Oct 22, 2023
New 3D-printed tumor model enables faster, less expensive and less painful cancer treatment
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: bioprinting, biotech/medical, computing, mathematics
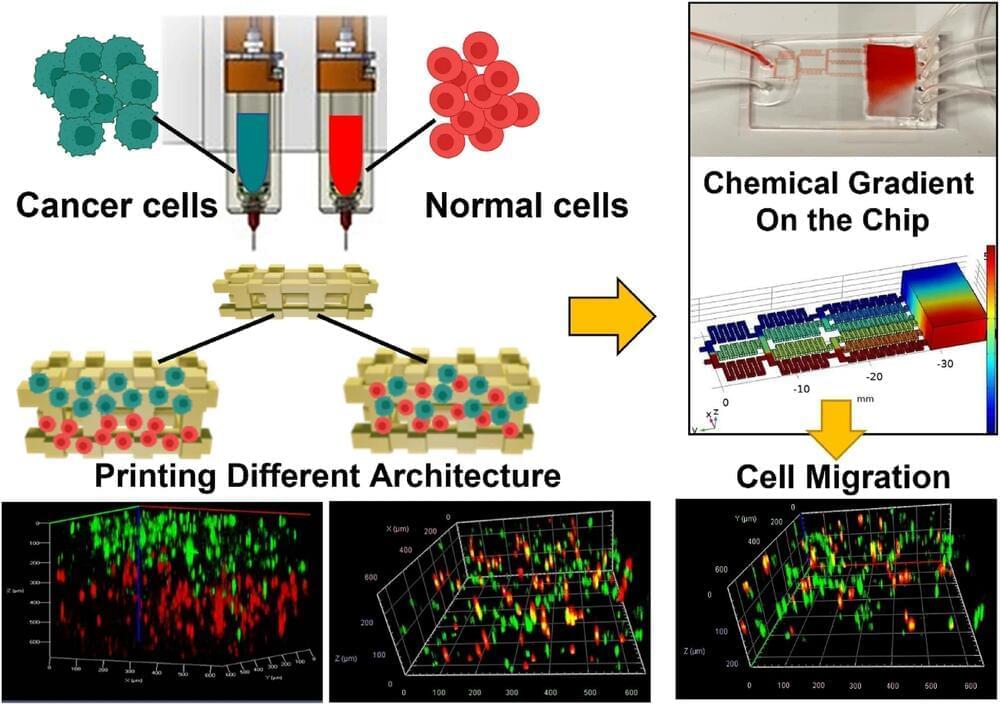
An international team of interdisciplinary researchers has successfully created a method for better 3D modeling of complex cancers. The University of Waterloo-based team combined cutting-edge bioprinting techniques with synthetic structures or microfluidic chips. The method will help lab researchers more accurately understand heterogeneous tumors: tumors with more than one kind of cancer cell, often dispersed in unpredictable patterns.
The research, “Controlled tumor heterogeneity in a co-culture system by 3D bio-printed tumor-on-chip model,” appears in Scientific Reports.
Traditionally, medical practitioners would biopsy a patient’s tumor, extract cells, and then grow them in flat petri dishes in a lab. “For 50 years, this was how biologists understood tumors,” said Nafiseh Moghimi, an applied mathematics post-doctoral researcher and the lead author of the study. “But a decade ago, repeated treatment failures in human trials made scientists realize that a 2D model does not capture the real tumor structure inside the body.”