Also known as Virgo A or NGC 4,486, M87 is the brightest object in the Virgo cluster of galaxies, the largest gravitationally bound type of structure in the universe. It came to fame in April 2019 after scientists from EHT released the first image of a black hole in its center.
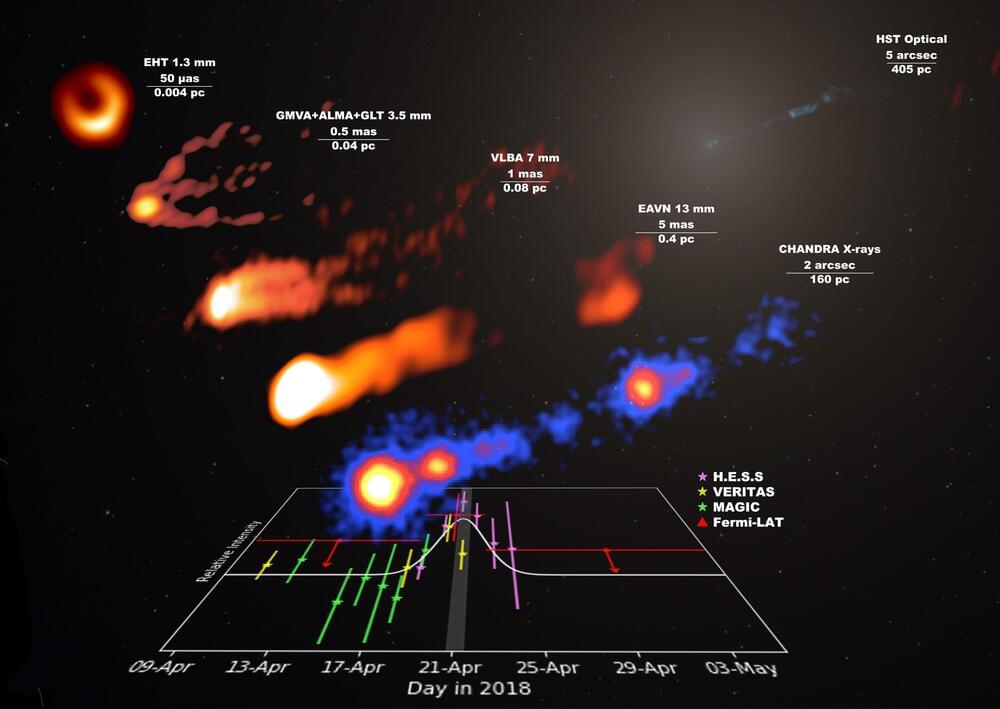
Led by the EHT multi wavelength working group, a study published in Astronomy and Astrophysics presents the data from the second EHT observational campaign conducted in April 2018, involving over 25 terrestrial and orbital telescopes.
The authors report the first observation of a high-energy gamma-ray flare in over a decade from the supermassive black hole M87, based on nearly simultaneous spectra of the galaxy spanning the broadest wavelength range ever collected.









Leave a reply