Feb 14, 2023
New Models Help Unveil the Mystery of Life’s Origins on Earth
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biological, chemistry
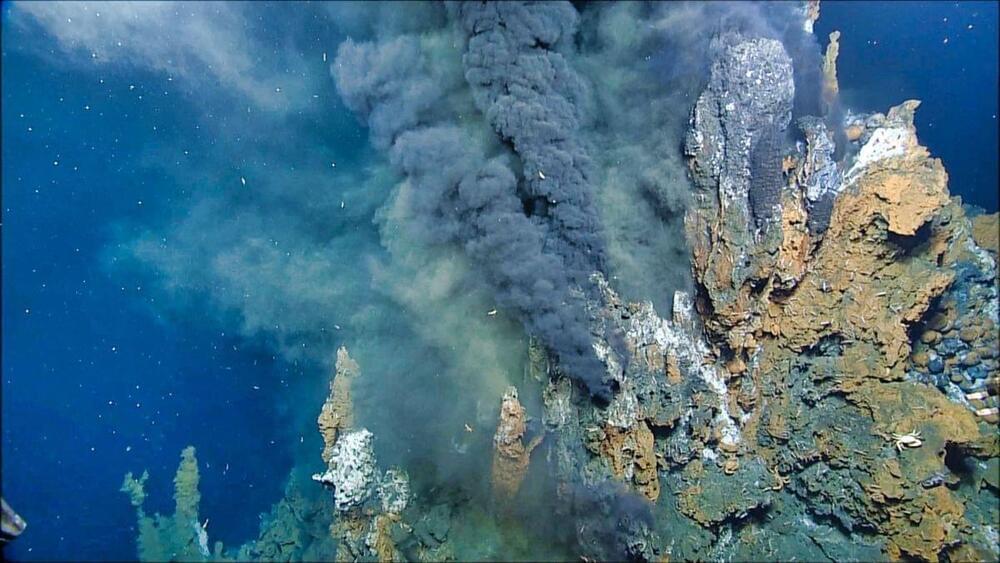
New research reveals clues about the physical and chemical characteristics of Earth when life is thought to have emerged.
About four billion years ago, the first signs of life emerged on Earth in the form of microbes. Although scientists are still determining exactly when and how these microbes appeared, it’s clear that the emergence of life is intricately intertwined with the chemical and physical characteristics of early Earth.
“It is reasonable to suspect that life could have started differently—or not at all—if the early chemical characteristics of our planet were different,” says Dustin Trail, an associate professor of earth and environmental sciences at the University of Rochester.