Nov 23, 2023
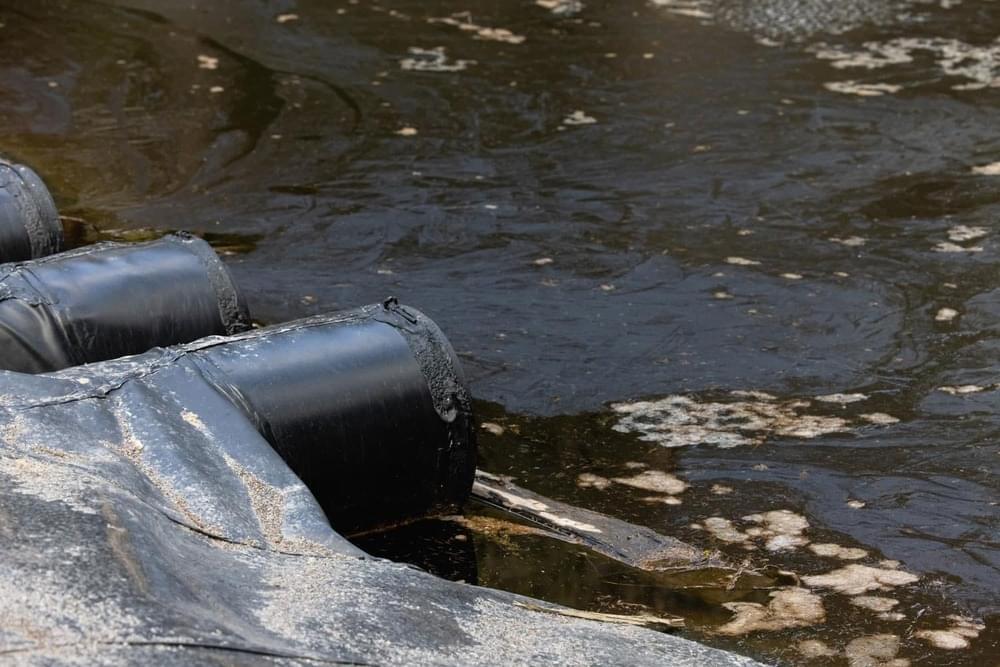
Micromotors can generate green energy from wastewater
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: chemistry, energy, sustainability
To enhance their catalytic efficiency in degrading organic pollutants, such as RB and urea, researchers further functionalized the surface of the micromotors with laccase, the bio-catalytic counterpart, for the generation of ammonia from urea. Urea is an emerging contaminant, being a common pollutant from residential activities (urea is the main component of urine) and from different industrial processes.
The chemical component laccase accelerates the conversion of urea into ammonia upon contact with contaminated water. This ammonia can be transformed into hydrogen, which is a clean and sustainable energy source.
“This is an interesting discovery. Today, water treatment plants have trouble breaking down all the urea, which can result in eutrophication when the water is released. This is a serious problem in urban areas in particular,” says Rebeca Ferrer, a PhD student from Dr. Katherine Villa’s group at ICIQ.