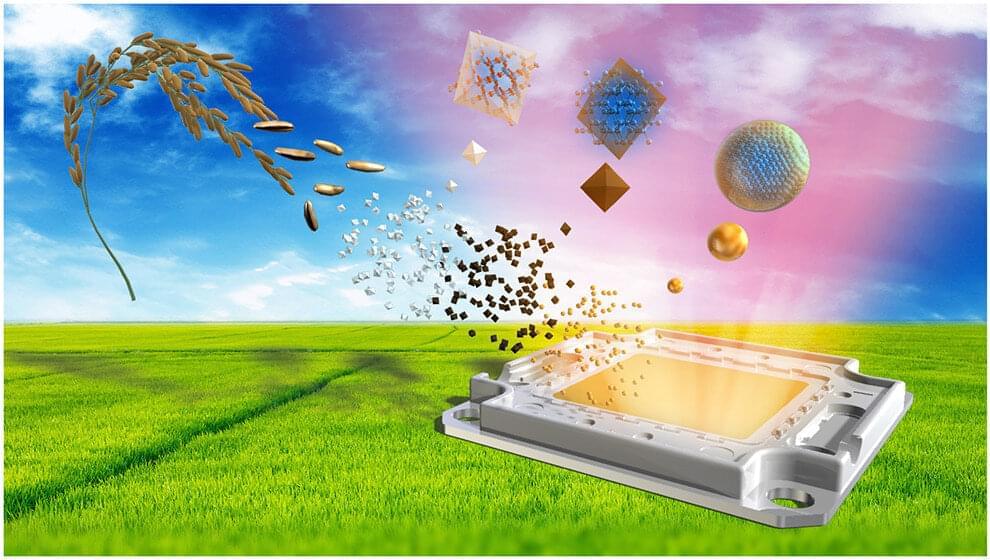
Milling rice to separate the grain from the husks produces about 100 million tons of rice husk waste globally each year. Scientists searching for a scalable method to fabricate quantum dots have developed a way to recycle rice husks to create the first silicon quantum dot (QD) LED light. Their new method transforms agricultural waste into state-of-the-art light-emitting diodes in a low-cost, environmentally friendly way.
The research team from the Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University, published their findings on January 28, 2022, in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
“Since typical QDs often involve toxic material, such as cadmium, lead, or other heavy metals, environmental concerns have been frequently deliberated when using nanomaterials. Our proposed process and fabrication method for QDs minimizes these concerns,” said Ken-ichi Saitow, lead study author and a professor of chemistry at Hiroshima University.