Sep 20, 2021
Tapping sewage as a source of useful materials
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry
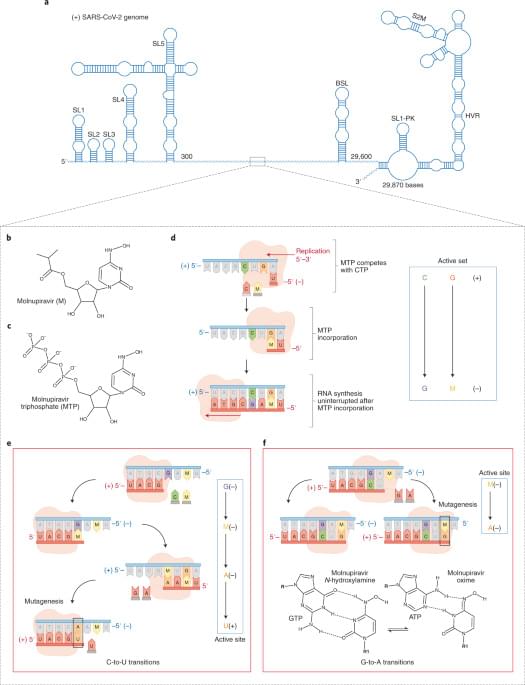
face_with_colon_three Basically we simply waste chemicals that are sometimes used in compost but actually have literally millions of tons of chemicals gone to waste rather reclaiming these very expensive chemicals. For instance some medicine costs thousands of dollars to make and will not recycle completely even current compost problems are not seeing the literally value of wasted medical refuse dissolved in waste water. Literally possibly trillion dollars or more down the drain from waste but this new reclaiming system will reap the benefits 😗 Even new innovative recycled toilet paper is a new concept but someday even vital chemicals will not be wasted with these new reclaiming systems.
With sometimes offbeat technology, innovators seek to extract certain chemicals from municipal waste by.
Continue reading “Tapping sewage as a source of useful materials” »