Archive for the ‘bioengineering’ category: Page 167
Feb 16, 2018
CRISPR Isn’t Just for Gene Editing Anymore
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics
A scientist cuts a DNA fragment under UV light for DNA sequencing. Image: AP Five years ago, when researchers first discovered that bacterial immune systems could be hijacked to edit DNA in living creatures, it was big news. The technology, called CRISPR, allowed scientists to more easily than ever cut and paste all those As, Cs, Ts, and Gs that make up the base pairs of DNA and encode the world’s living things. With CRISPR, scientists could use genetic engineering to tackle problems from disease to famine. But gene editing with CRISPR is so 2017. Recently, scientists have begun exploring n…
Feb 13, 2018
Creating designer babies with CRISPR will soon be possible
Posted by Brady Hartman in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
Summary: Designer babies have recently become possible, as new techniques have gained credibility from serious scientists. Here’s how they can do it. [This article first appeared on LongevityFacts. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
On Feb 8, the AHA named “Fixing a gene mutation in human embryos” as among the “top advances in heart disease and stroke research” of the past year. They joined a chorus of voices heralding this as a research breakthrough.
The announcement brought attention to the fact that US scientists have recently demonstrated the plausibility of using gene editing to make designer babies.
Feb 13, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Reaching The Finish Line Show — Ira S. Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, business, cryonics, disruptive technology, DNA, economics, futurism, genetics
Feb 9, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Transform U! Show — Ira S. Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, business, cryonics, DNA, futurism, genetics, health, neuroscience, transhumanism

Feb 8, 2018
Engineers use natural protein as nanoshuttle for anti-cancer vaccines
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
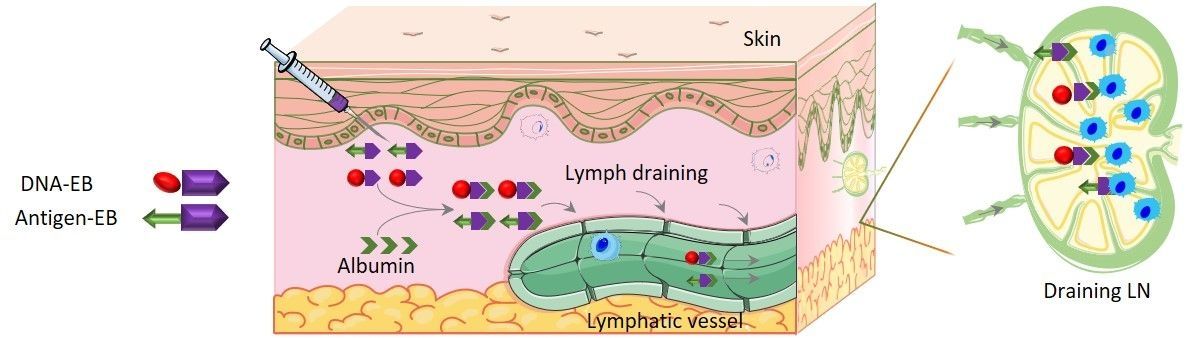
Cancer fighting nanovaccines have shown significant promise, but clinical application has been hampered by complications in large-scale manufacturing, quality control, and safety. Biomedical engineers at the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) developed a new technology that enables nanovaccines to bind to the albumin protein naturally present in the body. The albumin protein then delivers these nanocomplexes to the lymph nodes, resulting in potent immune activation against multiple tumor types in mouse cancer models. The use of natural albumin as a universal vaccine shuttle is a significant step towards the application of cancer nanovaccine immunotherapy in humans.
Nanovaccines that work to mount an immune response against a tumor basically consist of two components: the part that delivers the vaccine to the correct site, the lymph nodes, where immune system activation happens; and the part that activates the immune cells to expand and specifically target the tumor.
Continue reading “Engineers use natural protein as nanoshuttle for anti-cancer vaccines” »
Feb 3, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Grimerica Show — Ira S. Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cryonics, DNA, genetics, health, life extension, neuroscience, science, transhumanism

Feb 2, 2018
“Strategies for Living Longer with Ira Pastor” — Moments With Marianne
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cryonics, DNA, health, life extension, neuroscience, transhumanism
Feb 1, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Cafe Esoterica Radio Show (Part #1 ) — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, alien life, astronomy, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cosmology, cryonics, genetics, health, neuroscience
Jan 31, 2018
Revolutionary stealth virus holds promise for cancer therapy
Posted by Brady Hartman in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
Researchers solved a problem that has been holding back the use of viral vectors for cancer therapy. They re-engineered viruses with a novel stealth technique that enables them to be used to treat cancer.
Up until now, viral vectors couldn’t be used widely in cancer therapy. Researchers just announced that they re-engineered an adenovirus with a novel stealth technique that enables it to be used to fight tumors. [This article first appeared on the website LongevityFacts.com. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
Viral vectors are well-developed tools used by scientists to deliver genetic material into cells. Unfortunately, they haven’t worked well to treat cancer until a group of researchers in Switzerland re-engineered them to enable them to be used in cancer therapy.
Continue reading “Revolutionary stealth virus holds promise for cancer therapy” »