Apr 4, 2017
Nanofabrication Enables “Particle-Accelerator-on-a-Chip” Technology
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: biotech/medical, computing, nanotechnology
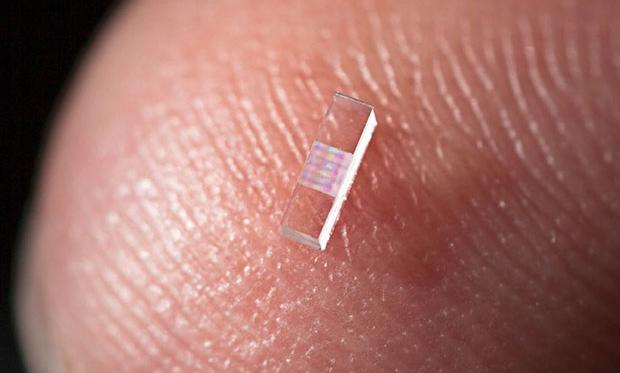
The key to this all working is the design of the nanostructures. If you just have a laser in free space, the particle will just oscillate back and forth, pushing it one way and then the other. It won’t ever gain in total energy. So you need some kind of structure that channels or modulates the fields in such a way that the particle will travel along mainly the peaks of the electromagnetic wave and not into the troughs so that it gets kicks but not deceleration.
In all of the experiments done so far, England explains that the particles are basically filling the whole wave, occupying and seeing both the peaks and troughs. This results in some particles being accelerated while others get decelerated.
“In the future, as one of the next experimental steps what we want is to bunch the particles to make very short little packets of particles that are spaced at exactly the right distance between the peaks so that they will ride only on the peaks,” says England. “So you can think of it as like… ocean waves, and you want your surfers to be positioned only on the peaks of the waves and not in the troughs.”
Continue reading “Nanofabrication Enables ‘Particle-Accelerator-on-a-Chip’ Technology” »