell Barqué, a researcher at the Meteorological Service of Catalonia and lead author of the study published in Frontiers in Environmental Science.








Leave a reply