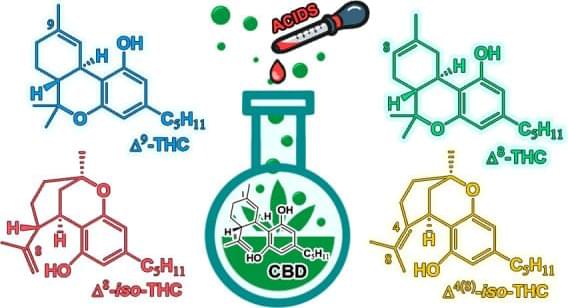
Circa 2020 Lewis acids such as in some candies can active thc in cannibidiol making a room temperature thc activation. Which has been unheard of until now leading to a breakthrough in thc activation at lower temperatures even room temperature through a lewis acid catalyst.
The chemical reactivity of cannabidiol is based on its ability to undergo intramolecular cyclization driven by the addition of a phenolic group to one of its two double bonds. The main products of this cyclization are Δ9-THC (trans-Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and Δ8-THC (trans-Δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol). These two cannabinoids are isomers, and the first one is a frequently investigated psychoactive compound and pharmaceutical agent. The isomers Δ8-iso-THC (trans-Δ-8-iso-tetrahydrocannabinol) and Δ4-iso-THC (trans-Δ-4,8-iso-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been identified as additional products of intramolecular cyclization. The use of Lewis and protic acids in different solvents has been studied to investigate the possible modulation of the reactivity of CBD (cannabidiol). The complete NMR spectroscopic characterizations of the four isomers are reported. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis and 1 H NMR spectra of the reaction mixture were used to assess the percentage ratio of the compounds formed.
Recent years have seen a dramatically increasing interest in phytocannabinoids. Isolated from Cannabis in 1940,1,2 cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most abundant phytocannabinoids in the species of Cannabis for textile uses.3,4 Despite the structural similarity between CBD and Δ9-THC (trans-Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) (Figure Figure1 1), CBD has a low agonistic effect for cannabinoid receptors; in particular, it is considered an allosteric negative modulator of CB1 and CB2 receptors (cannabinoid receptor types 1 and 2).5,6 Current evidence shows that CBD exerts pharmacological effects via specific molecular targets such as adenosine, glycine, opioid, serotonin, nonendocannabinoid G protein-coupled, nicotinic acetylcholine, and proliferator-activated receptors.7 Moreover, CBD shows anticonvulsant, antispasmodic, anxiolytic, antinausea, antirheumatoid arthritis, and neuroprotective properties.