Nov 26, 2018
Scientists discover a new route to antibiotics using gene editing
Posted by Paul Gonçalves in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
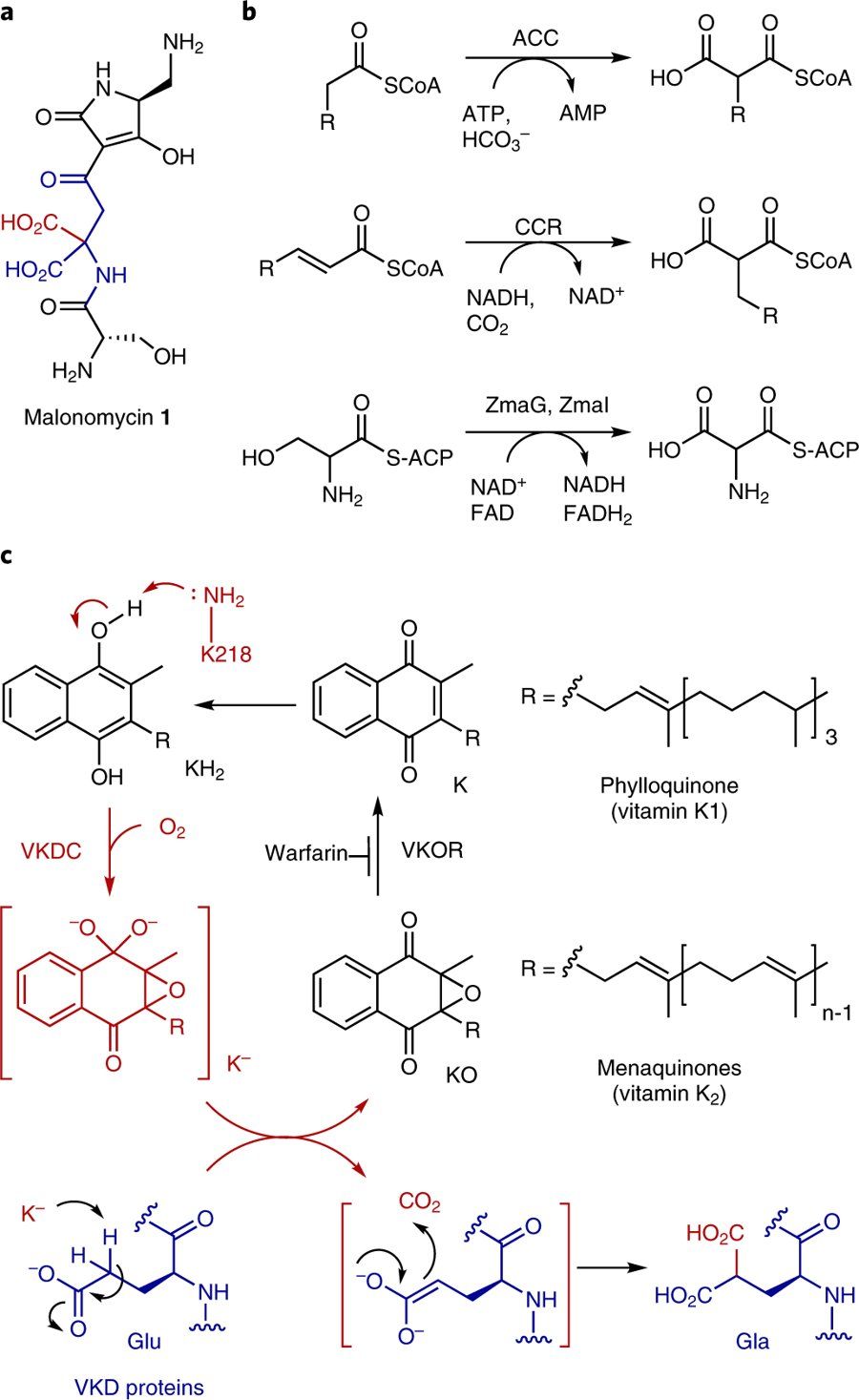
Scientists have discovered a new chemical process—also known as a biosynthetic pathway—in bacteria which could lead to a new generation of antibiotics being produced and manufactured.
Researchers at The University of Manchester’s School of Chemistry say their new pathway includes an enzyme, called a carboxylase, which adds CO2 to a precursor molecule producing a highly unusual antibiotic called malonomycin.
The team says the biosynthetic process used to produce this antibiotic could now possibly lead to the discovery and development of other drugs, helping in the fight against drug-resistant bugs and illnesses in the future.