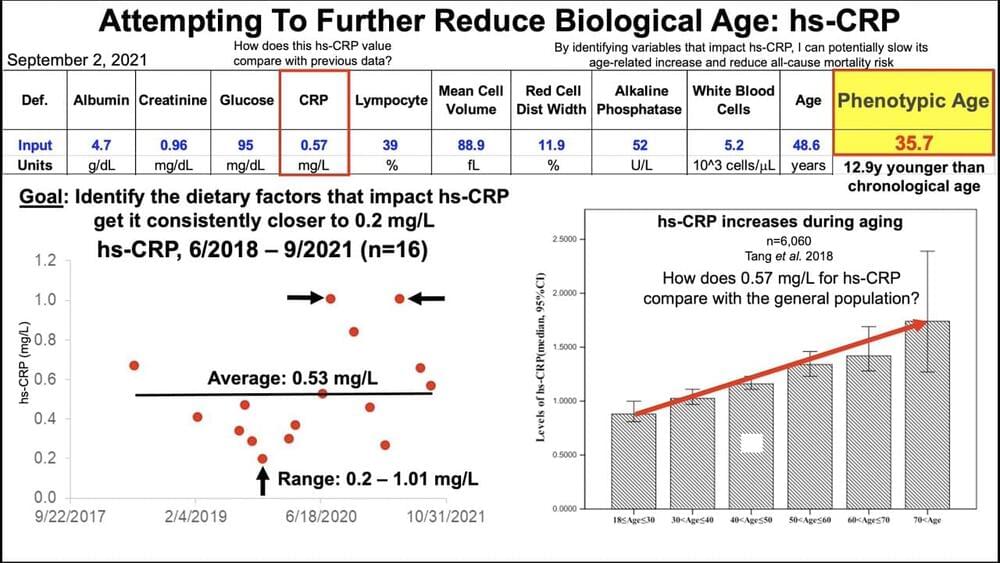
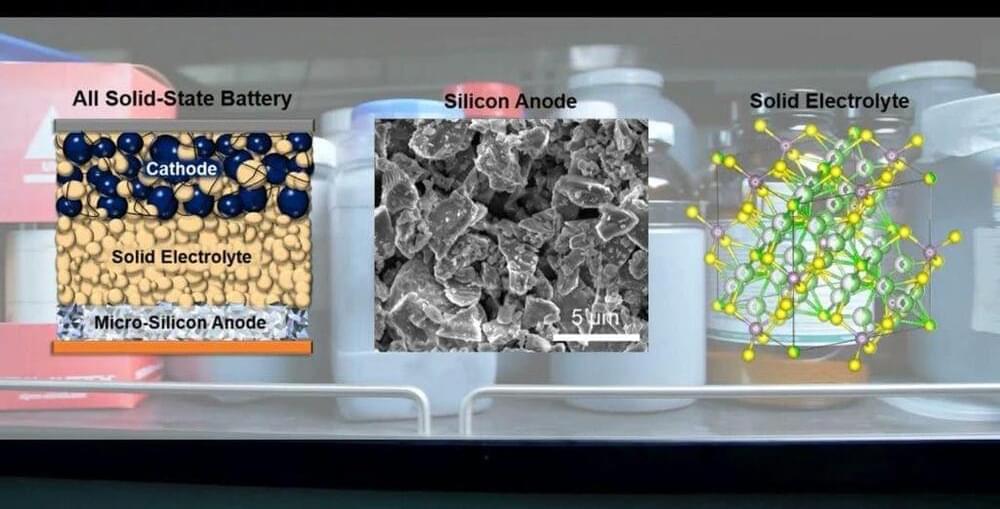
Sep 29, 2021
An autonomous robot may have already killed people — here’s how the weapons could be more destabilizing than nukes
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: biological, chemistry, military, policy, robotics/AI
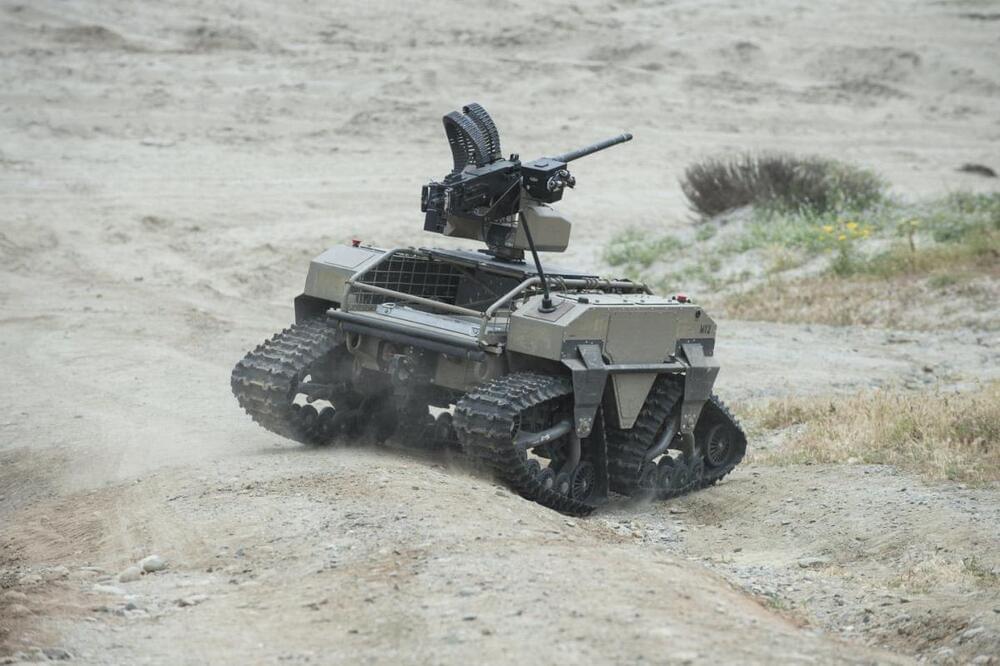
Autonomous weapon systems – commonly known as killer robots – may have killed human beings for the first time ever last year, according to a recent United Nations Security Council report on the Libyan civil war. History could well identify this as the starting point of the next major arms race, one that has the potential to be humanity’s final one.
Autonomous weapon systems are robots with lethal weapons that can operate independently, selecting and attacking targets without a human weighing in on those decisions. Militaries around the world are investing heavily in autonomous weapons research and development. The U.S. alone budgeted US$18 billion for autonomous weapons between 2016 and 2020.
Meanwhile, human rights and humanitarian organizations are racing to establish regulations and prohibitions on such weapons development. Without such checks, foreign policy experts warn that disruptive autonomous weapons technologies will dangerously destabilize current nuclear strategies, both because they could radically change perceptions of strategic dominance, increasing the risk of preemptive attacks, and because they could become combined with chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear weapons themselves.